Abstract
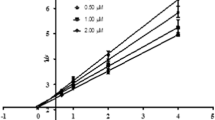
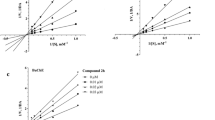
A series of fumaramide derivatives were synthesized from substituted benzanilines and their cholinesterase inhibitory activity was assayed according to Ellman’s method using galanthamine-HBr as the reference compound. Most of the fumaramide compounds showed inhibitory activity of both cholinesterase enzymes. Compounds 29 (IC50 = 0.14 μM) and 30 (IC50 = 16.50 μM) were found to be the most active inhibitors on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) enzymes, respectively. Molecular docking studies were performed with Surflex-Dock programme to provide the possible interactions between compounds and enzymes. A Lineweaver–Burk plot and molecular modelling studies showed that fumaramide compounds targeted both the catalytic anionic site and the peripheral anionic site of AChE. It was revealed that the nature of α,β-unsaturated 1,4-diketone moiety in fumaramide compounds brought about useful and efficient modification especially on AChE inhibition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 3:186–191
Castro A, Martinez A (2001) Peripheral and dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: implications in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mini Rev Med Chem 1:267–272
Castro A, Conde S, Rodriguez-Franco MI, Martinez A (2002) Non-cholinergic pharmacotherapy approaches to the future treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mini Rev Med Chem 2:37–50
Correa-Basurto J, Alcantara IV, Espinoza-Fonseca M, Trujillo-Ferrara JG (2005) p-Aminobenzoic acid derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 40:732–735
Correa-Basurto J, Espinoza-Raya J, Gonzalez-May M, Espinoza-Fonseca LM, Vasquez-Alcantara I, Trujillo-Ferrara JG (2006) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by two arylderivatives: 3a-acetoxy-5h-pyrrolo(1,2-a) (3,1)benzoxazin-1,5-(3ah)-dione and cis-N-P-acetoxy-phenylisomaleimide. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 21:133–138
Correa-Basurto J, Flores-Sandoval C, Marin-Cruz J, Royo-Dominguez A, Espinoza-Fonseca LM, Trujillo-Ferrara JG (2007) Docking and quantum mechanic studies on cholinesterases and their inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 42:10–19
Darvesh S, Hopkins DA, Geula C (2003) Neurobiology of butyrylcholinesterase. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:131–138
Decker M, Kraus B, Heilmann J (2008) Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of hybrid molecules out of quinazolinimines and lipoic acid lead to highly potent and selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors with antioxidant properties. Bioorg Med Chem 16:4252–4261
Doraiswamy PM (2002) Non-cholinergic strategies for treating and preventing Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drugs 16:811–824
Ellman GL, Courtney D, Andies V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Fallarero A, Oinonen P, Gupta S, Blom P, Galkin A (2008) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by coumarins: the case of coumarin 106. Pharmacol Res 58:215–221
Fawole OA, Amoo SO, Ndhlala AR, Light ME, Finnie JF, Van Staden J (2010) Anti-inflammatory, anticholinesterase, antioxidant and phytochemical properties of medicinal plants used for pain-related ailments in South Africa. J Ethnopharmacol 127:235–241
Giacobini E (2003) Cholinesterases: new roles in brain function and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 28:515–522
Greig NH, Utsuki T, Ingram DK, Wang Y, Pepeu G, Scali C, Yu QS, Mamczarz J, Holloway HW, Giordano T, Chen D, Furukawa K, Sambamurti K, Brossi A, Lahiri DK (2005) Selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibition elevates brain acetylcholine, augments learning and lowers Alzheimer beta-amyloid peptide in rodent. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:17213–17218
Grossberg GT (2003) Cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: getting on and staying on. Curr Ther Res 64:216–235
Harel M, Quinn DM, Nair HK, Silman I, Sussman JL (1996) The X-ray structure of a transition state analog complex reveals the molecular origins of the catalytic power and substrate specificity of acetylcholinesterase. J Am Chem Soc 118:2340–2346
Hasan A, Khan KM, Sher M, Maharvi GM, Nawaz SA, Choudhary MI, Rahman AU, Supuran CT (2005) Synthesis and inhibitory potential towards acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and lipoxygenase of some variably substituted chalcones. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 20:41–47
Jhee SS, Shiovitz T, Hartman RD, Messina J, Anand R, Sramek J, Cutler NR (2002) Centrally acting antiemetics mitigate nausea and vomiting in patients with Alzheimer’s disease who receive rivastigmine. Clin Neuropharmacol 25:122–123
Johannsen P (2004) Long-term cholinesterase inhibitor treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drugs 18:757–768
Kamal MA, Klein P, Luo W, Li Y, Holloway HW, Tweedie D, Greig NH (2008) Kinetics of human serum butyrylcholinesterase inhibition by a novel experimental Alzheimer therapeutic, dihydrobenzodioxepine cymserine. Neurochem Res 33:745–753
Knapp MJ, Knopman DS, Solomon PR, Pendlebury WW, Davis CS, Gracon SI (1994) A 30-week randomized controlled trial of high-dose tacrine in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. The tacrine study group. J Am Med Assoc 271:985–991
Li B, Stribley JA, Ticu A, Xie W, Schopfer LM, Hammond P, Brimijoin S, Hinrichs SH, Lockridge O (2000) Abundant tissue butyrylcholinesterase and its possible function in the acetylcholinesterase knockout mouse. J Neurochem 75:1320–1331
Marston A, Kissling J, Hostettmann K (2002) A rapid Tlc bioautographic method for the detection of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors in plants. Phytochem Anal 13:51–54
Mesulam MM, Guillozet A, Show P, Levey A, Duysen EGM, Lockridge O (2002) Acetylcholinesterase knockouts establish central cholinergic pathways and can use butyrylcholinesterase to hydrolyze acetylcholine. Neuroscience 110:627–639
Pang YP, Quiram P, Jelacic T, Hong F, Brimjoin S (1996) Highly potent, selective, and low cost bis-tetrahydroaminacrine inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Steps toward novel drugs for treating Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 271:23646–23649
Perry EK, Blessed G, Tomlinson BE (1978) Changes in brain cholinesterases in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 4:273–277
Schulz V (2003) Ginkgo extract or cholinesterase inhibitors in patients with dementia: what clinical trials and guidelines fail to consider. Phytomedicine 10:74–79
Shen T, Tai K, Henchman RH, McCammon JA (2002) Molecular dynamics of acetylcholinesterase. Acc Chem Res 35:332–340
Terry AV, Buccafusco JJ (2003) The cholinergic hypothesis of age and Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits: recent challenges and their implications for novel drug development. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:821–827
Trujillo-Ferrara J, Montoya Cano L, Espinoza-Fonseca M (2003) Synthesis, anticholinesterase activity and structure–activity relationships of M-aminobenzoic acid derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1825–1827
Vitorović-Todorović MD, Juranić IO, Mandić LM, Drakulić BJ (2010) 4-Aryl-4-oxo-N-phenyl-2-aminylbutyramides as acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Preparation, anticholinesterase activity, docking study, and 3d structure-activity relationship based on molecular interaction fields. Bioorg Med Chem 18:1181–1193
Wilkinson DG, Francis PT, Schwam E, Payne-Parris J (2004) Cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: the relationship between pharmacological effects and clinical efficacy. Drugs Aging 21:453–478
Yerdelen KO (2012) Solvent-free solid supported and phase transferred catalyzed synthesis of benzaniline derivatives using microwave irradiation. Int J Pharm Sci Res 3:126–129
Zhou X, Wang XB, Wang T, Kong LY (2008) Design, synthesis and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of novel coumarin analogues. Bioorg Med Chem 16:8011–8021
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by Ataturk University Research Fund (Project No: 2011/294), Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yerdelen, K.O., Gul, H.I. Synthesis and anticholinesterase activity of fumaramide derivatives. Med Chem Res 22, 4920–4929 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0493-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0493-8