Abstract
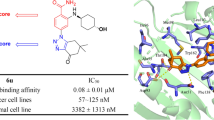
The anticancer activity of thiamine (vitamin B1) combined with its structural properties and docking studies suggested potential anti-heat shock protein 90α (Hsp90α) activity for this vitamin. In experimental testing, thiamine illustrated anti-Hsp90α IC50 value of 12.5 μM. Therefore, in an attempt to capitalize on the simple structure of thiamine and towards the development of new anti-Hsp90α inhibitors, we prepared and screened 56 pyridinium-based structures tailored to thiamine. The most potent among the prepared compounds illustrated anti-Hsp90α IC50 values of 7.4 and 7.6 μM.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila C, Boris AK, Brian SJ (2006a) Development and optimization of a useful assay for determining Hsp90s inherent ATPase activity. Bioorg Med Chem 14:1134–1142
Avila C, Kyle HM, Zeqiang M, Boris AK, Qi-Zhuang Y, Brian SB (2006b) High-throughput screening for Hsp90 ATPase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:3005–3008
Böhm HJ (1994) The development of a simple empirical scoring function to estimate the binding constant for a protein-ligand complex of known three-dimensional structure. J Comput-Aided Mol 8:243–256
Böhm HJ (1998) Prediction of binding constants of protein ligands: a fast method for the prioritization of hits obtained from de novo design or 3D database search programs. J Comput-Aided Mol 12:309–323
Chiosis G, Lucas B, Shtil A, Huezo H, Rosen N (2002) Development of a purine-scaffold novel class of Hsp90 binders that inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells and induce the degradation of Her2 tyrosine kinase. Bioorg Med Chem 10:3555–3564
Chiosis G, Rodina A, Moulick K (2006) Emerging Hsp90 inhibitors: from discovery to clinic. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 6:1–8
Christopher R, Edwards W, Bouchier IA (Eds) (1991) Oncology, chapter seven, Davidson’s principles and practice of medicine, 16th edn. ELBS Publisher, UK
ComõÂn-Anduix B, Boren J, Martinez S, Moro C, Centelles JJ, Trebukhina R, Petushok N, Lee W-N P, Boros LG, Cascante M (2001) The effect of thiamine supplementation on tumour proliferation: a metabolic control analysis study. Eur J Biochem 268:4177
Dey A, Cederbaum AI (2007) Geldanamycin, an inhibitor of Hsp90 increases cytochrome P450 2E1 mediated toxicity in HepG2 cells through sustained activation of the p38MAPK pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 461:275–286
Gehlhaar DK, Verkhivker GM, Rejto PA, Sherman CJ, Fogel DB, Fogel LJ, Freer ST (1995) Molecular recognition of the inhibitor AG-1343 by HIV-1 protease: conformationally flexible docking by evolutionary programming. Chem Biol 2:317–332
Gehlhaar DK, Bouzida D, Rejto PA (1999) In: Parrill L, Reddy MR, (eds) Rational drug design: novel methodology and practical applications. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 292–311
Gopalsamy A, Shi M, Golas J, Vogan E, Jacob J, Johnson M, Lee F, Nilakantan R, Petersen R, Svenson K, Chopra R, Tam MS, Wen Y, Ellingboe J, Arndt K, Boschelli F (2008) Discovery of benzisoxazoles as potent inhibitors of chaperone heat shock protein 90. J Med Chem 51:373–375
Hideyuki O, Masami K, Yuichi T, Yumiko U, Jun F, Takayuki N, Shiro S, Makoto S, Shunichi I, Yoshinori Y, Endang SR, Yutaka K, Michio I (2008) Conformational significance of EH21A1–A4, phenolic derivatives of geldanamycin, for Hsp90 inhibitory activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:1577–1580
Kasibhatla SR, Hong K, Biamonte MA, Busch DJ, Karjian PL, Sensintaffar JL, Kamal A, Lough RE, Brekken J, Lundgren K, Grecko R, Timony GA, Ran Y, Mansfield R, Fritz LC, Ulm E, Burrows FJ, Boehm MF (2007) Rationally designed high-affinity 2-amino-6-halopurine heat shock protein 90 inhibitors that exhibit potent antitumor activity. J Med Chem 50:2767–2778
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA (1979) An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem 100:95–97
Muegge I (2000) A knowledge-based scoring function for protein-ligand interactions: probing the reference state. Perspect Drug Discov Des 20:99–114
Muegge I (2001) Effect of ligand volume correction on PMF scoring. J Comput Chem 22:418–425
Muegge I, Martin YC (1999) A general and fast scoring function for protein-ligand interactions: a simplified potential approach. J Med Chem 42:791–804
Neckers L, Mollapour M, Tsutsumi S (2009) The complex dance of the molecular chaperone Hsp90. Trends Biochem Sci 34:223–226
Prodromou C, Pearl LH (2003) Structure and functional relationships of Hsp90. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 3:301–323
Rowlands MG, Newbatt YM, Prodromou C, Pearl LH, Workman P, Aherne W (2004) High-throughput screening assay for inhibitors of heat-shock protein 90 ATPase activity. Anal Biochem 327:176–183
Solit DB, Rosen N (2006) Hsp90: a novel target for cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1205–1214
Venkatachalam CM, Jiang X, Oldfield T, Waldman M (2003) Ligandfit: a novel method for the shape-directed rapid docking of ligands to protein active sites. J Mol Graph Model 21:289–307
Vieth M, Hirst JD, Dominy BN, Daigler H, Brooks CL III (1998) Assessing search strategies for flexible docking. J Comput Chem 19:1623–1631
Xiao L, Lu X, Ruden DM (2006) Effectiveness of Hsp90 inhibitors as anti-cancer drugs. Mini-Rev Med Chem 6:1137–1143
Acknowledgments
This project was partially sponsored by the Faculty of Graduate Studies (This work is part of PhD. Thesis of Mahmoud A.Al-Sha’er). The authors thank the Deanship of Scientific Research and Hamdi-Mango Center for Scientific Research at the University of Jordan for their generous funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Sha’er, M.A., Taha, M.O. Rational exploration of new pyridinium-based HSP90α inhibitors tailored to thiamine structure. Med Chem Res 21, 487–510 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9557-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9557-9