Abstract
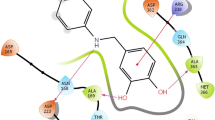
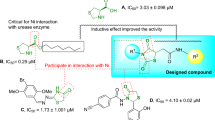
Discovery of new urease inhibitors is an important approach towards the treatment of diseases caused by ureolytic bacteria. Urease has an important role in several pathologies, such as urolithiasis, peptic and duodenal ulcers, etc. In this regard, urease inhibitory activity of heterocyclic synthetic compounds 1–14, belonging to different chemical classes was evaluated by employing in vitro biochemical assay, and saturation transfer difference-NMR technique. Compounds 1, 3–5, 7, 10, and 12 have shown urease inhibitory potential in vitro. Among them, compound 1 was found to be more potent (IC50 of 12.90 ± 0.63 µM) than a clinical drug, acetohydroxamic acid (IC50 = 41.5 ± 1.50 µM) (Standard). Compounds 3 (IC50 = 15.0 ± 1.10 µM), 4 (IC50 = 24.67 ± 2.87 µM), and 5 (IC50 = 25.50 ± 0.63 µM) were also identified as potent inhibitors of urease enzyme. These compounds showed strong interactions with the urease enzyme (receptor) in saturation transfer difference-NMR spectra. Specifically, aromatic protons of active compounds received maximum Rf saturation from the receptor protein, thus were inferred to be as in close proximity to the protein. New inhibitors identified through biochemical assay and saturation transfer difference-nuclear magnetic resonance techniques were then subjected to kinetic and molecular docking studies to investigate their mode of inhibition, and production of their interactions with the protein at atomic level, respectively. Active compounds were found to be non-cytotoxic against mouse fibroblast (3T3) cell line MTT assay. Present study thereby identifies new inhibitors of urease enzyme in vitro as leads for further investigation towards the development of novel mechanism-based urease inhibitors.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin M, Anwar F (2012) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through reduction with Solanum xanthocarpum L. berry extract: Characterization, antimicrobial and urease inhibitory activities against Helicobacter pylori. Int J Mol Sci 13:9923–9941
Amtul Z, Atta-ur-Rahman, Siddiqui RA, Choudhary MI (2002) Chemistry and mechanism of urease inhibition. Curr Med Chem 9:1323–1348
Arfan M, Ali M, Ahmad H, Anis I, Khan A, Choudhary MI, Shah MR (2010) Urease inhibitors from Hypericum oblongifolium Wall. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 25:296–299
Atia-tul-Wahab, Khan A, Marasini BP, Lodhi MA, Atta-ur-Rahman, Choudhary MI (2013) Discovery and study of the bindingepitopes of novel urease inhibitors by STD-NMR spectroscopy and biochemical analyses. Lett Drug Des Discov 10:515–521
Awllia JAJ, AL-Ghamdi M, Huwait E, Javaid S, Atia-tul-Wahab, Rasheed S, Choudhary MI (2015) Flavonoids as natural inhibitors of jack bean urease Enzyme. Lett Drug Des Discov 13:243–249
Balasubramanian A, Ponnuraj K (2010) Crystal structure of the first plant urease from Jack bean: 83 years of journey from its first crystal to molecular structure. J Mol Biol 400:274–283
Blaser MJ (1990) Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastro duodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis 161:626–633
Chen Y, Liao J, Chen M, Huang Q, Lu Q (2015) Gossypol: New class of urease inhibitors, molecular docking and inhibition assay. J Chem Pharm Res 7(1):10–15
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shaw DE, Shelley M, Perry JK, Francis P, Shenkin PS (2004) Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein–ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196
Halgren TA, Murphy RB, Friesner RA, Beard HS, Frye LL, Pollard WT, Banks JL (2004) Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Chapter 1: introduction 6 Schrödinger software release 2015-4 enrichment factors in database screening. J Med Chem 47:1750–1759
Hameed A, Anwar A, Khan KM, Malik R, Shahab F, Siddiq S, Basha FZ, Choudhary MI (2013) Urease inhibition and anticancer activity of novel polyfuntional 5,6-dihydropyrimidine derivatives and their structure–activity relationship. Eur J Chem 4:49–52
Khan KM, Ali M, Wadood A, Zaheer-ul-Haq, Khan M, Lodhi MA, Perveen S, Choudhary MI, Voelter W (2011) Molecular modeling-based antioxidant arylidene barbiturates as urease inhibitors. J Mol Graph Model 30:153–156
Khan KM, Rahim F, Khan A, Taha M, Saad SM, Ali S, Khan M, Najeebullah, Shaikh A, Perveen S, Choudhary MI (2015) Synthesis of benzophenone hydrazone analogs and their DPPH radical scavenging, and urease inhibitory activities. J Chem Soc Pak 37:157–161
Khan KM, Ullah Z, Lodhi MA, Ali M, Choudhary MI, Atta-ur-Rahman, Haq ZU (2006) Successful computer guided planned synthesis of (4R)-thiazolidine carboxylic acid and its 2-substituted analogues as urease inhibitors. Mol Divers 10:223–231
Khan MH, Hameed S, Yasin KA, Akhtar T, Khan KM (2010) Design, synthesis, and urease inhibition studies of some of 4-amino-5-aryl-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione. Monatsh Chem 14:479–484
Kosikowska P, Berlicki L (2011) Urease inhibitors as potential drugs for gastric and urinary tract infections: A patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 21:945–957
Macegoniuk K (2013) Inhibitors of bacterial and plants urease. A review. Folia Biologica et Oecologica 9:9–16
Mayer M, Meyer B (2001) Group epitope mapping by saturation transfer difference NMR to identify segments of a ligand in direct contact with a protein receptor. J Am Chem Soc 123:6108–6117
Meng X-Y, Zhang H-X, Mezei M, Cui M (2011) Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 7:146–157
Mobley HL, Hausinger RP (1998) Microbial ureases: significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiol Rev 53:85–108
Modolo LV, de Fatima A, França MGC, Horta LP, Faria CVN, da Silva DL, Morais VSS (2013) National Institute for industrial property (INPI), Patent # BR1020130173568, Brazil
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Olsson MH, Søndergard CR, Rostkowski M, Jensen JH (2011) Propka3: Consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions. J Chem Theory Comput 7:525–537
Romero V, Akpinar H, Assimos DG (2010) Kidney stones: A global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev Urol 12:e86–e96
Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27:221–234
Schrödinger (2015a) LigPrep, version 3.6, LLC, New York, NY
Schrödinger (2015b) LLC, New York, NY. Glide, version 6.9
Schrödinger (2015c) Prime, version 4.2, LLC, New York, NY.
Schrödinger (2015d) Protein Preparation Wizard 2015-4; Epik version 2.4, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2015; Impact version 5.9, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2015; Prime version 3.2, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2015
Scopes RK (2002) Enzyme activity and assays. eLS
Shahzad SA, Yar M, Khan ZA, Khan IU, Naqvi SAR, Mahmood N, Khan KM (2012) Microwave-assisted solvent free efficient synthesis of 1,3,4-oxazole-2(3H)-thiones and their in vitro urease inhibitory activity. Eur J Chem 3:143–146
Taleb-Contini SH, Salvador MJ, Watanabe E, Ito IY, de Oliveira DCR (2003) Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids and steroids isolated from two Chromolaena species. Braz J Pharm Sci 39(4):403–408
Thadhani VM, Khan A, Atia-tul-Wahab, Javaid S, Shafqat A, Zaheer-ul-Haq, Choudhary MI (2015) Study of binding epitopes by STD-NMR spectroscopy and molecular docking of urease inhibitors from lichens. Lett Drug Des Discov 13:282–294
Weatherburn MW (1967) Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39:971–974
Yu-Sen W, Dingjiang L, Daniel FW (2004) Competition STD NMR for the detection of high-affinity ligands and NMR-based screening. Magn Reson Chem 42:485–489
Zhang L, Mulrooney SB, Leung AF, Zeng Y, Ko BB, Hausinger RP, Sun H (2006) Inhibition of urease by bismuth (III): Implications for the mechanism of action of bismuth drugs. BioMetals 19:503–511
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at the King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, under grant no. (21-130-35-RG). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical, and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
A. Khan, J., Wahab, At., Javaid, S. et al. Studies on new urease inhibitors by using biochemical, STD-NMR spectroscopy, and molecular docking methods. Med Chem Res 26, 2452–2467 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1945-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1945-3