Abstract
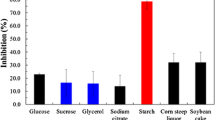
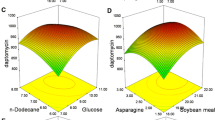
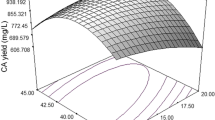
A new microbial strain showing broad spectrum antibacterial and antifungal activity was isolate from soil of Chhattisgarh and characterized as Streptomyces rimosus MTCC 10792 (gene sequence similarity 99.52%). The antibacterial compound was produced by the isolate purified by silica gel chromatography and chemically characterized as oxytetracycline and production of the antibiotic was statistically optimized using response surface methodology. The three independent variables, namely concentrations of glucose (10 g/l), soybean meal (10 g/l), and calcium carbonate (1 g/l) were found to be the most important for production antibiotic by a one-factor-at-a-time study. For optimization, the individual and interaction effects of the studied variables were evaluated by response surface methodology (RSM) using central composite design (CCD). Antibiotic production was increased nearly ten times (470 mg/l) as compared with the normal unoptimized production medium (47 mg/l) by applying statistical design.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Zeid AA, El-Diwany AI, Shaker HM, Salem HM (1981) Role of nitrogen sources in fermentative production of oxytetracycline by Streptomyces rimosus 93060. Agricultural Wastes 3(4):257–265
Adinarayana K, Ellaiah P (2002) Response surface optimization of the critical medium components for the production of alkaline proteases by a newly isolated Bacillus sp. J Pharm Pharm Sci 5:272–278
Akhnazarova S, Kefarov V (1982) Experiment optimization in chemistry and chemical engineering. Mir Publishers, Moscow
Asanza Teruel ML, Gontier E, Bienaime C, Nava Saucedo JE, Barbotin JN (1997) Response surface analysis of chlortetracycline and tetracycline production with K-carrageenan immobilized Streptomyces aureofaciens. Enzyme Microb Technol 21(5):314–320
Banna NE, Winkelmann G (1998) Pyrrolnitrin from Burkholderia cepacia: antibiotic activity against fungi and novel activities against Streptomycetes. J Appl Microbiol 85:69–78
Box GEP, Hunter WG, Hunter JS (1978) Statistics for experiments. Willey, New York, pp 291–334
Cuenca-Estrella M, Lee-Yang W, Ciblak MA, Beth A, Skaggs A, Mellado E, Warnock DW, Rodriguez-Tudela JL (2002) Comparative evaluation of NCCLS M27-A and EUCAST broth microdilution procedures for antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:3644–3647
Elibol M (2004) Optimization of medium composition for actinorhodin production by Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2) with response surface methodology. Process Biochem 39:1057–1062
Haaland PD (1989) Experimental design in biotechnology. Marcel Dekker, New York
Hamedi J, Malekzadeh F, Niknam V (2002) Improved production of erythromycin by Saccharopolyspora erythraea by various plant oils. Biotechnol Lett 24:697–700
Kaushik R, Saran S, Isar J, Saxena RK (2006) Statistical optimization of medium components and growth conditions by response surface methodology to enhance lipase production by Aspergillus carneus. J Mol Catal B Enzym 40:121–126
Khan S, Misra AK, Tripathi CKM, Mishra BN, Bihari V (2006) Response surface optimization of effective medium constituents for the production of alkaline protease from a newly isolated strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian J Exp Biol 44:151–156
Khuri AI, Cornell JA (1987) Response surfaces: design and analysis. Marcel Dekker, New York
Lavermicocca P, Valerio F, Visconti A (2003) A antifungal activity of phenyl lactic acid against molds isolated from bakery products. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:634–640
Mao X, Shen Y, Yang L, Chen S, Yang Y, Yang J (2007) Optimizing the medium compositions for accumulation of the novel FR-008/Candicidin derivatives CS101 by a mutant of Streptomyces sp. using statistical experimental methods. Process Biochem 42:878–883
Marwick JD, Wright PC, Burgess JG (1999) Bioprocess intensification for production of novel marine bacterial antibiotics through bioreactor operation and design. Mar Biotechnol 1:495–507
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (2000) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 5th edn. Approved Standard M7-A5. NCCLS, Wayne
Ruiz Medina A, Garia Marin MG, Fernández de Cordova ML, Molina Díaz A (2000) UV spectrophotometric flow-injection assay of tetracycline antibiotics retained on Sephadex QAE A-25 in drug formulations. Microchem J 65(3):325–331
Silva CJSM, Roberto IC (2001) Optimization of xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii FTI 20037 using response surface methodology. Process Biochem 36:1119–1124
Singh V, Tripathi CKM (2008) Production and statistical optimization of a novel olivanic acid by Streptomyces olivaceus MTCC 6820. Process Biochem 43:1313–1317
Singh V, Khan M, Khan S, Tripathi CKM (2009) Optimization of actinomycin V production by Streptomyces triostinicus using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82(2):379–385
Vahidi H, Kobarfard F, Namjoyan F (2004) Effect of cultivation conditions on growth and antifungal activity of Mycena leptocephala. Af J Biotechnol 3:606–609
Xiaobo Z, Haiying W, Linyu H, Yongcheng L, Zhongtao L (2006) Medium optimization of carbon and nitrogen sources for the production of eucalyptene A and xyloketal A from Xylaria sp. 2508 using response surface methodology. Process Biochem 41:293–298
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund, New Delhi, India for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Rai, V. & Tripathi, C.K.M. Production and optimization of oxytetracycline by a new isolate Streptomyces rimosus using response surface methodology. Med Chem Res 21, 3140–3145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9845-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9845-4