Abstract
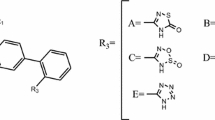
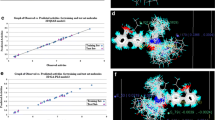
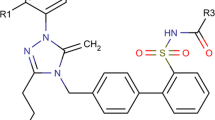
A series of 3H-1, -2, -4 triazolinone aryl and nonaryl substituents were subjected to QSAR analysis. Different statistically significant models were obtained, from which the most robust models for QSAR were obtained with r 2 = 0.7968 and q 2 = 0.7164 in model 1 for aryl triazolinones, and r 2 = 0.7499 and q 2 = 0.6290 for nonaryl triazolinones. The physicochemical descriptor HDonorCount and alignment-independent descriptors T_2_N_6, T_2_Cl_6, and T_2_N_4 were found to show significant correlation with biologic activity in aryl triazolinones. PolarSurfaceAreaExcludingPandS, HydrogenCount, and 6ChainCount were significant receptors in the case of nonaryl triazolinones.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almansa C, Gómez LA, Cavalcanti FL, de Arriba AF, García-Rafanell J, Forn J (1997) Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of a new series of potent AT1 selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists: 5-(biphenyl-4-ylmethyl) pyrazoles. J Med Chem 40:547–558. doi:10.1021/jm9604383
Balasubramanian N, Dhake A, Mourya VK (2007) QSAR studies of 4,5-dihydro-4-oxo-3H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridines as potent angiotensin II receptor antagonists by MLR and NLR analysis. Arkivoc 1:189–204
Belvisi L, Bravi G, Catalano G, Mabiliab M, Salimbeni A, Scolastico C (1996) A 3D QSAR CoMFA study of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. J Comput Aided Mol Des 10:567–582. doi:10.1007/BF00134180
Bernhart CA, Perreaut PM, Ferrari BP, Muneaux YA, Assens JL, Clement J, Haudricourt F, Muneaux CF, Taillades JE, Vignal MA, Gougat J, Giuraudou DR, Lacour CA, Roccon A, Cazaubon FC, Breliere JC, Fur GL, Nisato D (1993) A new series of imidazolones: highly specific and potent nonpeptide AT1 angiotensin II receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 36:3371–3380. doi:10.1021/jm00074a018
Buhlmayer P, Furet P, Criscione L, de Gaspro M, Schimidilin TS, LAttman R, Wood J (1994) Valsartan: a potent orally active angiotensin ii antagonist developed from a structurally new amino acid series. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4:29–34. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(01)81117-3
Chang LL, Ashton WT, Flanagan KL, Strelitz RA, Maccoss M, Greenlee WJ, Chang RS, Lotti VJ, Faust KA, Tsing BC, Bunting P, Zingaro GJ, Kivlighn SD, Siegl PKS (1993) Triazolinones as nonpeptide angiotensin II antagonists: synthesis and evaluation of potent 2,4,5-trisubstituted triazolinones. J Med Chem 36:2558–2568. doi:10.1021/jm00069a015
Datar PA, Coutinho EC, Srivastava S (2004a) Comparative study of 3D-QSAR techniques on angiotensin II receptor (AT1) antagonists. Lett Drug Design Disc 1:115–120 (6)
Datar PA, Desai PV, Coutinho EC (2004b) A 3D-QSAR of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor antagonists based on receptor surface analysis. J Chem Inf Model 44:210–220. doi:10.1021/ci0341520
Ellingboe JW, Antane M, Nguyen TT, Collini MD, Antane S, Bender R, Hartupee D, White V, McCallum J, Park CH (1994) Pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine angiotensin II antagonists. J Med Chem 37:542–550. doi:10.1021/jm00030a013
Judd DB, Dowle MD, Middlemiss D, Scopes DI, Ross BC, Jack TI, Pass M, Tranquillini E, Hobson JE, Panchal TA (1994) Bromobenzofuran-based nonpeptide antagonists of angiotensin II: GR138950, a potent antihypertensive agent with high oral bioavailability. J Med Chem 37:3108–3120. doi:10.1021/jm00045a016
Keenan RM, Weinstock J, Finkelstein JA, Franz RG, Gaitanopoulos DE, Girard GR, Hill DT, Morgan TM, Samanen JM, Peishoff CE (1993) Potent nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. 2. 1-(Carboxybenzyl)imidazole-5-acrylic acids. J Med Chem 36:1880–1892. doi:10.1021/jm00065a011
Khosla SC, Withdraw CD (1990) Remington’s Pharmaceutical Sciences. Mc. Pub. Co., p. 837
Kubo K, Kohara Y, Yoshimura Y, Inada Y, Shibouta Y, Furukawa Y, Kato T, Nishikawa K, Naka T (1993) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: synthesis and biological activity of potential prodrugs of benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem 36:2343–2349. doi:10.1021/jm00068a011
Kurup A, Garg R, Carini DJ, Hansch C (2001) Comparative QSAR: angiotensin II antagonists. Chem Rev 101:2727. doi:10.1021/cr000025g
Middlemiss D, Drew GM, Ross BC, Robertson MJ, Scopes DIC, Dowle MD, Akers J, Cardwell K, Clark KL, Coote S, Idred CD, Hamblett J, Hilditch A, Hirst GC, Jack T, Motana J, Panchal TA, Paton JMS, Shah P, Stuart G, Travers A (1991) Benzobromofurans: a new class of potent non peptide antagonists of angiotensin II. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1:711–716. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(01)81053-2
Pandya T, Chaturvedi SC (2004) QSAR study of a series of 2-, 3-, 6-substituted quinazolinones as AT1 selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Ind J Chem 43″3″:2440–2445
Pandya T, Chaturvedi SC (2005) Structure–activity relationship study of some triazolinone-based compounds with antagonistic balanced activity on angiotensin II receptor subtypes AT1 and AT2: a three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship investigation. Arzneimittelforschung 55:265–270
Pandya T, Pandey SK, Tiwari M, Chaturvedi SC, Saxena AK (2001) 3-D QSAR studies of triazolinone based balanced AT1/AT2 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 9:291–300
Ries UJ, Mihm G, Narr B, Hasselbach KM, Wittneben H, Entzeroth M, van Meel JC, Wienen W, Hauel NH (1993) 6-Substituted benzimidazoles as new nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: synthesis, biological activity, and structure–activity relationships. J Med Chem 36:4040–4051. doi:10.1021/jm00077a007
Salimbeni A, Canevotti R, Paleari F, Poma D, Caliari S, Fici F, Cirillo R, Renzetti AR, Subissi A, Belvisi L (1995) N-3-substituted pyrimidinones as potent, orally active, AT1 selective angiotensin II receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 38:4806–4820. doi:10.1021/jm00024a008
Swales JD, Heagerty AM (1977) Vascular renin-angiotensin system. Physiol Rev 57:313–370
Wong PC, Price WA Jr, Chiu AT, Duncia JV, Carini DJ, Wexler RR, Johnson AL, Timmermans PB (1990) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. XI. Pharmacology of EXP3174: an active metabolite of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255:211–217
Yan PZ, Chen BC, Shi H, Jian HJ, Hai LW, Guo LS, Ru QY (2007) QSAR study of angiotensin II antagonists using robust boosting partial least squares regression. Anal Chim Acta 593:68–74. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.04.031
Yanagisawa H, Amemiya Y, Kanazaki T, Shimoji Y, Fujimoto K, Kitahara Y, Sada T, Mizuno M, Ikeda M, Miyamoto S, Furukawa Y, Koike H (1996) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: synthesis, biological activities, and structure–activity relationships of imidazole-5-carboxylic acids bearing alkyl, alkenyl, and hydroxyalkyl substituents at the 4-position and their related compounds. J Med Chem 39:323–338. doi:10.1021/jm950450f
Yoo SE, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yi KY, Lee DW (1999) A comparative molecular field analysis and molecular modeling studies on pyridylimidazole type of angiotensin II antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 7:2971–2976. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(99)00245-X
Acknowledgment
The author thanks Vlife Science Technologies Pvt. Ltd for providing the software for the study, and the Head of the School of Pharmacy, Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, for providing the facilities for carrying out the study. Anupama Parate is thankful to the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, for providing financial assistance. The authors also thank the anonymous reviewers whose valuable comments and suggestions greatly helped in improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parate, A., Chaturvedi, S.C. Structural insights for 3H-1, -2, -4 triazolinones as angiotensin II receptor antagonists using QSAR techniques. Med Chem Res 19, 375–391 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9197-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9197-5