Abstract
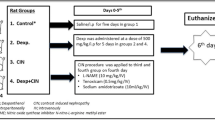
The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of ionic high-osmolar contrast medium on oxidative metabolism in liver, urinary bladder, and ovary tissues and to obtain information about possible protective effects of vitamin C. Twenty-one female rats, 14 weeks old, were used in this study. They were divided into three groups of seven rats: Sham (group I), contrast (group II), contrast + vitamin C (group III). Vitamin C was given orally to the animals in group III during the study period. On the fifth day, contrast medium was given via intravenous infusion as a single dose to the animals in groups II and III. On the sixth day of the study, the animals were killed with anesthesia by ketamine hydrochloride. Then, their liver, bladder, and ovary tissues were removed to measure analyses parameters. Our results suggested that contrast medium led to some increases in malondialdehyde levels in the liver, bladder, and ovary tissues and that vitamin C prevented these increases in the tissues. Nitric oxide level also was found to increase in the contrast-treated animals and vitamin C prevented this increase in the liver tissue. Ionic high-osmolar contrast medium leads to weak oxidant stress in rat liver, bladder, and ovary tissues, and vitamin C prevents this oxidant stress.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmayer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 673–677
Block G, Norkus E, Hudes M, Mandel S, Helzlsouer K (2001) Which plasma antioxidants are most related to fruit and vegetable consumption? Am J Epidemiol 154:1113–1118. doi:10.1093/aje/154.12.1113
Cameron E, Campbell A (1974) The orthomolecular treatment of cancer. II. Clinical trial of high-dose ascorbic acid supplements in advanced human cancer. Chem Biol Interact 9:285–315. doi:10.1016/0009-2797(74)90019-2
Cameron E, Pauling L (1976) Supplemental ascorbate in the supportive treatment of cancer: prolongation of survival times in terminal human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:3685–3689. doi:10.1073/pnas.73.10.3685
Cameron E, Pauling L (1978) Supplemental ascorbate in the supportive treatment of cancer: reevaluation of prolongation of survival times in terminal human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4538–4542. doi:10.1073/pnas.75.9.4538
Cetin M, Devrim E, Serin Kiliçoglu S, Ergüder IB, Namuslu M, Cetin R, Durak I (2008) Ionic high-osmolar contrast medium causes oxidant stress in kidney tissue: partial protective role of ascorbic acid. Ren Fail 30:567–572. doi:10.1080/08860220802064739
Chan PH (2001) Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:2–14. doi:10.1097/00004647-200101000-00002
Cooke MS, Mistry N, Wood C, Herbert KE, Lunec J (1997) Immunogenicity of DNA damaged by reactive oxygen species—implications for anti-DNA antibodies in lupus. Free Radic Biol Med 22:151–159. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00283-3
Dahle LK, Hill EG, Holman RT (1962) The thiobarbituric acid reaction and the autoxidations of polyunsaturated fatty acid methyl esters. Arch Biochem Biophys 98:253–261. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(62)90181-9
Darley-Usmar V, Halliwell B (1996) Blood radicals: reactive nitrogen species, reactive oxygen species, transition metal ions, and the vascular system. Pharm Res 13:649–662. doi:10.1023/A:1016079012214
Durak İ, Canbolat O, Kavutcu M, Öztürk HS, Yurtarslanı Z (1996) Activities of total, cytoplasmic and mitochondrial superoxide dismutase enzymes in sera and pleural fluids from patients with lung cancer. J Clin Lab Anal 10:17–20. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2825(1996)10:1<17::AID-JCLA4>3.0.CO;2-I
Durak I, Kavutcu M, Kacmaz M, Avci A, Horasanli E, Dikmen B, Cimen MY, Ozturk HS (2001) Effects of isoflurane on nitric oxide metabolism and oxidant status of guinea pig myocardium. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 45:119–122. doi:10.1034/j.1399-6576.2001.450118.x
Farinati F, Cardin R, Degan P, Rugge M, Mario FD, Bonvicini P, Naccarato R (1998) Oxidative DNA damage accumulation in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut 42:351–356
Gey KF (1990) The antioxidant hypothesis of cardiovascular-disease: epidemiology and mechanisms. Biochem Soc Trans 18:1041–1045
Heinrich MC, Kuhlmann MK, Grgic A, Heckmann M, Kramann B, Uder M (2005) Cytotoxic effects of ionic high-osmolar, nonionic monomeric, and nonionic iso-osmolar dimeric iodinated contrast media on renal tubular cells in vitro. Radiology 235:843–849. doi:10.1148/radiol.2353040726
Irmak MK, Fadillioglu E, Gulec M, Erdogan H, Yagmurca M, Akyol O (2002) Effects of electromagnetic radiation from a cellular telephone on the oxidant and antioxidant levels in rabbits. Cell Biochem Funct 20:279–283. doi:10.1002/cbf.976
Joshipura KJ, Hu FB, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Rimm EB, Speizer FE, Colditz G, Ascherio A, Rosner B et al (2001) The effect of fruit and vegetable intake on risk for coronary heart disease. Ann Intern Med 134:1106–1114
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Zhang R, Jung MS, Ham YM, Baik JS, Lee NH, Hyun JW (2006) Cytoprotective effect of phloroglucinol on oxidative stress induced cell damage via catalase activation. J Cell Biochem 97:609–620. doi:10.1002/jcb.20668
Klingmuller V (1985) Enteral resorption of ioxitalamate. Rontgenblatter 38:350–352
Laurindo FR, da Luz PL, Uint L, Rocha TF, Jaeger RG, Lopes EA (1991) Evidence for superoxide radical-dependent coronary vasospasm after angioplasty in intact dogs. Circulation 83:1705–1715
Lee H-C, Yen H-W, Sheu S-H (2006) Effects of different contrast media on glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities in the heart and kidneys of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Formos Med Assoc 105:530–535
Liu S, Manson JE, Lee IM, Cole SR, Hennekens CH, Willett WC, Buring JE (2000) Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: the Women’s Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr 72:922–928
Lowry O, Rosenbrough N, Farr L, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 182:265–275
Lucchi L, Iannone A, Bergamini S, Stipo L, Perrone S, Uggeri S, Gatti V, Ferrari F, Tomasi A, Albertazzi A (2005) Comparison between hydroperoxides and malondialdehyde as markers of acute oxidative injury during hemodialysis. Artif Organs 29:832–837. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1594.2005.00136.x
Miura Y (2004) Oxidative stress, radiation-adaptive responses, and aging. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 45:357–372. doi:10.1269/jrr.45.357
Murray RK (2000) Muscle and the cytoskeleton. In: Murray RK, Granner DK, Mayes PA, Rodwell VW (eds) Harper’s biochemistry, 25th edn. Appleton & Lange, Stamford, pp 729–730
Nakazono K, Watanabe N, Matsuno K, Sasaki J, Sato T, Inoue M (1991) Does superoxide underlie the pathogenesis of hypertension? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10045–10048. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.22.10045
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Palinski W, Miller E, Witztum JL (1995) Immunization of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-deficient rabbits with homologous malondialdehyde-modified LDL reduces atherogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:821–825. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.3.821
Parthasarathy S, Steinberg D, Witztum JL (1992) The role of oxidized low-density lipoproteins in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Med 43:219–225. doi:10.1146/annurev.me.43.020192.001251
Rauen U, Li T, Ioannidis I, de Groot H (2007) Nitric oxide increases toxicity of hydrogen peroxide against rat liver endothelial cells and hepatocytes by inhibition of hydrogen peroxide degradation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C1440–C1449. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00366.2006
Ridnour LA, Sim JE, Hayward MA, Wink DA, Martin SM, Buettner GR, Spitz DR (2000) A spectrophotometric method for the direct detection and quantitation of nitric oxide, nitrite, and nitrate in cell culture media. Anal Biochem 281:223–229. doi:10.1006/abio.2000.4583
Sharma SK, Kini A (2005) Effect of nonionic radiocontrast agents on the occurrence of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with mild-moderate chronic renal insufficiency: pooled analysis of the randomized trials. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 65:386–393. doi:10.1002/ccd.20404
Tardif J (2006) Antioxidants: the good, the bad and the ugly. Can J Cardiol 22:B61–B65
Ueta E, Tadokoro Y, Yamamoto T, Yamane C, Suzuki E, Nanba E, Otsuka Y, Kurata T (2003) The effect of cigarette smoke exposure and ascorbic acid intake on gene expression of antioxidant enzymes and other related enzymes in the livers and lungs of Shionogi rats with osteogenic disorders. Toxicol Sci 73:339–347. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfg082
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İmge Ergüder, B., Çetin, M., Namuslu, M. et al. High osmolar contrast medium causes mild oxidation in liver, bladder, and ovary tissues from rats: vitamin C has protective role. Med Chem Res 19, 515–523 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9207-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9207-7