Abstract
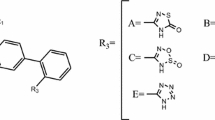
The quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) models were developed using multiple linear regression (MLR) and partial least square (PLS) for a set of 85 AT1 receptor antagonists of hydantoin series. The MLR and PLS generated comparable models with good predictive ability and all the other statistical values, such as r, r2, \( {\text{r}}_{{({\text{cv}})}}^{2} , \) and F and s values, were satisfactory. The results obtained from this study indicate the importance of steric (K-alpha3), hydrophobic (log P, and total lipole), and total energy (Cosmic total energy) in determining the activity of AT1 receptor antagonists. The results clearly explained that optimum hydrophobicity of substituent at R2 position is favorable for the activity and presence of a substituent of particular size and shape on phenyl ring at R3 position is essential for the activity. This information is pertinent to the further design of new AT1 receptor antagonist containing the hydantoin nucleus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cramer RD (1993) Partial Least Squares (PLS): its strengths and limitations. Perspect Drug Discov Des 1:269–278. doi:10.1007/BF02174528
Edmunds JJ, Klutchko S, Hamby JM, Bunker AM, Connolly CJC (1995) Derivatives of [[1–4(4-carboxybenzyl)imidazolyl]methylidene]hydantoins as orally active angiotensin II receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 38:3759–3771. doi:10.1021/jm00019a005
Fogarty DJ, Sanchez-Gomez MV, Matute C (2002) Multiple angiotensin receptor subtypes in normal and tumor astrocytes in vitro. Glia 39:304–313. doi:10.1002/glia.10117
Henrion D, Kubis N, Levy BI (2001) Physiological and pathophysiological functions of the AT(2) subtype receptor of angiotensin II: from large arteries to the microcirculation. Hypertension 38:1150–1157. doi:10.1161/hy1101.096109
Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Celerier J, ChapuisBernasconi C, Nguyen G, Wostl W, Maerki HP, Janzer RC, Corvol P, Gasc JM (2004) Renin and angiotensinogen expression and functions in growth and apoptosis of human glioblastoma. Br J Cancer 90:1059–1068. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601646
Kim KH (2007) Outliers in SAR and QSAR: 2. Is a flexible binding site a possible source of outliers? J Comput Aided Mol Des 21:421–435. doi:10.1007/s10822-007-9126-y
Kostis JB, Shelton B, Gossein G (1996) Adverse effects of enalapril in the studies of left ventricular dysfunction. Am Heart J 131:350–355. doi:10.1016/S0002-8703(96)90365-8
Kubinyi H (1996) Evolutionary variable selection in regression and PLS analyses. J Chemometr 10:119–133. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-128X(199603)10:2<119::AID-CEM409>3.0.CO;2-4
Kubo K, Kohar Y, Yoshimura Y, Shibouta Y, Furukawa Y (1993) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Synthesis and biological activity of potential prodrugs of benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem 36:2343–2349. doi:10.1021/jm00068a011
Kurup A, Grag R, Carini DJ, Hansch C (2001) Comparative QSAR: angiotensin II antagonists. Chem Rev 101:2727–2750. doi:10.1021/cr000025g
Lindgren F, Geladi P, Rannar S, Wold S (1994) Interactive variable selection (IVS) for PLS. J Chemometr 8:349–363. doi:10.1002/cem.1180080505
Meredith P (2004) Modern strategies in hypertension management. Eur Heart J Supplements 6(Suppl H):H23–H29
Mimran A, Ribstein J (1999) Angiotensin receptor blockers: pharmacology and clinical significance. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(Suppl 12):S273–S277
Morsing P, Vauquelin G (2001) How can the differences among AT1-receptor antagonists be explained? Cell Biochem Biophys 35:89–102. doi:10.1385/CBB:35:1:89
Tuccinardi T, Calderone V, Rapposelli S, Martinelli A (2006) Proposal of a new binding orientation for non-peptide AT1 antagonists. J Med Chem 49:4305–4316. doi:10.1021/jm060338p
Vallotton MB (1987) The renin-angiotensin system. Trends Pharmacol Sci 8:69–74. doi:10.1016/0165-6147(87)90013-7
Wildman SA, Crippen GM (1999) Prediction of physicochemical parameters by atomic contributions. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 39:868–873. doi:10.1021/ci990307l
Willenheimer R, Dahlof B, Rydberg E, Erhardt L (1999) AT1-receptor blockers in hypertension and heart failure: clinical experience and future directions. Eur Heart J 20:997–1008. doi:10.1053/euhj.1999.1547
Acknowledgment
Computational resources were provided by Banasthali University, and the authors thank the Vice Chancellor, for extending all the necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paliwal, S.K., Pal, M. & Siddiqui, A.A. Quantitative structure activity relationship analysis of angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonists. Med Chem Res 19, 475–489 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9205-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9205-9