Abstract
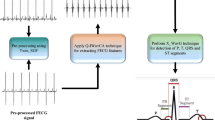
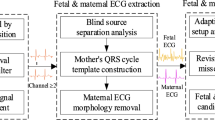
The noninvasive fetal electrocardiography monitoring system consists of composite signals such as maternal ECG (MECG) and fetal ECG (FECG) acquired from abdominal ECG (AECG) signals. These records allow for the collection of relevant and reliable information that contributes to the safety of the fetus during pregnancy. However, FQRS detection and FECG extraction are challenging due to the non-stationary complexity of FECG signals, similar frequency components, low detection rates, and overlap issues that can occur for FQRS in abdominal recordings. Therefore, improved biomedical signal processing methods are required to achieve high detection accuracy with fewer errors. This paper introduces an advanced framework for FECG signal extraction and QRS detection using a signal decomposition technique and improved threshold-based detection with an adaptive noise cancelation approach (ANC-SDITD) in AECG signals. It consists of three steps: Initially, a robust VSS-WALMS (variable step size-weighted adaptive least mean square) algorithm is used for signal denoising from AECG signals with the reserved amplitude information. The underlying FECG signals could be automatically extracted from the complexity of the AECG signals by removing the MECG signal using an empirical wavelet transform and inverse scattering entropy method. Finally, one method relies on an improved self-adaptive peak threshold detection algorithm to detect fetal QRS complexes. Experimental results show that the proposed ANC-SDITD approach is effective for FECG extraction and FQRS detection when simulated on a fetal ECG synthetic database. Performance results achieve higher statistical accuracy under extraction metrics, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) metrics, and statistical metrics compared to other algorithms. Also, it shows significant improvement compared to other techniques when the SNR ranges from 0 to 12 dB. SNR estimates good performance for the QRS complex between the noise level and the ECG channels.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.J. Al-Haddad, E. Oler, B. Armistead, N.A. Elsayed, D.R. Weinberger, R. Bernier, I. Burd, R. Kapur, B. Jacobsson, C. Wang, I. Mysorekar, The fetal origins of mental illness. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 221(6), 549–562 (2019)
Y.S. Alshebly, M. Nafea, Isolation of fetal ECG signals from abdominal ECG using wavelet analysis. IRBM. 41(5), 252–260 (2020)
F. Andreotti, J. Behar, S. Zaunseder, J. Oster, G.D. Clifford, An open-source framework for stress-testing non-invasive foetal ECG extraction algorithms. Physiol. Meas. 37(5), 627–648 (2016)
F. Andreotti, F. Gräßer, H. Malberg, S. Zaunseder, Non-invasive fetal ECG signal quality assessment for multichannel heart rate estimation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(12), 2793–2802 (2017)
G. Baldazzi, E. Sulas, M. Urru, R. Tumbarello, L. Raffo, D. Pani, Wavelet denoising as a post-processing enhancement method for non-invasive foetal electrocardiography. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 195, 105558 (2020)
C. Bandt, A new kind of permutation entropy used to classify sleep stages from invisible EEG microstructure. Entropy 19(5), 197 (2017)
K. Barnova, R. Martinek, R. Jaros, R. Kahankova, K. Behbehani, V. Snasel, System for adaptive extraction of non-invasive fetal electrocardiogram. Appl. Soft Comput. 113, 107940 (2021)
K. Barnova, R. Martinek, R. Jaros, R. Kahankova, Hybrid methods based on empirical mode decomposition for non-invasive fetal heart rate monitoring. IEEE Access. 8, 51200–51218 (2020)
J.A. Behar, L. Bonnemains, V. Shulgin, J. Oster, O. Ostras, I. Lakhno, Noninvasive fetal electrocardiography for the detection of fetal arrhythmias. Prenat. Diagn. 39(3), 178–187 (2019)
R.L. Berkowitz, M.E. D’Alton, J.D. Goldberg, D.F. O’Keeffe, J. Spitz, R. Depp, M.P. Nageotte, The case for an electronic fetal heart rate monitoring credentialing examination. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 210(3), 204–207 (2014)
J.L. Camargo-Olivares, R. Martin-Clemente, S. Hornillo-Mellado, M.M. Elena, I. Roman, The maternal abdominal ECG as input to MICA in the fetal ECG extraction problem. IEEE Signal Process Lett 18(3), 161–164 (2011)
Community Research and Development Information Service. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/home_en.html/ (accessed on 17 October 2018)
G. Da Poian, R. Bernardini, R. Rinaldo, Separation and analysis of fetal-ECG signals from compressed sensed abdominal ECG recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63(6), 1269–1279 (2015)
Z. Farzad Mohajeri, S. Aalipour, M. Sheikh, M. Shafaat, S. Hantoushzadeh, S. Borna, S. Khazardoost, Ultrasound measurement of fetal adrenal gland in fetuses with intrauterine growth restriction, an early predictive method for adverse outcomes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 32(9), 1485–91 (2019)
P. Ghobadi Azbari, S. Mohaqeqi, N. Ghanbarzadeh Gashti, M. Mikaili, Introducing a combined approach of empirical mode decomposition and PCA methods for maternal and fetal ECG signal processing. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 29(19), 3104–9 (2016)
R. Gulati, M. Zayek, F. Eyal, Presetting ECG electrodes for earlier heart rate detection in the delivery room. Resuscitation 128, 83–87 (2018)
D. Gurve, S. Krishnan, Separation of fetal-ECG from single-channel abdominal ECG using activation scaled non-negative matrix factorization. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24(3), 669–680 (2019)
Y. Hu, F. Li, H. Li, C. Liu, An enhanced empirical wavelet transform for noisy and non-stationary signal processing. Digital Signal Process. 60, 220–229 (2017)
R. Jaros, R. Martinek, R. Kahankova, J. Koziorek, Novel hybrid extraction systems for fetal heart rate variability monitoring based on non-invasive fetal electrocardiogram. IEEE Access 7, 131758–131784 (2019)
R. Kahankova, R. Martinek, R. Jaros, K. Behbehani, A. Matonia, M. Jezewski, J.A. Behar, A review of signal processing techniques for non-invasive fetal electrocardiography. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 13, 51–73 (2019)
M. Karaim, A. Noureldin, T.B. Karamat, Low-cost IMU data denoising using Savitzky–Golay filters. In: 2019 International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and their Applications (ICCSPA) IEEE pp 1–5 (2019)
E. Keenan, C. Karmakar, F.C. Brownfoot, M. Palaniswami, Personalized anatomic modeling for noninvasive fetal ECG: methodology and applications. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–2 (2021)
J. Kolarik, M. Golembiovsky, T. Docekal, R. Kahankova, R. Martinek, M. Prauzek, A low-cost device for fetal heart rate measurement. IFAC-PapersOnLine. 51(6), 426–431 (2018)
A.J. Krupa, S. Dhanalakshmi, N.L. Sanjana, N. Manivannan, R. Kumar, S. Tripathy, Fetal heart rate estimation using fractional Fourier transform and wavelet analysis. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 41(4), 1533–1547 (2021)
K.J. Lee, B. Lee, Sequential total variation denoising for the extraction of fetal ECG from single-channel maternal abdominal ECG. Sensors 16(7), 1020 (2016)
H. Liu, D. Chen, G. Sun, Detection of fetal ECG R wave from single-lead abdominal ECG using a combination of RR time-series smoothing and template-matching approach. IEEE Access 7, 66633–66643 (2019)
B. Lotfi, L. Huang, An approach for velocity and position estimation through acceleration measurements. Measurement 90, 242–249 (2016)
C.T. Mai, J.L. Isenburg, M.A. Canfield, R.E. Meyer, A. Correa, C.J. Alverson, P.J. Lupo, T. Riehle-Colarusso, S.J. Cho, D. Aggarwal, R.S. Kirby, National population-based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Res. 111(18), 1420–1435 (2019)
B.R. Manju, M.R. Sneha, ECG denoising using wiener filter and kalman filter. Procedia Comput. Sci. 171, 273–281 (2020)
N. Marchon, G. Naik, R. Pai, ECG electrode configuration to extract real time FECG signals. Procedia Comput. Sci. 125, 501–508 (2018)
R. Martinek, R. Kahankova, H. Nazeran, J. Konecny, J. Jezewski, P. Janku, P. Bilik, J. Zidek, J. Nedoma, M. Fajkus, Non-invasive fetal monitoring: A maternal surface ECG electrode placement-based novel approach for optimization of adaptive filter control parameters using the LMS and RLS algorithms. Sensors 17(5), 1154 (2017)
A. Maternia, T. Kupka, K. Horoba, J. Jezewski, R. Martinek, J. Wróbel, R. Kahankova, R. Czabanski, S. Graczyk, New Possibilities for Fetal Monitoring Using Unobtrusive Abdominal Electrocardiography. In: 2019 MIXDES-26th International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems IEEE, pp. 413–418 (2019)
A.K. Maurya, P. Agrawal, S. Dixit, Modified model and algorithm of LMS adaptive filter for noise cancellation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(5), 2351–2368 (2019)
Mindchild. Available online: http://www.mindchild.com/ (accessed on 17 October 2018)
M.R. Mohebbian, M.W. Alam, K.A. Wahid, A. Dinh, Single channel high noise level ECG deconvolution using optimized blind adaptive filtering and fixed-point convolution kernel compensation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 57, 101673 (2020)
Monica Healthcare. Available online: http://www.monicahealthcare.com/ (accessed on 17 October 2018)
D. Panigrahy, P.K. Sahu, Extraction of fetal ECG signal by an improved method using extended Kalman smoother framework from single channel abdominal ECG signal. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 40(1), 191–207 (2017)
M. Piela, T. Moroń, Spatio-temporal extension of independent component analysis for fetal ECG extraction. in International Conference on Information Technologies in Biomedicine. Springer, Cham, pp. 315–324 (2018)
A. Rashkovska, V. Avbelj, Abdominal fetal ECG measured with differential ECG sensor. in 2017 40th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO) IEEE, pp. 289–291 (2017)
A.K. Regan, M. Gissler, M.C. Magnus, S.E. Håberg, S. Ball, E. Malacova, N. Nassar, H. Leonard, G. Pereira, Association between interpregnancy interval and adverse birth outcomes in women with a previous stillbirth: an international cohort study. Lancet. 393(10180), 1527–1535 (2019)
S. Sahoo, B. Kanungo, S. Behera, S. Sabut, Multiresolution wavelet transform based feature extraction and ECG classification to detect cardiac abnormalities. Measurement 108, 55–66 (2017)
L.D. Sharma, R.K. Sunkaria, Novel T-wave detection technique with minimal processing and RR-interval based enhanced efficiency. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 10, 367–379 (2019)
A. Sharma, S. Patidar, A. Upadhyay, U.R. Acharya, Accurate tunable-Q wavelet transform based method for QRS complex detection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 75, 101–111 (2019)
V. Smith, S. Arunthavanathan, A. Nair, D. Ansermet, F. da Silva Costa, E.M. Wallace, A systematic review of cardiac time intervals utilising non-invasive fetal electrocardiogram in normal fetuses. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 18(1), 1–5 (2018)
F.R. Stöter, A. Liutkus, N. Ito, The 2018 signal separation evaluation campaign. in International Conference on Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, Springer, Cham, pp. 293–305 (2018)
M. Suganthy, S. Joy, P. Anandan, Detection of fetal arrhythmia by adaptive single channel electrocardiogram extraction. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 44(3), 683–692 (2021)
L.Y. Taha, E. Abdel-Raheem, A computationally efficient blind source extraction using idempotent transformation matrix. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(5), 2245–2265 (2019)
M. Wahbah, R. Al Sakaji, K. Funamoto, A. Krishnan, Y. Kimura, A.H. Khandoker, Estimating gestational age from maternal-fetal heart rate coupling parameters. IEEE Access. 9, 65369–79 (2021)
Y. Wang, Y. Fu, Z. He, Fetal electrocardiogram extraction based on fast ICA and wavelet denoising. in 2018 2nd IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC) IEEE, pp. 466–469 (2018)
Y. Zhang, S. Yu, Single-lead noninvasive fetal ECG extraction by means of combining clustering and principal components analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 58(2), 419–432 (2020)
S. Ziani, Y. El Hassouani, Fetal electrocardiogram analysis based on LMS adaptive filtering and complex continuous wavelet 1-D. in InInternational Conference on Big Data and Networks Technologies, Springer, Cham, pp. 360–366 (2019)
Funding
There is no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author has participated in writing the manuscript and has revised the final version. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by the author.
Informed Consent
There is no informed consent for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jebastine, J. Fetal ECG Extraction and QRS Detection Using Advanced Adaptive Filtering-Based Signal Decomposition and Peak Threshold Technique from Abdominal ECG Signals. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 6058–6088 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02386-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02386-3