Abstract
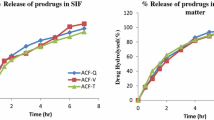
An ester-based mutual prodrug (aceclofenac–paracetamol; AC-PR) was synthesized (one-pot method) with an aim of improving the therapeutic index through prevention of gastrointestinal irritation and bleeding that is associated with aceclofenac. The release of aceclofenac and paracetamol from the ester prodrug (AC-PR) was studied by reverse phase HPLC in hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 1.2), phosphate buffer (pH 7.4), 80 % v/v human plasma, 10 % w/v rat intestinal homogenate and 10 % w/v rat liver homogenate (pH 7.4). The prodrug showed negligible hydrolysis at pH 1.2 as compared to pH 7.4, suggesting that very less of the prodrug would hydrolyze in stomach, but would release the parent drugs at pH 7.4 in adequate amounts. The prodrug showed enhanced anti-inflammatory activity and significant protection against acetic acid-induced writhings (analgesic activity) as compared to that of aceclofenac. Further, the prodrug produced reduced number of ulcers as compared to that of the parent drug. These results suggest that the synthesized mutual prodrug (AC-PR) is better in terms of activity and GIT toxicity than the parent drug.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison MC, Howatson AG, Torrance CJ, Lee FD, Russell RIG (1992) Gastrointestinal damage associated with the use of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med 327:749–754
Bandgar BP, Sarangdhar RJ, Viswakarma S, Ahamed FA (2011) Synthesis and biological evaluation of orally active prodrugs of indomethacin. J Med Chem 54(5):1191–1201
Buttgereit F, Burmester G, Simon LS (2001) Gastrointestestinal toxic side effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase-2-specific inhibitors. Am J Med 110:135–145
Cioli V, Putzolu S, Rossi V, Sorza Barcellona P, Corradino C (1979) The role of direct tissue contact in the production of gastrointestinal ulcers by anti-inflammatory drugs in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 50:283–289
Curry SH, Whelpton R (1983) Manual of laboratory pharmacokinetics. Wiley, New York, pp 87–98
Dogne JM, Supuran CT, Pratico D (2005) Adverse cardiovascular effects of the coxibs. J Med Chem 48:2251–2257
Dooley M, Spencer CM, Dunn CJ (2001) Aceclofenac: a reappraisal of its use in the management of pain and rheumatic disease. Drugs 61(9):1351–1378
Gopinath R, Rajan S, Meyyanathan, Krishnaveni N, Suresh B (2007) A RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of paracetamol and aceclofenac in tablets. Ind J Pharm Sci 69:137–140
Halen PK, Murumkar PR, Giridhar R, Yadav MR (2009) Prodrug designing of NSAIDs. Mini Rev Med Chem 9:124–139
Legrand E (2004) Aceclofenac in the management of inflammatory pain. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5(6):1347–1357
Palomer A, Cabre F, Pascual J, Campos J, Trujillo MA, Entrena A, Gallo MA, Garcia L, Mauleon D, Espinosa A (2002) Identification of novel cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors using pharmacophore models. J Med Chem 45:1402–1411
Rao PN, Kabir SN, Mohamed T (2010) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): progress in small molecule drug development. Pharmaceuticals 3(5):1530–1549
Rasheed A, Kumar CKA (2010) Design, synthesis, hydrolysis kinetics and pharmadynamic profiles of histidine and alanine conjugates of aceclofenac. Acta Pharm 60:99–109
Redasani VK, Bari SB (2012) Synthesis and evaluation of mutual prodrugs of ibuprofen with menthol, thymol and eugenol. Eur J Med Chem 56:134–138
Seigmund E, Cadmus R, Lu G (1957) A method for evaluating both non-narcotic and narcotic analgesics. Proc Soc Exp Biol 95:729–733
Seyda AA, Figen T (2010) A nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug: aceclofenac. FABAD J Pharm Sci 35:105–118
Sorbera LA, Leeson P, Castaner J, Castaner RM (2001) Valdecoxib and parecoxib sodium: analgesic, antiarthritic, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Drugs Future 26:133–140
Tan TM, Chen Y, Kong KH, Bai J, Li Y, Lim SG et al (1992) NSAID, ulcer and prostaglandins. J Rhematol 19:68–73
The Indian Pharmacopeia (1996) Govt of India, ministry of health and family welfare. The Controller of Publications, New Delhi, pp 142–144
The United States Pharmacopeia (1995) The national formulary, 18th edn. United States Pharmacopeial Convention Inc., Rockville, pp 1791–1798
Verrico MM, Weber RJ, McKaveney TP, Ansani NT, Towers AL (2003) Adverse drug events involving COX-2 inhibitors. Ann Pharmacother 37:1203–1213
Vogel HG, Vogel WH (1997) In drug discovery and evaluation, pharmacological assay, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 416–423
Winter CA, Risley EA, Nuss GW (1962) Carrageenan-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for anti-inflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Biol 111:544–547
Acknowledgments
Financial support provided by Department of Science and Technology (SERC-fast track proposal for young scientists) is gratefully acknowledged. Thanks are due to ARBRO Pharmaceuticals, New Delhi, for gift samples and HPLC analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Husain, A., Ahuja, P., Shaharyar, M. et al. Synthesis, biological activities, and pharmacokinetics studies of a mutual prodrug of aceclofenac and paracetamol. Med Chem Res 23, 1077–1083 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0696-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0696-z