Abstract
Purpose
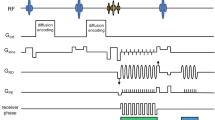
A new method for diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) using independent parallel transmission technique resulting in zoomed DWI was applied in four patients suffering from acute spinal cord ischemia.
Methods
Four patients with clinical symptoms of acute spinal cord ischemia were examined on a 3 T MR-system equipped with a two-channel transmit array. Scans included T2-weighted turbo spin echo, conventional DWI, and zoomed DWI. Image evaluation was performed with regard to overall image quality, anatomic delineation of the spinal cord, and the level of confidence to establish the diagnosis of spinal cord ischemia.
Results
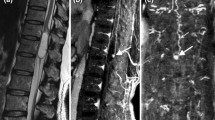
Through spatially selective excitation, zoomed DWI allows for acquisition of high-resolution images with reduced scan time due to a reduced field of view in phase-encoding direction, resulting in zoomed images. In all cases the ischemia was demonstrated in conventional DWI as well as zoomed DWI.
Conclusions
Compared to conventional DWI, zoomed DWI enables a faster image acquisition and allowed a more detailed analysis of the spinal lesion which may be critical to attribute the lesion to a particular vessel territory.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alblas CL, Bouvy WH, Lycklama ANGJ, Boiten J. Acute spinal-cord ischemia: evolution of MRI findings. J Clin Neurol (Seoul, Korea). 2012;8(3):218–23. doi:10.3988/jcn.2012.8.3.218.
Kuker W, Weller M, Klose U, Krapf H, Dichgans J, Nagele T. Diffusion-weighted MRI of spinal cord infarction—high resolution imaging and time course of diffusion abnormality. J Neurol. 2004;251(7):818–24. doi:10.1007/s00415-004-0434-z.
Saritas EU, Cunningham CH, Lee JH, Han ET, Nishimura DG. DWI of the spinal cord with reduced FOV single-shot EPI. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60(2):468–73. doi:10.1002/mrm.21640.
Schmitz BL, Aschoff AJ, Hoffmann MH, Gron G. Advantages and pitfalls in 3 T MR brain imaging: a pictorial review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(9):2229–37.
Turner R, von Kienlin M, Moonen CT, van Zijl PC. Single-shot localized echo-planar imaging (STEAM-EPI) at 4.7 T. Magn Reson Med. 1990;14(2):401–8.
Rieseberg S, Frahm J, Finsterbusch J. Two-dimensional spatially-selective RF excitation pulses in echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2002;47(6):1186–93. doi:10.1002/mrm.10157.
Riffel P, Michaely HJ, Morelli JN, Pfeuffer J, Attenberger UI, Schoenberg SO, et al. Zoomed EPI-DWI of the head and neck with two-dimensional, spatially-selective radiofrequency excitation pulses. Eur Radiol. 2014; doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3287-6.
Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(2):468–75. doi:10.1002/mrm.22024.
Novy J, Carruzzo A, Maeder P, Bogousslavsky J. Spinal cord ischemia: clinical and imaging patterns, pathogenesis, and outcomes in 27 patients. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(8):1113–20. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.8.1113.
Willinek WA, Gieseke J, Kukuk GM, Nelles M, Konig R, Morakkabati-Spitz N, et al. Dual-source parallel radiofrequency excitation body MR imaging compared with standard MR imaging at 3.0 T: initial clinical experience. Radiology. 2010;256(3):966-75. doi:10.1148/radiol.10092127.
Murtz P, Kaschner M, Traber F, Kukuk GM, Budenbender SM, Skowasch D, et al. Evaluation of dual-source parallel RF excitation for diffusion-weighted whole-body MR imaging with background body signal suppression at 3.0 T. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(11):3614–23. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.11.024.
Nelles M, Konig RS, Gieseke J, Guerand-van Battum MM, Kukuk GM, Schild HH, et al. Dual-source parallel RF transmission for clinical MR imaging of the spine at 3.0 T: intraindividual comparison with conventional single-source transmission. Radiology. 2010;257(3):743–53. doi:10.1148/radiol.10092146.
Andre JB, Zaharchuk G, Saritas E, Komakula S, Shankaranarayan A, Banerjee S, et al. Clinical evaluation of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging of the cervical and thoracic spine and spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(10):1860–6. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3134.
Blasche M, Riffel P, Lichy, M. TimTX TrueShape and syngo ZOOMit Technical and Practical Aspects. Magnetom Flash. 2012;1:74–84.
Zhang JS, Huan Y. Multishot diffusion-weighted MR imaging features in acute trauma of spinal cord. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(3):685–92. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-3051-3.
Sivadasan A, Alexander M, Patil AK, Mani S. Spectrum of clinicoradiological findings in spinal cord infarction: report of three cases and review of the literature. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2013;16(2):190–3. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.112464.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seeger, A., Klose, U., Bischof, F. et al. Zoomed EPI DWI of Acute Spinal Ischemia Using a Parallel Transmission System. Clin Neuroradiol 26, 177–182 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0342-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0342-2