Abstract
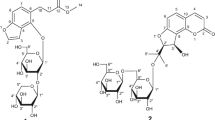
A new triterpene diglycoside, tibesaikosaponin V (TKV), was isolated from the methanol extract of the roots of Bupleurum chinense DC. by normal and reversed phase column chromatography. The chemical structure of this new compound was elucidated based on extensive spectroscopic analysis, including 1D and 2D NMR, HR-ESI-MS, and chemical degradation method. Our results indicated that TKV inhibited lipid accumulation and triacylglycerol content occurred without cytotoxicity to 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Furthermore, TKV significantly suppressed the mRNA expression of nuclear transcription factors such as, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα). These results suggest that TKV shows the ability to inhibit 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation of and may have therapeutic potential for obesity and its associated metabolic disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen R, Guo X, Cheng B, Gong Y, Ying B, Lin M (2018a) Saikosaponin a inhibits cigarette smoke-induced oxidant stress and inflammatory responses by activation of Nrf2. Inflammation 41:1297–1303
Chen X, Chen S, Liang W, Wang M, Li C, Wang S, Dong S, Yi L, Li C (2018b) Saikosaponin A attenuates perimenopausal depression-like symptoms by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Neurosci Lett 662:283–289
Choi KH, Lee HA, Park MH, Han J (2017) Cyanidin-3-rutinoside increases glucose uptake by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 54:1–6
Chyau C, Chu C, Chen S, Duh P (2018) The inhibitory effects of djulis (chenopodium formosanum) and its bioactive compounds on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Molecules 23:1780
Collins KH, Herzog W, MacDonald GZ, Reimer RA, Rios JL, Smith IC, Zernicke RF, Hart DA (2018) Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and musculoskeletal disease: common inflammatory pathways suggest a central role for loss of muscle integrity. Front Physiol 9:112
Committee of National Pharmacopoeia (2015) China pharmacopoeia, Vol. 1. Beijing, China, p 280
Fang W, Yang Y, Guo B, Cen S (2017) Anti-influenza triterpenoid saponins (saikosaponins) from the roots of Bupleurum marginatum var. stenophyllum. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:1654–1659
Fasshauer M, Blüher M (2015) Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36:461–470
Guo J, Cao Y, Ho C, Jin S, Huang Q (2017) Aged citrus peel (chenpi) extract reduces lipogenesis in differentiating 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Funct Foods 34:297–303
Jiang X, Wang L, Wang E, Zhang G, Chen B, Wang M, Li F (2018) Flavonoid glycosides and alkaloids from the embryos of Nelumbo nucifera seeds and their antioxidant activity. Fitoterapia 125:184–190
Kim E, Yi Y, Son Y, Han SY, Kim DH, Nam G, Hossain MA, Kim J, Park J, Cho JY (2018) BIOGF1K, a compound K-rich fraction of ginseng, plays an antiinflammatory role by targeting an activator protein-1 signaling pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage-like cells. J Ginseng Res 42:233–237
Kuang H, Sun S, Yang B, Xia Y, Feng W (2009) New megastigmane sesquiterpene and indole alkaloid glucosides from the aerial parts of Bupleurum chinense DC. Fitoterapia 80:35–38
Lee MS, Shin Y, Jung S, Kim SY, Jo YH, Kim CT, Yun MK, Lee SJ, Sohn J, Yu HJ, Kim Y (2017) The inhibitory effect of tartary buckwheat extracts on adipogenesis and inflammatory response. Molecules 22:1160
Li D, Wu J, Liu L, Wu Y, Li L, Huang X, Liu Q, Yang J, Song S, Wu C (2015) Cytotoxic triterpenoid glycosides (saikosaponins) from the roots of Bupleurum chinense. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25:3887–3892
Li F, Yang F, Liu X, Wang L, Chen B, Li L, Wang M (2017a) Cucurbitane glycosides from the fruit of Siraitia grosvenori and their effects on glucose uptake in human HepG2 cells in vitro. Food Chem 228:567–573
Li H, Zhao Y, Zeng M, Fang F, Li M, Qin T, Ye L, Li H, Qu R, Ma S (2017b) Saikosaponin D relieves unpredictable chronic mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in rats: involvement of HPA axis and hippocampal neurogenesis. Psychopharmacology 234:3385–3394
Li Y, Cai T, Zhang W, Zhu W, Lv S (2017c) Effects of Saikosaponin D on apoptosis in human U87 glioblastoma cells. Mol Med Rep 16:1459–1464
Liang H, Zhao YY, Qiu HY, Huang J, Zhang RY (1998) A new saikosaponin from Bupleurum chinense DC. Acta Pharm Sin 33:37–41
Liang H, Cui YJ, Zhao YY, Wang B, Yang WX, Yu Y (2001a) Saikosaponin v-2 from Bupleurum Chinense. Chin Chem Lett 12:331–332
Liang H, Han ZY, Zhao YY, Wang B, Cui YX, Yang WX, Yu Y (2001b) Saikosaponin q-1 from Bupleurum chinense. Acta Bot Sin 43:198–200
Liang ZT, Qin MJ, Wang ZT, Yu GD (2001c) The advance on the research of saponins of Bupleurum. Nat Prod Res Dev 13:67–72
Liu QX, Liang H, Zhao YY, Wang B, Yang WX, Yu Y (2001) Saikosaponin v-1 from roots of Bupleurum chinense DC. J Asian Nat Prod Res 3:139–144
Lorrai I, Maccioni P, Carai MA, Capra A, Castelli MP, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2017) Suppressing effect of saikosaponin A, an active ingredient of Bupleurum falcatum, on chocolate self-administration and reinstatement of chocolate seeking in rats. Neurosci Lett 638:211–217
Moseti D, Regassa A, Kim W (2016) Molecular regulation of adipogenesis and potential anti-adipogenic bioactive molecules. Int J Mol Sci 17:124
Nishina A, Itagaki M, Sato D, Kimura H, Hirai Y, Phay N, Makishima M (2017) The rosiglitazone-like effects of vitexilactone, a constituent from Vitex trifolia L. in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Molecules 22:2030
Ohashi K, Shibata R, Murohara T, Ouchi N (2014) Role of anti-inflammatory adipokines in obesity-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab 25:348–355
Patel TP, Rawal K, Bagchi AK, Akolkar G, Bernardes N, Dias DD, Gupta S, Singal PK (2016) Insulin resistance: an additional risk factor in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Heart Fail Rev 21:11–23
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA (2006) Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:885–896
Tsuyoshi H, Wong VK, Han Y, Orisaka M, Yoshida Y, Tsang BK (2017) Saikosaponin-d, a calcium mobilizing agent, sensitizes chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by facilitating mitochondrial fission and G2/M arrest. Oncotarget 8:99825
Wang HW, Liu M, Zhong TD, Fang XM (2015) Saikosaponin-d attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:15137–15145
Wang Y, Guo Q, Cheng Z, Zeng K, Liang H, Tu P, Chen S, Zhang Q (2017) New saikosaponins from the roots of Bupleurum chinense. Phytochem Lett 21:183–189
Yu J, Deng A, Wu L, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Wang W, Qin H (2013) Osteoclast-inhibiting saikosaponin derivatives from Bupleurum Chinense. Fitoterapia 85:101–108
Zhang T, Zhou J, Wang Q (2007) Flavonoids from aerial part of Bupleurum chinense DC. Biochem Syst Ecol 35:801–804
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the West Light Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y7C1031100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21561142003, 31600281 and 41501262) Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20171269), and Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Wu, ZW., Luo, Y. et al. A new triterpene diglycoside from the roots of Bupleurum chinense DC. and its inhibitory effect on adipogensis in 3T3-L1 cells. Med Chem Res 28, 239–245 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2279-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2279-5