Abstract
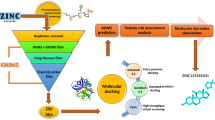
Calpain, a member of the group of cysteine protease enzymes, has been recognized as a promising drug target for several diseases, including cataract. In the present study, an attempt was made to identify potential inhibitors of calpain by employing a pharmacophore-based virtual screening and docking approach. A knowledge-based 3D pharmacophore model was generated, based on the features of established calpain inhibitors SJA6017, MDL28170, E64D, SNJ 1715, calpastatin and CHEMBL 1921830, using the PHASE module of Schrödinger Suite. The best pharmacophore model (AAADH) derived consisted of five features, namely three hydrogen bond acceptors, one hydrogen bond donor and one hydrophobic region. This common pharmacophore hypothesis was then used to perform virtual screening against a binding database, with due consideration to the Lipinski ‘rule of five’ and absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion properties were calculated using the Qikprop module, so as to obtain a pool of lead molecules. The short-listed lead molecules were then subjected to docking analysis with that of the mutated calpain 1 (1KXR) to reduce the false positive and false negative results against the target receptor. Interaction data and its corresponding interaction energy, along with binding energy calculated for the hit ligand (650709) and mutated receptor (1KXR) complex, suggest that compound 650709 has a more effective inhibitory potential than that of the other established calpain inhibitors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal R, Iezhitsa I, Awaludin NA, Ahmad Fisol NF, Bakar NS, Agarwal P, Abdul Rahman TH, Spasov A, Ozerov A, Mohamed Ahmed Salama MS, Mohd Ismail N (2013) Effects of magnesium taurate on the onset and progression of galactose-induced experimental cataract: in vivo and in vitro evaluation. Exp Eye Res 110:35–43
Azuma M, Shearer TR (1992) Involvement of calpain in diamide-induced cataract in cultured lenses. FEBS Lett 307:313–317
Azuma M, Shearer TR, Matsumoto T, David LL, Murachi T (1990) Calpain II in two in vivo models of sugar cataract. Exp Eye Res 51:393–401
Azuma M, David LL, Shearer TR (1992) Superior prevention of calcium ionophore cataract by E64d. Biochim Biophys Acta 1180:215–220
Bassnett S, Shi Y, Vrensen GF (2011) Biological glass: structural determinants of eye lens transparency. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 366:1250–1264
Berman HM, Battistuz T, Bhat TN, Bluhm WF, Bourne PE, Burkhardt K, Feng Z, Gilliland GL, Iype L, Jain S, Fagan P, Marvin J, Padilla D, Ravichandran V, Schneider B, Thanki N, Weissig H, Westbrook JD, Zardecki C (2002) The protein data bank. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:899–907
Bhadauriya A, Dhoke GV, Gangwal RP, Damre MV, Sangamwar AT (2013) Identification of dual acetyl-CoA carboxylases 1 and 2 inhibitors by pharmacophore based virtual screening and molecular docking approach. Mol Divers 17:139–149
Biswas S, Harris F, Dennison S, Singh J, Phoenix DA (2004) Calpains: targets of cataract prevention? Trends Mol Med 10:78–84
Brian G, Taylor H (2001) Cataract blindness: challenges for the 21st century. Bull World Health Organ 79:249–256
Carragher NO (2006) Calpain inhibition: a therapeutic strategy targeting multiple disease states. Curr Pharm Des 12:615–638
Chang DF, Braga-Mele R, Mamalis N, Masket S, Miller KM, Nichamin LD, Packard RB, Packer M (2007) Prophylaxis of postoperative endophthalmitis after cataract surgery: results of the 2007 ASCRS member survey. J Cataract Refract Surg 33:1801–1805
Cuerrier D, Moldoveanu T, Inoue J, Davies PL, Campbell RL (2006) Calpain inhibition by alpha-ketoamide and cyclic hemiacetal inhibitors revealed by X-ray crystallography. Biochemistry 45:7446–7452
David LL, Shearer TR (1986) Purification of calpain II from rat lens and determination of endogenous substrates. Exp Eye Res 42:227–238
David LL, Shearer TR (1993) Beta-crystallins insolubilized by calpain II in vitro contain cleavage sites similar to beta-crystallins insolubilized during cataract. FEBS Lett 324:265–270
David LL, Shearer TR, Shih M (1993) Sequence analysis of lens beta-crystallins suggests involvement of calpain in cataract formation. J Biol Chem 268:1937–1940
Delaye M, Tardieu A (1983) Short-range order of crystallin proteins accounts for eye lens transparency. Nature 302:415–417
Dixon SL, Smondyrev AM, Rao SN (2006) PHASE: a novel approach to pharmacophore modeling and 3D database searching. Chem Biol Drug Des 67:370–372
Donkor IO (2011) Calpain inhibitors: a survey of compounds reported in the patent and scientific literature. Expert Opin Ther Pat 21:601–636
Elanchezhian R, Sakthivel M, Geraldine P, Thomas PA (2009) The effect of acetyl-L-carnitine on lenticular calpain activity in prevention of selenite-induced cataractogenesis. Exp Eye Res 88:938–944
Epik PPW (2011) Epik PPW, version 2.3. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein–ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196
Fukiage C, Azuma M, Nakamura Y, Tamada Y, Nakamura M, Shearer TR (1997) SJA6017, a newly synthesized peptide aldehyde inhibitor of calpain: amelioration of cataract in cultured rat lenses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1361:304–312
Glide (2011) Glide, version 5.7. Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J (2003) The calpain system. Physiol Rev 83:731–801
Halgren T (2007) New method for fast and accurate binding-site identification and analysis. Chem Biol Drug Des 69:146–148
Halgren TA, Murphy RB, Friesner RA, Beard HS, Frye LL, Pollard WT, Banks JL (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J Med Chem 47:1750–1759
Impact (2011) Impact, version 5.8. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Lampi KJ, Kadoya K, Azuma M, David LL, Shearer TR (1992) Comparison of cell-permeable calpain inhibitors and E64 in reduction of cataract in cultured rat lenses. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 117:53–57
Lengauer T, Lemmen C, Rarey M, Zimmermann M (2004) Novel technologies for virtual screening. Drug Discov Today 9:27–34
LigPrep (2011) LigPrep, version 2.4. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3–26
Liu T, Lin Y, Wen X, Jorissen RN, Gilson MK (2007) BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D198–D201
Maestro (2011) Maestro, version 9.2. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Mathur P, Gupta SK, Wegener AR, Breipohl W, Ahrend MH, Sharma YD, Gupta YK, Vajpayee RB (2000) Comparison of various calpain inhibitors in reduction of light scattering, protein precipitation and nuclear cataract in vitro. Curr Eye Res 21:926–933
Mobley DL, Dill KA (2009) Binding of small-molecule ligands to proteins: “what you see” is not always “what you get”. Structure 17:489–498
Moldoveanu T, Hosfield CM, Lim D, Jia Z, Davies PL (2003) Calpain silencing by a reversible intrinsic mechanism. Nat Struct Biol 10:371–378
Muegge I (2003) Selection criteria for drug-like compounds. Med Res Rev 23:302–321
Muralidharan AR, Leema G, Annadurai T, Anitha TS, Thomas PA, Geraldine P (2012) Deciphering the potential efficacy of acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) in maintaining connexin-mediated lenticular homeostasis. Mol Vis 18:2076–2086
Nakajima E, Walkup RD, Ma H, Shearer TR, Azuma M (2006) Low activity by the calpain system in primate lenses causes resistance to calcium-induced proteolysis. Exp Eye Res 83:593–601
Pascolini D, Mariotti SP (2012) Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol 96:614–618
Phase (2011) Phase, version 3.0. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Pradeep H, Rajanikant GK (2012) A rational approach to selective pharmacophore designing: an innovative strategy for specific recognition of Gsk3beta. Mol Divers 16:553–562
Prime (2011) Prime, version 3.0. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Qikprop (2011) Qikprop, version 3.2. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Reddy KK, Singh SK, Tripathi SK, Selvaraj C, Suryanarayanan V (2013) Shape and pharmacophore-based virtual screening to identify potential cytochrome P450 sterol 14alpha-demethylase inhibitors. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 33(4):234–243
Resnikoff S, Pascolini D, Etya’ale D, Kocur I, Pararajasegaram R, Pokharel GP, Mariotti SP (2004) Global data on visual impairment in the year 2002. Bull World Health Organ 82:844–851
Reverter D, Strobl S, Fernandez-Catalan C, Sorimachi H, Suzuki K, Bode W (2001) Structural basis for possible calcium-induced activation mechanisms of calpains. Biol Chem 382:753–766
Rooban BN, Lija Y, Biju PG, Sasikala V, Sahasranamam V, Abraham A (2009) Vitex negundo attenuates calpain activation and cataractogenesis in selenite models. Exp Eye Res 88:575–582
Sato K, Kawashima S (2001) Calpain function in the modulation of signal transduction molecules. Biol Chem 382:743–751
Selvaraj C, Singh S, Tripathi S, Reddy K, Rama M (2012) In silico screening of indinavir-based compounds targeting proteolytic activity in HIV PR: binding pocket fit approach. Med Chem Res 21:4060–4068
Shearer TR, Azuma M, David LL, Murachi T (1991) Amelioration of cataracts and proteolysis in cultured lenses by cysteine protease inhibitor E64. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 32:533–540
Shoichet BK (2004) Virtual screening of chemical libraries. Nature 432:862–865
Sitemap (2011) Sitemap, version 2.5. Schrödinger LLC, New York
Stuart BG, Coxon JM, Morton JD, Abell AD, McDonald DQ, Aitken SG, Jones MA, Bickerstaffe R (2011) Molecular modeling: a search for a calpain inhibitor as a new treatment for cataractogenesis. J Med Chem 54:7503–7522
Tabin G, Chen M, Espandar L (2008) Cataract surgery for the developing world. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 19:55–59
Tang D, Borchman D, Yappert MC, Vrensen GF, Rasi V (2003) Influence of age, diabetes, and cataract on calcium, lipid-calcium, and protein–calcium relationships in human lenses. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:2059–2066
Teli MK, Rajanikant GK (2012) Identification of novel potential HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors by in silico screening. Mol Divers 16:193–202
Thangapandian S, John S, Sakkiah S, Lee KW (2011) Potential virtual lead identification in the discovery of renin inhibitors: application of ligand and structure-based pharmacophore modeling approaches. Eur J Med Chem 46:2469–2476
Tikhonova IG, Sum CS, Neumann S, Engel S, Raaka BM, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC (2008) Discovery of novel agonists and antagonists of the free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFAR1) using virtual screening. J Med Chem 51:625–633
Todd B, Moore D, Deivanayagam CC, Lin GD, Chattopadhyay D, Maki M, Wang KK, Narayana SV (2003) A structural model for the inhibition of calpain by calpastatin: crystal structures of the native domain VI of calpain and its complexes with calpastatin peptide and a small molecule inhibitor. J Mol Biol 328:131–146
Wistow G (2012) The human crystallin gene families. Hum Genomics 6:26
Yang SY (2010) Pharmacophore modeling and applications in drug discovery: challenges and recent advances. Drug Discov Today 15:444–450
Yoshida H, Murachi T, Tsukahara I (1984) Degradation of actin and vimentin by calpain II, a Ca2+-dependent cysteine proteinase, in bovine lens. FEBS Lett 170:259–262
Acknowledgments
Financial assistance provided by Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi in the form of Senior Research Fellowship to the first author is gratefully acknowledged (Ref. No. 09/475 (0185)/2012-EMR-I). Financial assistance provided by University Grants Commission-Basic Scientific Research (UGC-BSR) in the form of one time grant to the corresponding author is gratefully acknowledged. The authors Sanjeev Kumar Singh and Chandrabose Selvaraj also gratefully acknowledge CSIR for the funding grant (Ref. No. 37(1491)/11/EMR-II).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
44_2013_842_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 1 Comparative molecular dynamics analysis of native and mutant 1KXR protein. RMSD values of the native (black line) and mutant 1KXR (red line) systems versus simulation time (10,000 ns). X and Y axes represent Time (ns), and RMSD, respectively
44_2013_842_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 2 RMSF representations of native and mutant 1KXR in the dynamic state. Here black and red represent the native and the mutant. respectively
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muralidharan, A.R., Selvaraj, C., Singh, S.K. et al. Virtual screening based on pharmacophoric features of known calpain inhibitors to identify potent inhibitors of calpain. Med Chem Res 23, 2445–2455 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0842-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0842-7