Abstract
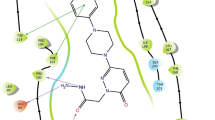
Several studies have revealed that phthalides are suitable scaffolds for the design of high potency monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, in which C6-substituted phthalides have been shown high binding affinities to the MAO-A and MAO-B isoenzyme without delineating the underlying mechanism. By means of molecular modeling, we proposed a structural basis of such activity, in which these compounds could successfully dock into the active pocket of human MAO isoforms with predicted affinities in comparison to phthalide. Our study indicated that the interaction of hydrogen bond was more important factor for C6-substituted phthalides binding to MAO-A, and the orientations of inhibitors and the bound residues had the major impact on the binding to MAO-B. These results, therefore, suggested that C6-substituted phthalides served as promising leads for the development of drug treatments to neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhafez OM, Amin KM, Ali HI, Abdalla MM, Batran RZ (2012) Monoamine oxidase-A and B inhibiting effect and molecular modeling of some synthesized coumarin derivatives. Neurochem Int 62(2):198–209
Binda C, Newton-Vinson P, Hubálek F, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2001) Structure of human monoamine oxidase B, a drug target for the treatment of neurological disorders. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9(1):22–26
Binda C, Mattevi A, Edmondson DE (2002) Structure-function relationships in flavoenzyme-dependent amine oxidations: a comparison of polyamine oxidase and monoamine oxidase. J Biol Chem 277(27):23973–23976
Binda C, Hubálek F, Li M, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2004a) Crystal structure of human monoamine oxidase B, a drug target enzyme monotopically inserted into the mitochondrial outer membrane. FEBS Lett 564(3):225–228
Binda C, Hubálek F, Li M, Herzig Y, Sterling J, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2004b) Crystal structures of monoamine oxidase B in complex with four inhibitors of the N-propargylaminoindan class. J Med Chem 47(7):1767–1774
Bonivento D, Milczek EM, McDonald GR, Binda C, Holt A, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2010) Potentiation of ligand binding through cooperative effects in monoamine oxidase B. J Biol Chem 285(47):36849–36856
Cheng YC, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of the inhibitor which causes 50 % inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
De Colibus L, Li M, Binda C, Lustig A, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2005) Three-dimensional structure of human monoamine oxidase A (MAO A): relation to the structures of rat MAO A and human MAO B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(36):12684–12689
Edmondson DE, Binda C, Mattevi A (2004) The FAD binding sites of human monoamine oxidases A and B. Neurotoxicology 25(1):63–72
Fernandez HH, Chen JJ (2007) Monoamine oxidase‐B inhibition in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacotherapy 27(12P2):174S–185S
Fowler CJ, Ross SB (1984) Selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A and B: biochemical, pharmacological, and clinical properties. Med Res Rev 4(3):323–358
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36(22):3219–3228
Hubálek F, Binda C, Khalil A, Li M, Mattevi A, Castagnoli N, Edmondson DE (2005) Demonstration of isoleucine 199 as a structural determinant for the selective inhibition of human monoamine oxidase B by specific reversible inhibitors. J Biol Chem 280(16):15761–15766
Lasbennes F, Sercombe R, Seylaz J (1983) Monoamine oxidase activity in brain microvessels determined using natural and artificial substrates: relevance to the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3(4):521–528
Manley-King CI, Bergh JJ, Petzer JP (2011a) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by C5-substituted phthalimide analogues. Bioorg Med Chem 19(16):4829–4840. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2011.06.070
Manley-King CI, Bergh JJ, Petzer JP (2011b) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by selected C5-and C6-substituted isatin analogues. Bioorg Med Chem 19(1):261–274
Mondovì B (1985) Structure and functions of amine oxidases. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19(14):1639–1662
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791
Son S-Y, Ma J, Kondou Y, Yoshimura M, Yamashita E, Tsukihara T (2008) Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-Å resolution: the control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(15):5739–5744. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710626105
Strydom B, Bergh JJ, Petzer JP (2013) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by phthalide analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23(5):1269–1273
Van der Walt EM, Milczek EM, Malan SF, Edmondson DE, Castagnoli N Jr, Bergh JJ, Petzer JP (2009) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by (E)-styrylisatin analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(9):2509–2513
Wallace AC, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM (1995) LIGPLOT: a program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng 8(2):127–134
Westlund K, Denney R, Kochersperger L, Rose R, Abell C (1985) Distinct monoamine oxidase A and B populations in primate brain. Science 230(4722):181–183
Westlund K, Denney R, Rose R, Abell C (1988) Localization of distinct monoamine oxidase A and monoamine oxidase B cell populations in human brainstem. Neuroscience 25(2):439–456
Yamada M, Yasuhara H (2004) Clinical pharmacology of MAO inhibitors: safety and future. Neurotoxicology 25(1):215–221
Youdim MB, Bakhle Y (2006) Monoamine oxidase: isoforms and inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease and depressive illness. Br J Pharmacol 147(S1):S287–S296
Youdim MB, Edmondson D, Tipton KF (2006) The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(4):295–309
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Arthur J. Olson for his kindness in offering us the AUTODOCK 4.2 program. We also gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 21275067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P.Z., Tian, Y.L., Zhai, H.L. et al. Molecular modeling study on the structural basis of binding mechanism of C6-substituted phthalides with monoamine oxidases. Med Chem Res 23, 3624–3631 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-0941-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-0941-0