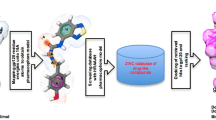
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) enters into the host cell using its non-covalently bonded envelope glycoproteins 120 and 41 (gp120 and gp41). HIV-1 gp41 plays an instrumental role in the membrane fusion and entry of viral genome into the host cytosol. Binding of virus to host cell receptors triggers a cascade of conformational changes in gp120 and gp41. During the fusion, core of gp41 comprising C-heptad repeat coils into the highly conserved, deep hydrophobic pocket of N-heptad repeat forming a six-helix bundle (6-HB). The apposition of the host cell membrane and viral membrane is initiated with the formation of 6-HB. The inhibition of 6-HB formation has been proved to be an effective way to thwart the viral and host cell fusion. In this work, we have performed computational study on 62 6-HB formation inhibitors reported in the literature. An integrated computational protocol using molecular docking and molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area calculations was employed to these known inhibitors to understand mode of interaction with receptor. Our study revealed reasonably good agreement between computational parameters and experimental inhibitory potentials of these molecules. The results encouraged us to design novel gp41 6-HB formation inhibitors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JS, Coligan JE, Barin F, McLane MF, Sodroski JG, Rosen CA, Haseltine WA, Lee TH, Essex M (1985) Major glycoprotein antigens that induce antibodies in AIDS patients are encoded by HTLV-III. Science 228:1091–1094
Berger EA (1997) HIV entry and tropism: the chemokine receptor connection. AIDS 11:S3–S16
Chan DC, Fass D, Berger JM, Kim PS (1997) Core structure of gp41 from the HIV envelope glycoprotein. Cell 89:263–273
Chan DC, Chutkowski CT, Kim PS (1998) Evidence that a prominent cavity in the coiled-coil of HIV type 1 gp41 is an attractive drug target. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15613–15617
Chandrika M, Viswanadham VN (2013) Could MM-GBSA be accurate enough for calculation of absolute protein/ligand binding free energies. J Mol Graph Model 46:41–51
Craik DJ, Fairlie DavidP, Liras Spiros, Price David (2012) The future of peptide based drugs. Chem Biol Drug Des 81:136–147
Ernst JT, Kutzki O, Debnath AK, Jiang S, Lu H, Hamilton AD (2002) Design of a protein surface antagonist based on alpha-helix mimicry: inhibition of gp41 assembly and viral fusion. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 41:278–281
Fei Yu, Lu Lu, Lanying Du, Zhu Xiaojie, Debnath AsimK, Jiang Shibo (2013) Approaches for Identification of HIV-1 Entry Inhibitors Targeting gp 41 pocket. Viruses 5:127–149
Gallo SA, Finnegan CM, Viard M, Raviv Y, Dimitrov A, Rawat SS, Puri A, Durell S, Blumenthal R (2003) The HIV Env-mediated fusionreaction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1614:36–50
Greenidge PA, Kramer Christian, Mozziconacci Jean-Christophe, Wolf RomainM (2013) MM/GBSA binding energy prediction on the pdbbind data set: successes, failures, and directions for further improvement. J Chem Inf Model 53:201–209
Guimarães CRW, Cardozo Mario (2008) MM-GB/SA rescoring of docking poses in structure-based lead optimization. J Chem Inf Model 48:958–970
Gustchina E, Li M, Louis JM, Anderson DE, Lloyd J, Frisch C, Bewley CA, Gustchina A, Wlodawer A, Clore GM (2010) Structural basis of HIV-1 neutralization by affinity matured fabs directed against the internal trimeric coiled-coil of gp41. PLoS Pathog 6:e1001182–e1001182
Hayes JM, Archontis G (2011) MM-GB(PB)SA calculations of protein-ligand binding free energies. J R Soc Interface 8:171–190
He Y, Liu S, Jing W, Lu H, Cai D, Chin DJ, Debnath AK, Kirchhoff F, Jiang S (2007) Conserved residue Lys574 in the cavity of HIV-1 gp41 coiled-coil domain is critical for six-helix bundle stability and virus entry. J Biol Chem 282:25631–25639
He Y, Liu S, Li J, Lu H, Qi Z, Liu Z, Debnath AK, Jiang S (2008) Conserved salt-bridge between the N- and C-terminal heptad repeat regions of HIV-1 gp41 core structure is critical for virus entry and inhibition. J Virol 82:11129–11139
He X-Y, Zou Peng, Qui Jiayin, Hou Ling, Jiang Shibo, Liu Shuwen, Xie Lan (2011) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-substituted 2,5-dimethyl-N-(3-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl)pyrroles as novel potential HIV-1 gp41 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 19:6726–6734
Jacobs A, Garg H, Viard M, Raviv Y, Puri A, Blumenthal R (2008) HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated fusion and pathogenesis: implications for therapy and vaccine development. Vaccine 26:3026–3035
Jiang S, Debnath AK (2000) A salt bridge between an N-terminal coiledcoil of gp41 and an antiviral agent targeted to the gp41 core is important for anti-HIV-1 activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 270:153–157
Jiang S, Zhao Q, Debnath AK (2002) Peptide and non-peptide HIV fusion inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des 8:563–580
Kaminski GA, Friesner RA, Tirado-Rives J, Jorgensen WL (2001) Evaluation and reparametrization of the OPLS-AA force field for proteins via comparison with accurate quantum chemical calculations on peptides. J Phys Chem B 105:6474–6487
Kilby JM, Eron JJ (2003) Novel therapies based on mechanisms of HIV-1 cell entry. N Engl J Med 348:2228–2238
Lalezari JP, Henry K, O’Hearn M, Montaner JS, Piliero PJ, Trottier B, Walmsley S, Cohen C, Kuritzkes DR, Eron JJ Jr, Chung J, DeMasi R, Donatacci L, Drobnes C, Delehanty J, Salgo M (2003) Enfuvirtide, an HIV-1 fusion inhibitor, for drug-resistant HIV infection in north and south America. N Engl J Med 348:2175–2185
Liu K, Lu H, Hou L, Qi Z, Teixeira C, Barbault F, Fan BT, Liu S, Jiang S, Xie L (2008) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of N-carboxyphenylpyrrole derivatives as potent HIV fusion inhibitors targeting gp41. J Med Chem 51:7843–7854
Malashkevich VN, Chan DC, Chutkowski CT, Kim PS (1998) Crystal structure of the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) gp41 core: conserved helical interactions underlie the broad inhibitory activity of gp41 peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(16):9134–9139
Rastelli G, Rio AD, Degliesposti G, Sgobba M (2010) Fast and accurate predictions of binding free energies using MM-PBSA and MM-GBSA. J Comput Chem 31:797–810
Roux KH, Taylor KA (2007) AIDS virus envelope spike structure. Curr Opin Struct Biol 17:244–252
Sattentau QJ, Moore JP (1991) Conformational changes induced in the humanimmunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein by soluble CD4 binding. J Exp Med 174:407–415
Sattentau QJ, Moore JP (1993) Conformational changes induced in the envelope glycoproteins of the human and simian immunodeficiency viruses by soluble receptor binding. J Virol 67:7383–7393
Schrödinger, Suite 10.0, Schrödinger, LLC New York, NY, 2009
Tan K, Liu J, Wang J, Shen S, Lu M (1997) Atomic structure of thermostable subdomain of HIV-1 gp41. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(23):12303–12308
Trkola A, Dragic Tatjana, Arthos James, Binley JamesM, Olson WilliamC, Allaway GrahamP, Cheng-Mayer Cecilia, Robinson James, Maddon Paul J, Moore John P (1996) CD4-dependent, antibody-sensitive interactions between HIV-1and its co-receptor CCR-5. Nature 384:184–187
Wang Y, Lu H, Zhu Q, Jiang S, Liao Y (2010) Structure-based design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new N-carboxyphenylpyrrole derivatives as HIV fusion inhibitors targeting gp41. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:189–192
Weissenhorn W, Dessen A, Harrison SC, Skehel JJ, Wiley DC (1997) Atomic structure of the ectodomain from HIV-1 gp41. Nature 387:426–430
Xiao-Yang He LuLu, Qiu Jiayin, Zou Peng, Fei Yu, Jiang Xing-Kai, Li Lin, Jiang Shibo, Liu Shuwen, Xie Lan (2013) Small molecule fusion inhibitors: design, synthesis and biological evaluation of (Z)-3-(5-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidinylidene) methyl)-N-(3-carboxy-4-hydroxy)phenyl-2,5-dimethylpyrroles and related derivatives targeting HIV-1 gp41. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:7539–7548
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to University College of Science, Osmania University, Hyderabad, India, where the work was carried out. The authors also acknowledge Schrödinger Inc. for Glide and Prime software used for molecular docking and MM/GBSA calculations. This research was carried out by fellowship given by UGC and research grant given by DST (SB/EMEQ-004/2013), New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munnaluri, R., Sivan, S.K. & Manga, V. Molecular docking and MM/GBSA integrated protocol for designing small molecule inhibitors against HIV-1 gp41. Med Chem Res 24, 829–841 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1185-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1185-8