Abstract
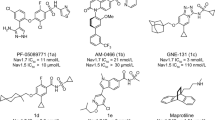
Sponges of the genus Agelas produce compounds that modulate the activity of voltage-gated sodium ion channels and contribute novel scaffolds for the development of compounds with activity against a plethora of biological targets. In particular, clathrodin and dibromosceptrin were reported to decrease the average maximum amplitude of inward sodium currents in isolated chick embryo sympathetic ganglia cells; we envisaged these compounds as a starting point to design novel Nav channel modulators. This endeavor was part of our long-term goal of designing a comprehensive library of Agelas alkaloid analogs that would cover a broader chemical space and allow us to examine the activity of such compounds on Nav channels. Our series of compounds was designed by maintaining the terminal structural features found in clathrodin while rigidizing the central part of the molecule and replacing the 3-aminopropene linker with a 4-methylenepiperazine moiety. Synthesised compounds were screened for inhibitory action against the human voltage-gated sodium channel isoforms Nav 1.3, Nav 1.4, cardiac Nav 1.5, and Nav 1.7 using an automated patch clamp electrophysiology technique. The results demonstrate that we have obtained a series of compounds with a modest but selective inhibitory activity against the Nav 1.3 channel isoform. The most potent compound showed selective activity against the Nav 1.3 channel isoform with an IC50 of 19 μM and is a suitable starting point for further development of selective Nav 1.3 channel modulators. Such compounds could prove to be beneficial as a pharmacological tool towards the development of novel therapeutically useful compounds in the treatment of pain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Magid AF, Carson KG, Harris BD, Maryanoff CA, Shah RD (1996) Reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones with sodium triacetoxyborohydride. Studies on direct and indirect reductive amination procedures. J Org Chem 61:3849–3862
Andavan GSB, Lemmens-Gruber R (2011) Voltage-gated sodium channels: mutations, channelopathies and targets. Curr Med Chem 18:377–397
Anderluh M, Cesar J, Štefanič P, Kikelj D, Janeš D, Murn J, Nadrah K, Tominc M, Addicks E, Giannis A, Stegnar M, Sollner Dolenc M (2005) Design and synthesis of novel platelet fibrinogen receptor antagonists with 2H-1,4-benzoxazine-3(4H)-one scaffold. A systematic study. Eur J Med Chem 40:25–49
Anger T, Madge DA, Mulla M, Riddall D (2001) Medicinal chemistry of neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel blockers. J Med Chem 44:115–137
Bickmeyer U, Drechsler C, Kock M, Assmann M (2002) Brominated pyrrole alkaloids from marine Agelas sponges reduce depolarization-induced cellular calcium elevation. Toxicon 44:45–51
Bölcskei H, Tarnawa I, Kocsis P (2008) Voltage-gated sodium channel blockers. 2001–2006: an overview. Med Chem Res 17:356–368
Burek F, Burek J (2013) BioLib: taxonomic tree of plants and animals with photos. http://www.biolib.cz/en/image/id26477/. Accessed 12 Dec 2013
Cafieri F, Carnuccio R, Fattorusso E, Taglialatela Scafati O, Vallefuoco T (1997) Antihistaminic activity of bromopyrrole alkaloids isolated from Caribbean Agelas sponges. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 7:2283–2288
Catterall WA (2000) From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron 26:13–25
Clare JJ, Tate SN, Nobbs M, Romanos MA (2000) Voltage-gated sodium channels as therapeutic targets. Drug Discov Today 5:506–520
England S, de Groot MJ (2009) Subtype-selective targeting of voltage-gated sodium channels. Brit J Pharmacol 158:1413–1425
Grant JA, Gallardo MA, Pickup BT (1996) A fast method of molecular shape comparison: a simple application of a Gaussian description of molecular shape. J Comput Chem 17:1653–1666
Hawkins PC, Nicholis A (2012) Conformer generation with OMEGA: learning from the data set and the analysis of failures. J Chem Inf Model 52:2919–2936
Hawkins PCD, Skillman AG, Nicholis A (2007) Comparison of shape-matching and docking as virtual screening tools. J Med Chem 50:74–82
Hawkins PCD, Skillman AG, Warren GL, Ellingson BA, Stahl MT (2010) Conformer generation with OMEGA: algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the protein databank and the Cambridge structural database. J Chem Inf Model 50:572–584
Hodnik Ž, Tomašič T, Mašič LP, Chan F, Kirby RW, Madge DJ, Kikelj D (2013) Novel state-dependent voltage-gated sodium channel modulators, based on marine alkaloids from Agelas sponges. Eur J Med Chem 70:154–164
Jukič M, Kikelj D, Anderluh M (2013) Isoform selective voltage-gated sodium channel modulators and the therapy of pain. Curr Med Chem 20:1–24
Keifer PA, Schwartz RE, Moustapha ESK, Hughes RG Jr, Rittschof D, Rinehart KL (1991) Bioactive bromopyrrole metabolites from the Caribbean sponge Agelas conifer. J Org Chem 56:2965–2975
Laport MS, Santos OCS, Muricy G (2009) Marine sponges: potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 10:86–105
Little TL, Webber SE (1994) A simple and practical synthesis of 2-aminoimidazoles. J Org Chem 59:7299–7305
Neuman DJ (2008) Natural products as leads to potential drugs: an old process or the new hope for drug discovery. J Med Chem 51:2589–2599
OEDocking, version 3.0.1, OpenEye Scientific Software, Inc., Santa Fe, NM, USA, www.eyesopen.com, 2013
Olofson A, Yakushijin K, Horne DA (1998) Synthesis of marine sponge alkaloids oroidin, clathrodin, and dispacamides. Preparation and transformation of 2-amino-4,5-dialkoxy-4,5-dihydroimidazolines from 2-aminoimidazoles. J Org Chem 63:1248–1253
OMEGA, version 2.4.6, OpenEye Scientific Software, Inc., Santa Fe, NM, USA, www.eyesopen.com, 2013
Shrikhande JJ, Gawande MB, Jayaram RV (2008) A catalyst-free N-benzyloxycarbonylation of amines in aqueous micellar media at room temperature. Tetrahedron Lett. 49:4799–4803
Peat AJ, Sebahar PR, Youngman M, Chong PY, Zhang H (2008) Chemical Compounds WO2008154271-A1
Perdicaris S, Vlachogianni T, Valavanidis A (2013) Bioactive natural substances from marine sponges: new developments and prospects for future pharmaceuticals. Nat Prod Chem Res 1:1–8
Rasapalli S, Kumbam V, Dhawane AN, Golden JA, Lovely CJ, Rheingold AL (2013) Total synthesis of oroidin, hymenidin and clathrodin. Org Biomol Chem 11:4133–4137
Richards JJ, Ballard TE, Huigens RW, Melander C (2008) Synthesis and screening of an oroidin library against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. ChemBioChem 9:1267–1279
Rivera Rentas AL, Rosa R, Rodriguez AD, De Motta GE (1995) Effect of alkaloid toxins from tropical marine sponges on membrane sodium currents. Toxicon 33:491–497
Storey BT, Sullivan WW, Moyer CL (1964) The pKa values of some 2-amino imidazolium ions. J Org Chem 29:3118–3120
Sun J, Dong Y, Cao L, Wang X, Wang S, Hu Y (2004) Highly efficient chemoselective deprotection of O,O-acetals and O,O-ketals catalyzed by molecular iodine in acetone. J Org Chem 69:8932–8934
Taylor CP (1996) Voltage-gated Na+ channels as targets for anticonvulsant, analgesic and neuroprotective drugs. Curr Pharm Des 2:375–388
Teixeira C, Serradji N, Amroune S, Storck K, Rogez-Kreus C, Clayette P, Barbault F, Maurel F (2013) Is the conformational flexibility of piperazine derivatives important to inhibit HIV-1 replication? J Mol Graph Model 44:91–103
Termin A, Martinborough E, Wilson D (2008) Chapter 3. Recent advances in voltage-gated sodium channel blockers: therapeutic potential as drug targets in the CNS. Annu Rep Med Chem 43:43–60
Tomašić T, Hartzoulakis B, Zidar N, Chan F, Kirby RW, Madge DJ, Peigneur S, Tytgat J, Kikelj D (2013) Ligand- and structure-based virtual screening for clathrodin-derived human voltage-gated sodium channel modulators. J Chem Inf Model 53:3223–3232
Tuccinardi T, Ortore G, Amelia Santos M, Marques SM, Nuti E, Rosello A, Martinelli AJ (2009) Multitemplate Alignment method for the development of a reliable 3D-QSAR model for the analysis of MMP3 inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model 49:1715–1724
vROCS, version 3.2.0.4, OpenEye Scientific Software, Inc., Santa Fe, NM, USA, www.eyesopen.com, 2013
Vuorela P, Leinonenb M, Saikkuc P, Tammelaa P, Rauhad JP, Wennberge T, Vuorela H (2004) Natural products in the process of finding new drug candidates. Curr Med Chem 11:1375–1389
Waxman SG, Kocsis JD, Black JA (1994) Type III sodium channel mRNA is expressed in embryonic but not adult spinal sensory neurons, and is reexpressed following axotomy. J Neurophysiol 72:466–471
Yoke Chong P, Peat AJ, Sebahar PR, Youngman M, Zhang H (2010) Chemical Compounds US Patent 2010/0216746 A1 26th Aug 2010
Žula A, Kikelj D, Ilaš J (2013) 2-Aminoimidazoles in medicinal chemistry. Mini-Rev Med Chem 13:1921–1943
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the European Union FP7 Integrated Project MAREX: Exploring Marine Resources for Bioactive Compounds: From Discovery to Sustainable Production and Industrial Applications (Project No. FP7-KBBE-2009-3-245137). We thank OpenEye Scientific Software, Inc. for free academic licenses of their software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jukič, M., Frlan, R., Chan, F. et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of piperazine derivatives as novel isoform selective voltage-gated sodium (Nav) 1.3 channel modulators. Med Chem Res 24, 2366–2380 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1300-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1300-x