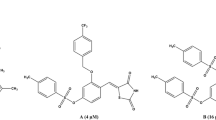
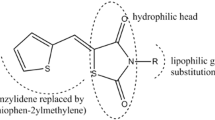
Abstract
As a disease closely related to the metabolic syndrome, diabetes has become a public health issue that severely affects many people’s quality of life. The search for novel anti-diabetic agents remains the cornerstone to control this challenging disease. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), a negative regulator of insulin and leptin signaling pathways, has turned out to be a potential target of type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. In recent years, the development of novel anti-diabetic drugs based on PTP1B inhibitors has captured the attention of many researchers. Thiazole, a five-membered heterocycle containing sulfur and nitrogen atoms, has been considered as an essential core skeleton for various active compounds. Furthermore, thiazolidines, representing a series of compounds with saturated thiazole rings, widely exist in natural products and synthetic compounds with a variety of pharmacological activities. Here, we focus on the emphasis of PTP1B in diabetes and the development of PTP1B inhibitors based on thiazole and thiazolidine derivatives in the past decade. Many PTP1B inhibitors and their chemical structures, selectivity, potency, and structure-activity relationship have been elaborated. The great majority of PTP1B inhibitors containing thiazole and thiazolidine moieties described in this review exhibit preferable activities, which would be of importance for the rational design and efficient application of PTP1B inhibitors with anti-diabetes activity.
































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verma M, Gupta SJ, Chaudhary A, Garg VK. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors as antidiabetic agents - a brief review. Bioorg Chem. 2017;70:267–83.
Hussain H, Green IR, Abbas G, Adekenov SM, Hussain W, Ali I. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitors as potential anti-diabetes agents: patent review (2015-2018). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2019;29:689–702.
He RJ, Yu ZH, Zhang RY, Zhang ZY. Protein tyrosine phosphatases as potential therapeutic targets. Acta Pharm Sin. 2014;35:1227–46.
Tonks NK, Diltz CD, Fischer EH. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:6722–30.
Johnson TO, Ermolieff J, Jirousek MR. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors for diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:696–709.
Zhang S, Zhang Z. PTP1B as a drug target: recent developments in PTP1B inhibitor discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2007;12:373–81.
Maghraby MT, Abou-Ghadir OMF, Abdel-Moty SG, Ali AY, Salem OIA. Novel class of benzimidazole-thiazole hybrids: the privileged scaffolds of potent anti-inflammatory activity with dual inhibition of cyclooxygenase and 15-lipoxygenase enzymes. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020;28:115403.
Sayed AR, Gomha SM, Taher EA, Muhammad ZA, El-Seedi HR, Gaber HM, et al. One-pot synthesis of novel thiazoles as potential anti-cancer agents. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2020;14:1363–75.
Dhameliya TM, Tiwari R, Banerjee A, Pancholia S, Sriram D, Panda D, et al. Benzo[d]thiazole-2-carbanilides as new anti-TB chemotypes: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and structure-activity relationship. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;155:364–80.
Isac E, de APG, da Costa TL, de Lima NF, de SMMAD, Fraga CM, et al. Nitazoxanide induces in vitro metabolic acidosis in Taenia crassiceps cysticerci. Exp Parasitol. 2016;171:17–22.
Yallur BC, Katrahalli U, Krishna PM, Hadagali MD. BSA binding and antibacterial studies of newly synthesized 5,6-Dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-2-carbaldehyde. Spectrochim Acta Part A. 2019;222:117192.
Lino CI, Goncalves de Souza I, Borelli BM, Silverio Matos TT, Santos Teixeira IN, Ramos JP, et al. Synthesis, molecular modeling studies and evaluation of antifungal activity of a novel series of thiazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;151:248–60.
Grozav A, Porumb ID, Gaina LI, Filip L, Hanganu D. Cytotoxicity and antioxidant potential of novel 2-(2-((1H-indol-5yl)methylene)-hydrazinyl)-thiazole derivatives. Molecules. 2017;22. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020260.
Mishra CB, Kumari S, Tiwari M. Thiazole: a promising heterocycle for the development of potent CNS active agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;92:1–34.
Moreira DR, Costa SP, Hernandes MZ, Rabello MM, de Oliveira Filho GB, de Melo CM, et al. Structural investigation of anti-Trypanosoma cruzi 2-iminothiazolidin-4-ones allows the identification of agents with efficacy in infected mice. J Med Chem. 2012;55:10918–36.
Balzarini J, Orzeszko-Krzesinska B, Maurin JK, Orzeszko A. Synthesis and anti-HIV studies of 2- and 3-adamantyl-substituted thiazolidin-4-ones. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44:303–11.
El-Kashef H, Badr G, Abo El-Maali N, Sayed D, Melnyk P, Lebegue N, et al. Synthesis of a novel series of (Z)-3,5-disubstituted thiazolidine-2,4-diones as promising anti-breast cancer agents. Bioorg Chem. 2020;96:103569.
Trotsko N, Kosikowska U, Paneth A, Plech T, Malm A, Wujec M. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of new thiazolidine-2,4-dione-based chlorophenylthiosemicarbazone hybrids. Molecules. 2018;23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051023.
Abdellatif KRA, Fadaly WAA, Kamel GM, Elshaier Y, El-Magd MA. Design, synthesis, modeling studies and biological evaluation of thiazolidine derivatives containing pyrazole core as potential anti-diabetic PPAR-gamma agonists and anti-inflammatory COX-2 selective inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2019;82:86–99.
Nanjan MJ, Mohammed M, Prashantha Kumar BR, Chandrasekar MJN. Thiazolidinediones as antidiabetic agents: a critical review. Bioorg Chem. 2018;77:548–67.
Kaur Manjal S, Kaur R, Bhatia R, Kumar K, Singh V, Shankar R, et al. Synthetic and medicinal perspective of thiazolidinones: a review. Bioorg Chem. 2017;75:406–23.
Nirwan S, Chahal V, Kakkar R. Thiazolidinones: synthesis, reactivity, and their biological applications. J Heterocycl Chem. 2019;56:1239–53.
Sahiba N, Sethiya A, Soni J, Agarwal DK, Agarwal S. Saturated five-membered thiazolidines and their derivatives: from synthesis to biological applications. Top Curr Chem. 2020;378:34.
Kharroubi AT. Diabetes mellitus: the epidemic of the century. World J Diabetes. 2015;6:850.
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus—present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;8:228–36.
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pr. 2018;138:271–81.
Shi Y, Hu FB. The global implications of diabetes and cancer. Lancet. 2014;383:1947–8.
Kullmann S, Heni M, Hallschmid M, Fritsche A, Preissl H, Häring H-U. Brain insulin resistance at the crossroads of metabolic and cognitive disorders in humans. Physiol Rev. 2016;96:1169–209.
Winocour PH. Diabetes and chronic kidney disease: an increasingly common multi-morbid disease in need of a paradigm shift in care. Diabet Med. 2018;35:300–5.
Ofstad AP, Atar D, Gullestad L, Langslet G, Johansen OE. The heart failure burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus—a review of pathophysiology and interventions. Heart Fail Rev. 2018;23:303–23.
Jenny L, Melmer A, Laimer M, Hardy ET, Lam WA, Schroeder V. Diabetes affects endothelial cell function and alters fibrin clot formation in a microvascular flow model: a pilot study. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2020;17:1479164120903044.
Dowarah J, Singh VP. Anti-diabetic drugs recent approaches and advancements. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020;28:115263.
Thareja S, Aggarwal S, Bhardwaj TR, Kumar M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors: a molecular level legitimate approach for the management of diabetes mellitus. Med Res Rev. 2012;32:459–517.
Budiyani L, Purnamasari D, Simadibrata M, Abdullah M. Insulin resistance in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Acta Med Indones. 2018;50:336–42.
Bjornstad P, Eckel RH. Pathogenesis of lipid disorders in insulin resistance: a brief review. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2018;18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-018-1101-6.
Li J, Bai L, Wei F, Zhao J, Wang D, Xiao Y et al. Therapeutic mechanisms of herbal medicines against insulin resistance: a review. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00661.
Gregg EW, Li Y, Wang J, Burrows NR, Ali MK, Rolka D, et al. Changes in diabetes-related complications in the United States, 1990-2010. N. Engl J Med. 2014;370:1514–23.
Mahapatra DK, Asati V, Bharti SK. Chalcones and their therapeutic targets for the management of diabetes: structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;92:839–65.
Kerru N, Singh-Pillay A, Awolade P, Singh P. Current anti-diabetic agents and their molecular targets: a review. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;152:436–88.
Ghorbani A, Rashidi R, Shafiee-Nick R. Flavonoids for preserving pancreatic beta cell survival and function: a mechanistic review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;111:947–57.
Chen Y-T, Tang C-L, Ma W-P, Gao L-X, Wei Y, Zhang W, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel 2-ethyl-5-phenylthiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors with improved cellular efficacy. Eur J Med Chem. 2013;69:399–412.
Bharatham K, Bharatham N, Kwon YJ, Lee KW. Molecular dynamics simulation study of PTP1B with allosteric inhibitor and its application in receptor based pharmacophore modeling. J Comput-Aided Mol Des. 2008;22:925–33.
Puius YA, Zhao Y, Sullivan M, Lawrence DS, Almo SC, Zhang Z-Y. Identification of a second aryl phosphate-binding site in protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B: a paradigm for inhibitor design. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:13420–5.
Tonks NK. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: from genes, to function, to disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:833–46.
Cho H. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and obesity. Vitam Horm. 2013;91:405–24.
Zhao BT, Nguyen DH, Le DD, Choi JS, Min BS, Woo MH. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from natural sources. Arch Pharmacal Res. 2017;41:130–61.
Proenca C, Freitas M, Ribeiro D, Sousa JLC, Carvalho F, Silva AMS, et al. Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B by flavonoids: a structure - activity relationship study. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;111:474–81.
Ghareb N, El-Sayed NM, Abdelhameed R, Yamada K, Elgawish MS. Toward a treatment of diabesity: rational design, synthesis and biological evaluation of benzene-sulfonamide derivatives as a new class of PTP-1B inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2019;86:322–38.
Mendes NF, Castro G, Guadagnini D, Tobar N, Cognuck SQ, Elias LLK, et al. Knocking down amygdalar PTP1B in diet-induced obese rats improves insulin signaling/action, decreases adiposity and may alter anxiety behavior. Metabolism. 2017;70:1–11.
Figueiredo H, Figueroa ALC, Garcia A, Fernandez-Ruiz R, Broca C, Wojtusciszyn A, et al. Targeting pancreatic islet PTP1B improves islet graft revascularization and transplant outcomes. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:eaar6294/1-eaar/15.
Wang M-Y, Cheng X-C, Chen X-B, Li Y, Zang L-L, Duan Y-Q, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel N-aryl-ω-(benzoazol-2-yl)-sulfanylalkanamides as dual inhibitors of α-glucosidase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018;92:1647–56.
Wiesmann C, Barr KJ, Kung J, Zhu J, Erlanson DA, Shen W, et al. Allosteric inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:730–7.
Wang L-J, Jiang B, Wu N, Wang S-Y, Shi D-Y. Natural and semisynthetic protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitors as anti-diabetic agents. RSC Adv. 2015;5:48822–34.
Erbe DV, Wang S, Zhang YL, Harding K, Kung L, Tam M, et al. Ertiprotafib improves glycemic control and lowers lipids via multiple mechanisms. Mol Pharm. 2005;67:69–77.
Smith AM, Maguire-Nguyen KK, Rando TA, Zasloff MA, Strange KB, Yin VP. The protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor MSI-1436 stimulates regeneration of heart and multiple other tissues. NPJ. npj Regen Med. 2017;2:4.
Varshney K, Gupta S, Rahuja N, Rawat AK, Singh N, Tamarkar AK, et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and docking studies of substituted aryl thiazolyl phenylsulfonamides as potential protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. Chem Med Chem. 2012;7:1185–90.
Zhang L, Ge Y, Song HM, Wang QM, Zhou CH. Design, synthesis of novel azolyl flavonoids and their protein tyrosine Phosphatase-1B inhibitory activities. Bioorg Chem. 2018;80:195–203.
Sun L, Wang P, Xu L, Gao L, Li J, Piao H. Discovery of 1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole derivatives containing rhodanine-3-alkanoic acid groups as potential PTP1B inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019;29:1187–93.
Mahapatra MK, Kumar R, Kumar M. Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico studies of 5-(3-methoxybenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione analogues as PTP1B inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2017;71:1–9.
Bhattarai BR, Kafle B, Hwang JS, Khadka D, Lee SM, Kang JS, et al. Thiazolidinedione derivatives as PTP1B inhibitors with antihyperglycemic and antiobesity effects. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009;19:6161–5.
Fukuda S, Ohta T, Sakata S, Morinaga H, Ito M, Nakagawa Y, et al. Pharmacological profiles of a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor, JTT-551. Diabetes, Obes Metab. 2010;12:299–306.
Ito M, Fukuda S, Sakata S, Morinaga H, Ohta T. Pharmacological effects of JTT-551, a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor, in diet-induced obesity mice. J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:680348.
Wei Y, Chen Y-T, Shi L, Gao L-X, Liu S, Cui Y-M, et al. Discovery and structural modification of novel inhibitors of PTP1B inspired by the ACT fragment of scleritodermin A. Med Chem Comm. 2011;2:1104–9.
Navarrete-Vazquez G, Paoli P, Leon-Rivera I, Villalobos-Molina R, Medina-Franco JL, Ortiz-Andrade R, et al. Synthesis, in vitro and computational studies of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibition of a small library of 2-arylsulfonylaminobenzothiazoles with antihyperglycemic activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:3332–41.
Navarrete-Vazquez G, Ramirez-Martinez M, Estrada-Soto S, Nava-Zuazo C, Paoli P, Camici G, et al. Synthesis, in vitro and in silico screening of ethyl 2-(6-substituted benzo[d]thiazol-2-ylamino)-2-oxoacetates as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;53:346–55.
Liu J, Jiang F, Jin Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Liu W, et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 2-substituted ethenesulfonic acid ester derivatives as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;57:10–20.
Tang YB, Lu D, Chen Z, Hu C, Yang Y, Tian JY, et al. Design, synthesis and insulin-sensitising effects of novel PTP1B inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23:2313–8.
Ganou CA, Eleftheriou PT, Theodosis-Nobelos P, Fesatidou M, Geronikaki AA, Lialiaris T, et al. Docking analysis targeted to the whole enzyme: an application to the prediction of inhibition of PTP1B by thiomorpholine and thiazolyl derivatives. SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2018;29:133–49.
Rakse M, Karthikeyan C, Deora GS, Moorthy NSHN, Rathore V, Rawat AK, et al. Design, synthesis and molecular modelling studies of novel 3-acetamido-4-methyl benzoic acid derivatives as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Eur J Med Chem. 2013;70:469–76.
Wu J, Ma Y, Zhou H, Zhou L, Du S, Sun Y, et al. Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitors through De Novo Evoluton, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular dynamics simulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526:273–80.
Bhattarai BR, Kafle B, Hwang JS, Ham SW, Lee KH, Park H, et al. Novel thiazolidinedione derivatives with anti-obesity effects: dual action as PTP1B inhibitors and PPAR-gamma activators. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010;20:6758–63.
Liu Z, Huang Y, Zhang W, Ma L, Li J, Wang X, et al. Soluble polymer-supported synthesis of 5-arylidene thiazolidinones and pyrimidinones using a novel traceless linker strategy. J Comb Chem. 2008;10:632–6.
Liu Z, Chai Q, Li YY, Shen Q, Ma LP, Zhang LN, et al. Discovery of novel PTP1B inhibitors with antihyperglycemic activity. Acta Pharm Sin. 2010;31:1005–12.
Aher NG, Kafle B, Cho H. Thiazolidinone derivatives as competitive inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2013;34:1275–7.
Wang Z, Liu Z, Lee W, Kim SN, Yoon G, Cheon SH. Design, synthesis and docking study of 5-(substituted benzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24:3337–40.
Meng G, Zheng M, Wang M, Tong J, Ge W, Zhang J, et al. Design and synthesis of new potent PTP1B inhibitors with the skeleton of 2-substituted imino-3-substituted-5-heteroarylidene-1,3-thiazolidine-4-one: Part I. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;122:756–69.
Thareja S, Verma SK, Haksar D, Bhardwaj TR, Kumar M. Discovery of novel cinnamylidene-thiazolidinedione derivatives as PTP-1B inhibitors for the management of type 2 diabetes. RSC Adv. 2016;6:108928–40.
Thareja S, Aggarwal S, Bhardwaj TR, Kumar M. Self-organizing molecular field analysis of 2,4-thiazolidinediones: a 3D-QSAR model for the development of human PTP1B inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2010;45:2537–46.
Verma SK, Thareja S. Molecular docking assisted 3D-QSAR study of benzylidene-2,4-thiazolidinedione derivatives as PTP-1B inhibitors for the management of Type-2 diabetes mellitus. RSC Adv. 2016;6:33857–67.
Mahapatra MK, Kumar R, Kumar M. N-alkylated thiazolidine-2,4-dione analogs as PTP1B inhibitors: synthesis, biological activity, and docking studies. Med Chem Res. 2017;26:1176–83.
Mahapatra MK, Kumar R, Kumar M. Exploring sulfonate esters of 5-arylidene thiazolidine-2,4-diones as PTP1B inhibitors with anti-hyperglycemic activity. Med Chem Res. 2017;27:476–87.
Maccari R, Paoli P, Ottana R, Jacomelli M, Ciurleo R, Manao G, et al. 5-Arylidene-2,4-thiazolidinediones as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:5137–49.
Ottana R, Maccari R, Ciurleo R, Paoli P, Jacomelli M, Manao G, et al. 5-Arylidene-2-phenylimino-4-thiazolidinones as PTP1B and LMW-PTP inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:1928–37.
Maccari R, Ottana R, Ciurleo R, Paoli P, Manao G, Camici G, et al. Structure-based optimization of benzoic acids as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase. ChemMedChem 2009;4:957–62.
Ottana R, Maccari R, Amuso S, Wolber G, Schuster D, Herdlinger S. et al. New 4-[(5-arylidene-2-arylimino-4-oxo-3-thiazolidinyl)methyl]benzoic acids active as protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors endowed with insulinomimetic effect on mouse C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;50:332–43.
Ottana R, Maccari R, Mortier J, Caselli A, Amuso S, Camici G, et al. Synthesis, biological activity and structure-activity relationships of new benzoic acid-based protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors endowed with insulinomimetic effects in mouse C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Eur J Med Chem. 2014;71:112–27.
Ottana R, Paoli P, Nass A, Lori G, Cardile V, Adornato I. et al. Discovery of 4-[(5-arylidene-4-oxothiazolidin-3-yl)methyl]benzoic acid derivatives active as novel potent allosteric inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B: In silico studies and in vitro evaluation as insulinomimetic and anti-inflammatory agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;127:840–58.
Maccari R, Del Corso A, Paoli P, Adornato I, Lori G, Balestri F, et al. An investigation on 4-thiazolidinone derivatives as dual inhibitors of aldose reductase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, in the search for potential agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018;28:3712–20.
Hidalgo-Figueroa S, Estrada-Soto S, Ramirez-Espinosa JJ, Paoli P, Lori G, Leon-Rivera I, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of thiazolidine-2,4-dione/benzazole derivatives as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP-1B): Antihyperglycemic activity with molecular docking study. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:1302–10.
Liu H, Sun D, Du H, Zheng C, Li J, Piao H, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of tryptophan-derived rhodanine derivatives as PTP1B inhibitors and anti-bacterial agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;172:163–73.
Liu W-S, Wang R-R, Wang S-Q, Dong W-L, Wang R-L, Yue H. et al. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular dynamics studies of 4-thiazolinone derivatives as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019;38:1–11.
Patel AD, Pasha TY, Lunagariya P, Shah U, Bhambharoliya T, Tripathi RKP. A library of thiazolidin-4-one derivatives as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitors: an attempt to discover novel antidiabetic agents. Chem Med Chem. 2020;15:1229–42.
Eleftheriou P, Geronikaki A, Petrou A. PTP1b inhibition, a promising approach for the treatment of diabetes Type II. Curr Top Med Chem. 2019;19:246–63.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Key Laboratory of Organofluorine Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2018-10), the Hunan Province Cooperative Innovation Center for Molecular Target New Drug Study (0223-0007-000004), the Undergraduate Research Learning and Innovative Experiment Project (G201910555028, S201910555024, S201910555143, X2019177, X2019178, X2019179, 2018XJXZ349, 2018XJXZ350, 2018XJXZ351, 2018XJXZ360, 2018XJXZ363), Hunan Provincial Hengyang Joint Fund (2020JJ6052), Program for Innovative Talent Team of Hengyang (2017-1), the Key Project of Hengyang Science and Technology Department (2017KJ166) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Co-first author: Xu Yao
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, K., Yao, X., Tang, T. et al. Thiazole-based and thiazolidine-based protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors as potential anti-diabetes agents. Med Chem Res 30, 519–534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02668-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02668-4