Abstract
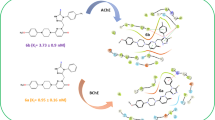
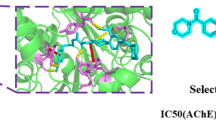
New dual binding site acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors have been designed and synthesized as a new drug candidate for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) through the binding to both catalytic and peripheral sites of the enzyme. Therefore, a series of thienopyridine analogs of tacrine were synthesized and investigated for their ability to inhibit the activity of AChE in comparison with tacrine. All the compounds were found to inhibit AChE activity, especially compounds 7b and 11a, which were found to be more potent than tacrine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badia A, Banos JE, Camps P, Contreras J, Gorbig DM, Torrero DM, Simon M, Vivas NM (1998) Synthesis and evaluation of tacrine–huperzine a hybrids as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors of potential interest for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem 6:427–440
Bartus RT, Dean RL, Beer B, Lippa AS (1982) The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 217:408–414
Bolognesi ML, Andrisano V, Bartolini M, Banzi R, Melchiorre C (2005) Propidium-based polyamine ligands as potent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced amyloid-β aggregation. J Med Chem 48:24–27
Butini S, Guarino E, Campiani G, Brindisi M, Coccone SS, Fiorini I, Novellin o E, Belinskaya T, Saxena A, Gemma S (2008) Tacrine based human cholinesterase inhibitors: synthesis of peptidic-tethered derivatives and their effect on potency and selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:5213–5216
Camps P, Achab RE, Gorbig DM, Morral J, Torrero DM, Badia A, Banos JE, Vivas NM, Barril X, Orozco M, Luque FJ (1999) Propidium-based polyamine ligands as potent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced amyloid-β aggregation. J Med Chem 42:3227–3242
Carlier PR, Han YF, Chow ESH, Wang CPLLH, Lieu TX, Wong HS, Pang P (1999) Evaluation of short-tether bis-THA AChE inhibitors. A further test of the dual binding site hypothesis. Bioorg Med Chem 7:351–357
Davis KL, Powchik P (1995) Tacrine. Lancet 345:625–630
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new andrapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Gewald K, Schinke E, Böttcher H (1966) 2-Amino-thiophene aus methylenaktiven nitrilen, carbonylverbindungen and schwefel. Chem Ber 99:94–100
Ishihara Y, Kato K, Goto G (1991) Central cholinergic agents. I. Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, 2-[ω-[N-akyl-N-(ω-phenyl-alkyl)amino]alkyl]-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-diones, Based on a new hypothesis of the enzymes active site. Chem Pharm Bull 39:3225–3235
Kwon YE, Park JY, TaiNo K, Shin JH, Lee SK, Eun JS, Yang JH, Shin TY, Kim DK, Chae BS, Leem J-Y, Kim KH (2007) Synthesis, in vitro assay, and molecular modeling of new piperidine derivatives having dual inhibitory potency against acetylcholinesterase and Abeta1-42 aggregation for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Bioorg Med Chem 15:6596–6607
Lang F, Zewge D, Houpis IN, Volante RP (2001) Amination of aryl halide using copper catalysis. Tetrahedron Lett 42:3251–3254
Mary A, Renko DZ, Guillou C, Thal C (1998) Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of bis-interacting ligands in the galanthamine series. Bioorg Med Chem 6:1835–1850
Rosini M, Andrisano V, Bartolini M, Balognesi ML, Hrelia P, Minarini A, Tarozzi A, Melchiorre C (2005) Rational approach to discover multipotent anti-Alzheimer drugs. J Med Chem 48:360–363
Ruiz PM, Rubio L, Palomero EG, Dorronsoro I, Millan MM, Valenzuela R, Usan P, Austria C, Bartolini M, Andrisano V, Chanal AB, Orozco M, Luque FJ, Medina M, Martinez A (2005) Design synthesis, and biological evaluation of dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: new disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease. J Med Chem 48:7223
Tariot PN, Federoff HJ (2003) Current treatment for Alzheimer disease and future prospects. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 17:105–113
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the staff members of the Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University, for carrying out the pharmacological screening of the newly synthesized compounds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badran, M.M., Hakeem, M.A., Abuel-Maaty, S.M. et al. Design and synthesis of thienopyridines as novel templates for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Med Chem Res 22, 4087–4095 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0403-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0403-5