Abstract
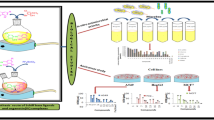
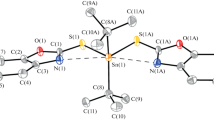
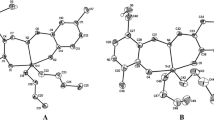
A multicomponent reaction was used as a synthetic strategy to prepare organotin (IV) complexes, 2-amino-3-hydroxypyridine, saliciladehydes 5-R-substituted (H, CH3, OCH3, C(CH)3, F, Cl, Br, I, NO2), and dibutyltin(IV) oxide were used as starting materials. The complexes were analyzed by IR, UV–Visible, MS, NMR of 1H, 13C, 119Sn. The complex 3a was structurally identified by X-ray crystallography, which revealed a dimeric arrangement where the tin atom possess a distorted hexacoordinated environment in which the deprotonated phenolic oxygen atoms and the nitrogen atom of the azomethine from the ligand are coordinated to the metallic center, and one of the phenoxy oxygens bridges with the tin through an intermolecular interaction forming a planar Sn2O2 core. As strategy of molecular design, isosteric and bioisosteric replacement of halogens were employed. All organotin compounds were assessed for their in vitro cytotoxic activity on cancer cell lines K‐562 (chronic myelogenous leukemia), U‐251 (glioblastoma), HCT‐15 (human colorectal cancer), MCF‐7, MDA-MB-231 (human breast cancer), and SKLU‐1 (non‐small‐cell lung cancer). They evidenced an elevated cytotoxic activity, and the inhibitory percentage values stated higher activity than the cis-platin. The K-562 and MDA-MB-231 cells were more sensitive to organotin (IV) complexes than HCT-15 and MCF-7. The organotin (IV) compounds were also tested in vivo for brine shrimp lethality to examine their toxic properties.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Aziz AA, Seda SH. Synthesis, structural features and biochemical activity assessment of N,N′-bis-(2-mercaptophenylimine)-2,5-thiophenedicarboxaldehyde Schiff base and its Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes. Appl Organomet Chem. 2017;31:e3879.
Abu-Dief AM, Mohamed IMA. A review on versatile applications of transition metal complexes incorporating Schiff bases. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2015;4:119–33.
Al Zoubi W, Al-Hamdani AAS, Kaseem M. Synthesis and antioxidant activities of Schiff bases and their complexes: a review. Appl Organomet Chem. 2016;30:810–7.
Al Zoubi W, Ko YG. Schiff base complexes and their versatile applications as catalysts in oxidation of organic compounds: part I. Appl Organomet Chem. 2017;31:e3574.
Asadi M, Asadi Z, Sadi SB, Zarei L, Baigi FM, Amirghofran Z. Synthesis, characterization and the interaction of some new water-soluble metal Schiff base complexes with human serum albumin. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014;122:118–29.
Qin W, Long S, Panunzio M, Biondi S. Schiff bases: a short survey on an evergreen chemistry tool. Molecules. 2013;18:12264–89.
da Silva CM, da Silva DL, Modolo LV, Alves RB, de Resende MA, Martins CVB, et al. Schiff bases: A short review of their antimicrobial activities. J Adv Res. 2011;2:1–8.
Ganguly R, Sreenivasulu B, Vittal JJ. Amino acid-containing reduced Schiff bases as the building blocks for metallasupramolecular structures. Coord Chem Rev. 2008;252:1027–50.
Liu X, Hamon J-R. Recent developments in penta-, hexa- and heptadentate Schiff base ligands and their metal complexes. Coord Chem Rev. 2019;389:94–118.
Gasser G, Ott I, Metzler-Nolte N. Organometallic anticancer compounds. J Med Chem. 2011;54:3–25.
Haas KL, Franz KJ. Application of metal coordination chemistry to explore and manipulate cell biology. Chem Rev. 2009;109:4921–60.
Hambley TW. Developing new metal-based therapeutics: challenges and opportunities. Dalton Trans. 2007;43:4929–37.
Ndagi U, Mhlongo N, Soliman ME. Metal complexes in cancer therapy—an update from drug design perspective. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2017;11:599–616.
Zaki M, Arjmand F, Tabassum S. Current and future potential of metallo drugs: revisiting DNA-binding of metal containing molecules and their diverse mechanism of action. Inorg Chim Acta. 2016;444:1–22.
Tzubery A, Tshuva EY. Cytotoxic titanium(IV) complexes of salalen-based ligands. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2017;12:1695–705.
Dasari S, Bernard Tchounwou P. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;740:364–78.
Jung Y, Lippard SJ. Direct cellular responses to platinum-induced DNA damage. Chem Rev. 2007;107:1387–407.
Oberoi HS, Nukolova NV, Kabanov AV, Bronich TK. Nanocarriers for delivery of platinum anticancer drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65:1667–85.
Mjos KD, Orvig C. Metallodrugs in medicinal inorganic chemistry. Chem Rev. 2014;114:4540–63.
Adeyemi JO, Onwudiwe DC. Organotin(IV) dithiocarbamate complexes: chemistry and biological activity. Molecules. 2018;23:2571.
Antonenko TA, Shpakovsky DB, Vorobyov MA, Gracheva YA, Kharitonashvili EV, Dubova LG, et al. Antioxidative vs. cytotoxic activities of organotin complexes bearing 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol moieties. Appl Organomet Chem. 2018;32:e4381.
Devi J, Yadav J, Singh N. Synthesis, characterisation, in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of diorganotin(IV) complexes derived from salicylaldehyde Schiff bases. Res Chem Intermed. 2019;45:3943–68.
Hu L, Wang H, Xia T, Fang B, Shen Y, Zhang Q, et al. Two-photon-active organotin(IV) complexes for antibacterial function and superresolution bacteria imaging. Inorg Chem. 2018;57:6340–8.
Iqbal H, Ali S, Shahzadi S. Antituberculosis study of organotin(IV) complexes: a review. Cogent Chem. 2015;1:1.
Dubé D, Brideau C, Deschênes D, Fortin R, Friesen RW, Gordon R, et al. 2-Heterosubstituted-3-(4-methylsulfonyl)phenyl-5-trifluoromethyl pyridines as selective and orally active cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999;9:1715–20.
Galván-Hidalgo JM, Chans GM, Ramírez-Apan T, Nieto-Camacho A, Hernández-Ortega S, Gómez E. Tin(IV) Schiff base complexes derived from pyridoxal: synthesis, spectroscopic properties and cytotoxicity. Appl Organomet Chem. 2017;31:e3704.
Galvan-Hidalgo JM, Gomez E, Ramirez-Apan T, Nieto-Camacho A, Hernandez-Ortega S. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of dibutyltin complexes derived from pyridoxamine and salicylaldehydes. Med Chem Res. 2015;24:3621–31.
Galván-Hidalgo JM, Ramírez-Apan T, Nieto-Camacho A, Hernández-Ortega S, Gómez E. Schiff base Sn(IV) complexes as cytotoxic agents: synthesis, structure, isosteric and bioisosteric replacement. J Organomet Chem. 2017;848:332–43.
Sheldrick GM. SHELXS-2014 and SHELXL-2014. Germany: University of Gottingen; 2014.
Monks A, Scudiero D, Skehan P, Shoemaker R, Paull K, Vistica D, et al. Feasibility of a high-flux anticancer drug screen using a diverse panel of cultured human tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991;83:757–66.
Rocha-Del Castillo E, Gómez-García O, Andrade-Pavón D, Villa-Tanaca L, Ramírez-Apan T, Nieto-Camacho A, et al. Dibutyltin(IV) complexes derived from L-DOPA: synthesis, molecular docking, cytotoxic and antifungal activity. Chem Pharm Bull. 2018;66:1104–13.
Reed LJ, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am J Epidemiol. 1938;27:493–7.
Sedaghat T, Habibi R, Motamedi H, Khavasi HR. Synthesis, structural characterization and antibacterial activity of diorganotin(IV) complexes with ONO tridentate Schiff bases containing pyridine ring. Chin Chem Lett. 2012;23:1355–8.
Öztaş NA, Yenişehirli G, Ancın N, Öztaş SG, Özcan Y, İde S. Synthesis, characterization, biological activities of dimethyltin(IV) complexes of Schiff bases with ONO-type donors. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2009;72:929–35.
Kawakami K, Tanaka T. Remarkable configurational changes of some dimethyltin complexes derived from ONO tridentate schiff bases in strong donor solvents. J Organomet Chem. 1973;49:409–15.
Matsubayashi G-e, Tanaka T, Nishigaki S, Nakatsu K. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of some N′-substituted pyridine-2-carbaldimine adducts of n-butyltrichlorotin(IV) and the molecular structure of n-butyltrichloro(N′-phenylpyridine-2-carbaldimine-NN′)-tin(IV). J Chem Soc Dalton Trans. 1979;3:501–5.
Holeček J, Nádvorník M, Handlíř K, Lyčka A. 13C and 119Sn NMR spectra of Di-n-butyltin(IV) compounds. J Organomet Chem. 1986;315:299–308.
Roy M, Roy S, Devi NM, Singh CB, Singh KS. Synthesis, structural characterization and antimicrobial activities of diorganotin(IV) complexes with azo-imino carboxylic acid ligand: crystal structure and topological study of a doubly phenoxide-bridged dimeric dimethyltin(IV) complex appended with free carboxylic acid groups. J Mol Struct. 2016;1119:64–70.
Basu Baul TS, Chaurasiya A, Lyčka A, Rojas-León I, Höpfl H. Molecular aggregations of bicyclodioxazastannone produced from multicomponent reactions involving functionalized 2-hydroxybenzaldehydes, α- or β-amino acids and a dimethyltin precursor. J Organomet Chem. 2019;898:120859.
Öztaş SG, Şahin E, Ancın N, İde S, Tüzün M. Structural and spectral studies of N-(3-hydroxypyridine-2-yl)salicylideneimine and N-(3-hydroxypyridine-2-yl)-5-bromosalicylideneimine and their dimethyltin(IV) complexes. Z Kristallogr Cryst Mater. 2003;218:492.
Patani GA, LaVoie EJ. Bioisosterism: a rational approach in drug design. Chem Rev. 1996;96:3147–76.
de las M, Oliva M, Gallucci N, Zygadlo JA, Demo MS. Cytotoxic activity of argentinean essential oils on Artemia salina. Pharm Biol. 2007;45:259–62.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank PAPIIT IN204417 and IN206020 for financial assistance and the technical support for the determination of the IR and mass spectrometry to María del Carmen García, María del Rocío Patiño, and Javier Pérez.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galván-Hidalgo, J.M., Roldán-Marchán, D.M., González-Hernández, A. et al. Organotin (IV) complexes from Schiff bases ligands based on 2-amino-3-hydroxypyridine: synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxicity. Med Chem Res 29, 2146–2156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02630-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02630-4