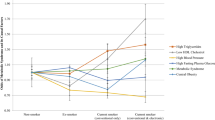
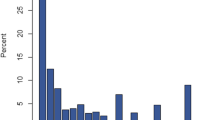
Abstract
Objectives
To assess the initiation rate and determinants of tobacco smoking among adults.
Methods
In the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study, a population-based cohort from Iran, 6101 participants ≥ 18 years old who had never smoked tobacco at baseline (phase II: 2002–2006) were followed until phase VI (2015–2018). Sex-specific initiation rates per 1000 person-years for self-reported tobacco smoking and hazard ratios (HR) for its potential determinants (using Cox proportional hazards models) were calculated.
Results
The age- and sex-adjusted smoking initiation rate was 13.77 [95% confidence interval (CI) 12.59–14.94] per 1000 person-years, of which 78% was attributed to water pipe use. Initiation rate was remarkably higher among men [19.1 (16.9–21.2)] than women [8.3 (7.4–9.2)] and declined in older age-groups. Among both genders, being married was protective [men: HR 0.67 (CI 95% 0.48–0.92); women: 0.58 (0.45–0.74)], while intermediate-level education (compared with high level) [men: 1.61 (1.14–2.26); women: 1.33 (0.95–1.84, p value = 0.092)] and passive smoking [men: 1.76 (1.36–2.28); women: 1.82 (1.42–2.33)] increased the risk. Educational intervention decreased the risk among women [0.74 (0.58–0.94)].
Conclusions
The majority of adult smoking initiators started smoking with water pipe. The initiation rate was remarkably higher in men and younger age-groups. Passive smoking, being single and lower education were risk factors. Educational intervention was protective among women.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akl EA, Jawad M, Lam WY, Obeid R, Irani J (2013) Motives, beliefs and attitudes towards waterpipe tobacco smoking: a systematic review. Harm Reduct J 10:12
Azizi F, Ghanbarian A, Momenan AA, Hadaegh F et al (2009) Prevention of non-communicable disease in a population in nutrition transition: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study phase II. Trials 10:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-10-5
Bernat DH, Klein EG, Forster JL (2012) Smoking initiation during young adulthood: a longitudinal study of a population-based cohort. J Adolesc Health 51:497–502
Edwards R, Carter K, Peace J, Blakely T (2013) An examination of smoking initiation rates by age: results from a large longitudinal study in New Zealand. Aust N Z J Public Health 37:516–519
Forouzanfar MH, Afshin A, Alexander LT et al (2016) Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1659–1724
Fotouhi A, Khabazkhoob M, Hashemi H, Mohammad K (2009) The prevalence of cigarette smoking in residents of Tehran. Arch Iran Med 12:358–364
Freedman KS, Nelson NM, Feldman LL (2012) Smoking initiation among young adults in the United States and Canada, 1998–2010: a systematic review. Prev Chronic Dis 9:E05
Gakidou E, Afshin A, Abajobir AA et al (2017) Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390:1345–1422
Goodchild M, Nargis N, d’Espaignet ET (2018) Global economic cost of smoking-attributable diseases. Tob Control 27:58–64
Henningfield JE, Clayton R, Pollin W (1990) Involvement of tobacco in alcoholism and illicit drug use. Br J Addict 85:279–292
IPAQ Research Committee (2005) Guidelines for data processing and analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)-short and long forms. www.ipaq.ki.se. Accessed 17 Sept 2008
Jahangiri-Noudeh Y, Akbarpour S, Lotfaliany M et al (2014) Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors in people with and without diabetes mellitus: a Middle Eastern cohort study. PLoS ONE 9:e112639
Jawad M, Charide R, Waziry R, Darzi A, Ballout RA, Akl EA (2018) The prevalence and trends of waterpipe tobacco smoking: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 13:e0192191
Kaczynski AT, Manske SR, Mannell RC, Grewal K (2008) Smoking and physical activity: a systematic review. Am J Health Behav 32:93–110. https://doi.org/10.5555/ajhb.2008.32.1.93
Kollath-Cattano C, Osman A, Thrasher JF (2017) Evaluating the perceived effectiveness of pregnancy-related cigarette package health warning labels among different gender/age groups. Addict Behav 66:33–40
Kviz FJ, Clark MA, Crittenden KS, Warnecke RB, Freels S (1995) Age and smoking cessation behaviors. Prev Med 24:297–307. https://doi.org/10.1006/pmed.1995.1048
Leonardi-Bee J, Jere ML, Britton J (2011) Exposure to parental and sibling smoking and the risk of smoking uptake in childhood and adolescence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 66:847–855
Lindstrom M (2010) Social capital, economic conditions, marital status and daily smoking: a population-based study. Public Health 124:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2010.01.003
Mansournia MA, Etminan M, Danaei G, Kaufman JS, Collins G (2017) Handling time varying confounding in observational research. BMJ 359:j4587. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j4587
Marcon A, Pesce G, Calciano L et al (2018) Trends in smoking initiation in Europe over 40 years: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 13:e0201881
Meysamie A, Ghaletaki R, Haghazali M et al (2010) Pattern of tobacco use among the Iranian adult population: results of the national survey of risk factors of non-communicable diseases (SuRFNCD-2007). Tob Control 19:125–128
Meysamie A, Ghaletaki R, Zhand N, Abbasi M (2012) Cigarette smoking in Iran. Iran J Public Health 41:1
Mirbolouk M, Derakhshan A, Charkhchi P, Guity K, Azizi F, Hadaegh F (2016) Incidence and predictors of early adulthood pre-diabetes/type 2 diabetes, among Iranian adolescents: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Pediatr Diabetes 17:608–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12343
Moosazadeh M, Ziaaddini H, Mirzazadeh A, Ashrafi-Asgarabad A, Haghdoost AA (2013) Meta-analysis of smoking prevalence in Iran. Addict Health 5:140
National Center for Chronic Disease P, Health Promotion Office on S, Health (2012) Reports of the surgeon general. In: Preventing tobacco use among youth and young adults: a report of the surgeon General. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US), Atlanta (GA)
Nemati S, Rafei A, Freedman ND, Fotouhi A, Asgary F, Zendehdel K (2017) Cigarette and water-pipe use in Iran: geographical distribution and time trends among the adult population; A pooled analysis of national STEPS surveys, 2006–2009. Arch Iran Med 20:295-301
Newell SA, Girgis A, Sanson-Fisher RW, Savolainen NJ (1999) The accuracy of self-reported health behaviors and risk factors relating to cancer and cardiovascular disease in the general population: a critical review. Am J Prev Med 17:211–229
O’Loughlin JL, Dugas EN, O’Loughlin EK, Karp I, Sylvestre M-P (2014) Incidence and determinants of cigarette smoking initiation in young adults. J Adolesc Health 54(26–32):e24
Parizadeh D, Momenan AA, Amouzegar A, Azizi F, Hadaegh F (2018) Tobacco smoking: findings from 20 years of the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Int J Endocrinol Metab 16(4 Suppl):e84738
Reitsma MB, Fullman N, Ng M et al (2017) Smoking prevalence and attributable disease burden in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 389:1885–1906
Ruiz-Alejos A, Carrillo-Larco RM, Miranda JJ, Anderson CAM, Gilman RH, Smeeth L, Bernabé-Ortiz A (2018) Addressing the impact of urban exposure on the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: The PERU MIGRANT Study. Sci Rep 8:5512. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23812-6
Sarraf-Zadegan N, Boshtam M, Shahrokhi S, Naderi GA, Asgary S, Shahparian M, Tafazoli F (2004) Tobacco use among Iranian men, women and adolescents. Eur J Public Health 14:76–78
Sozmen K, Unal B, Saidi O et al (2015) Cardiovascular risk factor trends in the Eastern Mediterranean region: evidence from four countries is alarming. Int J Public Health 60(Suppl 1):S3–S11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-014-0610-6
Thomas RE, Baker PR, Thomas BC (2016) Family-based interventions in preventing children and adolescents from using tobacco: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad Pediatr 16:419–429
Villanti AC, Cantrell J, Pearson JL, Vallone DM, Rath JM (2013) Perceptions and perceived impact of graphic cigarette health warning labels on smoking behavior among US young adults. Nicotine Tob Res 16:469–477
Waziry R, Jawad M, Ballout RA, Al Akel M, Akl EA (2016) The effects of waterpipe tobacco smoking on health outcomes: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol 46:32–43
Wellman RJ, Dugas EN, Dutczak H, O’Loughlin EK, Datta GD, Lauzon B, O’Loughlin J (2016) Predictors of the onset of cigarette smoking: a systematic review of longitudinal population-based studies in youth. Am J Prev Med 51:767–778
World Health Organization (2017) WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2017: monitoring tobacco use and prevention policies. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/255874/9789241512824-eng.pdf. Accessed 01 Aug 2019
World Health Organization (2018) WHO global report on trends in prevalence of tobacco smoking 2000–2025. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/272694/9789241514170-eng.pdf. Accessed 01 Aug 2019
Yi Z, Mayorga ME, Lich KH, Pearson JL (2017) Changes in cigarette smoking initiation, cessation, and relapse among US adults: a comparison of two longitudinal samples. Tob Induc Dis 15:17
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Ms. Niloofar Shiva for critical editing of English grammar and syntax of the manuscript. The authors would also like to express their appreciation to the TLGS participants and staff for their kind cooperation.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parizadeh, D., Moazzeni, S.S., Hasheminia, M. et al. Sex-specific initiation rates of tobacco smoking and its determinants among adults from a Middle Eastern population: a cohort study. Int J Public Health 64, 1345–1354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-019-01307-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-019-01307-z