Abstract
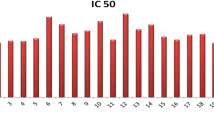
The enzyme aldoreductase which plays an important role in pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy was purified from bovine lens, and its inhibitory activity was studied with the synthesized flavone derivatives 1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone as the starting material. Experimental study revealed that 2-chloroflavone shows less inhibitory activity of 60–70% than other flavones used in the study. To validate experimental results computationally, docking studies of new flavone derivatives synthesized were performed with the enzyme aldose reductase, and the results indicate that 3-iodo, 4-methyl, 5-chloroflavone and 2-chloroflavone bind with higher and lesser affinities. Docking studies with site directed mutagenesis of Val47Ile, Tyr48His, Pro121Phe, Trp219Tyr, Cys298Ala, Leu300Pro, Ser302Arg, and Cys303Asp of the enzyme altered the inhibition activity of aldose reductase. The regression value (R 2) of 0.81 between the docking scores of the known inhibitors and the experimental logIC50 indicates the reliability of the docking studies. Biological activity and carcinogenic properties predict that 3-iodo, 4-methyl, 5-chloroflavone is the best flavone inhibitor against aldose reductase.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyer-Mears A, Cruz E (1985) Reversal of diabetic cataract by sorbinil, an aldose reductase inhibitor. Diabetes 34:15–21
Bhatnagar A, Srivastava SK (1992) Aldose reductase: congenial and injurious profiles of an enigmatic enzyme. Biochem Med Metab Biol 48:91–121
Bohren KM, Grimshaw CE, Lai CJ, Harrison DH, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Gabbay KH (1994) Tyrosine-48 is the proton donor and histidine-110 directs substrate stereochemical selectivity in the reduction reaction of human aldose reductase: enzyme kinetics and crystal structure of the Y48H mutant enzyme. Biochemistry 33:2021–2032
Bostrom J, Greenwood JR, Gottfries J (2003) Assessing the performance of OMEGA with respect to retrieving bioactive conformations. J Mol Graph Model 21:449–462
Brownlee JM, Carlson E, Milne AC, Pape E, Harrison DH (2006) Structural and thermodynamic studies of simple aldose reductase inhibitor complexes. Bioorg Chem 34:424–444
De Winter HL, von Itzstein M (1995) Aldose reductase as a target for drug design: molecular modeling calculations on the binding of acyclic sugar substrates to the enzyme. Biochemistry 34:8299–8308
Dvornik D (1987) Hyperglycaemia in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. In: Porte D (ed) Aldose reductase inhibition: an approach to the prevention of diabetic complications. McGraw Hill, New York
Eldridge MD, Murray CW, Auton TR, Paolini GV, Mee RP (1997) Empirical scoring functions: I. The development of a fast empirical scoring function to estimate the binding affinity of ligands in receptor complexes. J Comput Aided Mol Des 11:425–445
Gabbay KH, Spack N, Loo S, Hirsch HJ, Ackil A (1979) Aldose reductase inhibition: studies with alrestatin. Metabolism 28:471–476
Gehlhaar DK, Verkhivker GM, Rejto PA, Sherman CJ, Fogel DB, Fogel LJ, Freer ST (1995) Molecular recognition of the inhibitor AG-1343 by HIV-1 protease: conformationally flexible docking by evolutionary programming. Chem Biol 2:317–324
Grimshaw CE, Bohren KM, Lai CJ, Gabbay KH (1995a) Human aldose reductase: subtle effects revealed by rapid kinetic studies of the C298A mutant enzyme. Biochemistry 34:14366–14373
Grimshaw CE, Bohren KM, Lai CJ, Gabbay KH (1995b) Human aldose reductase: pK of tyrosine 48 reveals the preferred ionization state for catalysis and inhibition. Biochemistry 34:14374–14384
Harrison DH, Bohren KM, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Gabbay KH (1994) An anion binding site in human aldose reductase: mechanistic implications for the binding of citrate cacodylate and glucose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry 33:2011–2020
Hayman S, Kinoshita H (1965) Isolation and properties of lens aldose reductase. J Biol Chem 240:877–882
Hoffman PL, Wermuth B, Von Wartburg JP (1980) Human brain aldehyde reductases: relationship to succinil semi aldehyde reductase and aldose reductase. J Neurochem 35:354–366
Inagaki K, Miwa I, Yashiro T, Okuda J (1982) Inhibition of aldose reductases from rat and bovine lenses by hydantoin derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull 30:3244–3254
Judzewitsch RG, Jaspan JB, Polonsky KS, Weinberg CR, Halter JB, Halar E, Pfeifer MA, Vukadinovich C, Bernstein L, Schneider M, Liang KL, Gabbay KH, Rubenstein AH, Porte D Jr (1983) Aldose reductase inhibition improves nerve conduction velocity in diabetic patients. N Engl J Med 308:119–125
Jung SH, Lee JM, Lee HJ, Kim CY, Lee EH, Um BH (2007) Aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts inhibitory effect of Phyllostachys nigra. Biol Pharm Bull 30:1569–1572
Kinoshita T, Miyake H, Fujii T, Takakura S, Goto T (2002) The structure of human recombinant aldose reductase complexed with the potent inhibitor zenarestat. Acta Crystallogr D 58:622–626
Kawamura M, Hamanaka N (1997) Development of epariestat (Kinedak), aldose reductase inhibitor. J Synth Org Chem Japan 37:651–657
Larson ER, Lipinski CA, Sarges R (1988) Medicinal chemistry of aldose reductase inhibitors. Med Res Rev 8:159–186
Lee YS, Hodoscek M, Brooks BR, Kador PF (1998) Catalytic mechanism of aldose reductase studied by the combined potentials of quantum mechanics and molecular mechanics. Biophys Chem 70:203–216
Martyn CN, Reid W, Young RJ, Ewing DJ, Clark BF (1987) Six-month treatment with sorbinil in asymptomatic diabetic neuropathy. Failure to improve abnormal nerve function. Diabetes 36:987–990
Masson EA, Boulton AJ (1990) Aldose reductase inhibitors in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy: a review of the rationale and clinical evidence. Drugs 39:190–202
Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Toguchida I, Yoshikawa M (2002) Structural requirements of flavonoids and related compounds for aldose reductase inhibitory activity. Chem Pharm Bull 50:788–795
McGann MR, Almond HR, Nicholls A, Grant JA, Brown FK (2003) Gaussian docking functions. Biopolymers 68:76–90
Mylari BL, Larson ER, Beyer TA, Zembrowski WJ, Aldinger CE, Dee MF, Siegel TW, Singleton DH (1991) Novel, potent aldose reductase inhibitors: 3,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-[[5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-benzothiazolyl] methyl]-1-phthalazineacetic acid (zopolrestat) and congeners. J Med Chem 34:108–122
Nakai N, Fujii Y, Kobashi K, Nomura K (1985) Aldose reductase inhibitors: flavonoids alkaloids acetophenones benzophenones and spirohydantoins of chroman. Arch Biochem Biophys 239:491–496
Narayanan S (1993) Aldose reductase and its inhibition in the control of diabetic complications. Ann Clin Lab Sci 23:148–158
O’Brien MM, Schofield PJ, Edwards MR (1982) Inhibition of human brain aldose reductase and hexonate dehydrogenase by alrestatin and sorbinil. J Neurochem 39:810–814
Poulsom R (1986) Inhibition of hexonate dehydrogenase and aldose reductase from bovine retina by sorbinil statil M79175 and valproate. Biochem Pharmacol 35:2955–2959
Raskin P, Rosenstock J (1987) Aldose reductase inhibitors and diabetic complications: a review. Am J Med 83:298–306
Robison WG Jr, Nagata M, Laver N, Hohman TC, Kinoshita JH (1989) Diabetic-like retinopathy in rats prevented with an aldose reductase inhibitor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30:2285–2292
Schulz-Gasch T, Stahl M (2003) Binding site characteristics in structure based virtual screening: evaluation of current docking tools. J Mol Model 9:47–57
Stahl M, Rarey M (2001) Detailed analysis of scoring functions for virtual screening. J Med Chem 44:1035–1042
Steuber H, Heine A, Podjarny A, Klebe G (2008) Merging the binding sites of aldose and aldehyde reductase for detection of inhibitor selectivity-determining features. J Mol Biol 379:991–1016
Terashima H, Hama K, Yamamoto R, Tsuboshima M, Kikkawa R, Hatanaka I, Shigeta YJ (1984) Effects of a new aldose reductase inhibitor on various tissues in vitro. Pharmacol Exp Ther 229:226–230
Urzhumtsev AG, Skovoroda TP, Vyu Lunin (1996) A procedure compatible with X-PLOR for the calculation of electron-density maps weighted using an R-free-likelihood based approach. J Appl Crystallogr 29:741–744
Varma SD, Kinoshita JH (1976) Inhibition of lens aldose reductase by flavonoids—their possible role in the prevention of diabetic cataracts. Biochem Pharmacol 25:2505–2513
Varma SD, Mikuni I, Kinoshita JH (1975) Flavonoids as inhibitors of lens aldose reductase. Science 188:1215–1216
Varnai P, Warshel A (2000) Computer simulation studies of the catalytic mechanism of human aldose reductase. J Am Chem Soc 122:3849–3860
Varnai P, Richards WG, Lyne PD (1999) Modelling the catalytic reaction in human aldose reductase. Proteins 37:218–227
Warren JC, Murdock GM, Ma Y, Goodman SR, Zimmer WE (1993) Molecular cloning of testicular 20-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 32:1401–1406
Wermuth B, Monder C (1983) Aldose and aldehyde reductase exhibit isocorticosteroid reductase activity. Eur J Biochem 127:279–284
Williamson JR, Chang K, Frangos M et al (1993) Hyperglycemic pseudohypoxia and diabetic complications. Diabetes 42:801–813
Yabe-Nishimura C (1998) Aldose reductase in glucose toxicity: a potential target for the prevention of diabetic complications. Pharmacol Rev 50:21–33
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director, Global institute of Biotechnology, Himayatnagar, Hyderabad for his kind support for providing the software necessary to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nataraj Sekhar, P., Kavi Kishor, P.B., Zubaidha, P.K. et al. Experimental validation and docking studies of flavone derivatives on aldose reductase involved in diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. Med Chem Res 20, 930–945 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-010-9412-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-010-9412-4