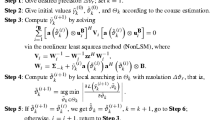Abstract
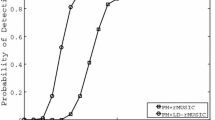
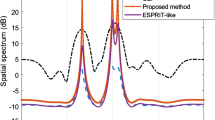
To address the issue that existing direction-finding approaches perform poorly under impulse noise and do not work well in underdetermined scenarios, a novel sparse array direction-finding approach on the background of impulse noise is proposed in this work. The approach introduces an infinite norm Gaussian kernel to restrain the impulse noise and obtains accurate estimates via the maximum likelihood algorithm. Meanwhile, a novel quantum transient search optimization (QTSO) algorithm is designed to solve the corresponding cost function. In addition, we prove the convergence of QTSO and derive the Cramér–Rao bound of sparse array direction finding in the presence of impulse noise. Compared with some traditional direction-finding approaches, the proposed approach shows excellent performance through simulation results in different schemes, which can also be a general framework to address other complex direction-finding problems.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
My manuscript has no associated data.
References
B.G. Byun, D.S. Yoo, Compuationally efficient propagator method for DoA with coprime array. J. Adv. Navig. Technol. 20(3), 258–264 (2016)
P. Chen, Z. Chen, B. Zheng, X. Wang, Efficient DOA estimation method for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces aided UAV swarm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 70, 743–755 (2022)
K. Dervis, A. Bahriye, A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 214(1), 108–132 (2009)
Y. Du, H. Gao, M. Chen, Direction of arrival estimation method based on quantum electromagnetic field optimization in the impulse noise. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 32(3), 527–537 (2021)
H. Gao, M. Chen, Y. Du, A. Jakobsson, Monostatic MIMO radar direction finding in impulse noise. Digit. Signal Process. 3, 103198 (2021)
H. Gao, Y. Du, C. Li, Quantum fireworks algorithm for optimal cooperation mechanism of energy harvesting cognitive radio. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 29(1), 18–30 (2018)
H. Gao, J. Li, M. Diao, Direction finding of bistatic MIMO radar based on quantum-inspired grey wolf optimization in the impulse noise. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 75, 1–14 (2018)
J. He, T. Shu, L. Li, T.-K. Truong, Mixed near-field and far-field localization and array calibration with partly calibrated arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 70, 2105–2118 (2022)
J. He, L. Li, T. Shu, Sparse nested arrays with spatially spread square acoustic vector sensors for high-accuracy underdetermined direction finding. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 57(4), 2324–2336 (2021)
J. He, Z. Liu, K.T. Wong, Snapshot-instantaneous \(\Vert \cdot \Vert _{infin}\) normalization against heavy-tail noise. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 44(3), 1221–1227 (2008)
J. He, L. Li, T. Shu, 2-D direction finding using parallel nested arrays with full co-array aperture extension. Signal Process. 178, 107795 (2021)
J. Kenndey, R. Eberhart, Particle swarm optimization, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 1995, pp. 1942–1948 (1995)
P. Li, J. Li, G. Zhao, Low complexity DOA estimation for massive UCA with single snapshot. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 33(1), 22–27 (2022)
W. Li, W. Liao, A. Fannjiang, Super-resolution limit of the ESPRIT algorithm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 66(7), 4593–4608 (2020)
X. Li, J. Sun, L. Jin et al., Bi-parameter CGM model for approximation of \(\alpha \)-stable PDF. Electron. Lett. 44(18), 1096–1098 (2008)
J. Li, Y. He, P. Ma et al., Direction of arrival estimation using sparse nested arrays with coprime displacement. IEEE Sens. J. 21(4), 5282–5291 (2020)
T. Liu, J.M. Mendel, A subspace-based direction-finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(8), 1605–1613 (2001)
W. Liu, P.P. Pokharel, J.C. Principe, Correntropy: properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(11), 5286–5298 (2007)
X. Ma, C.L. Nikias, Joint estimation of time delay and frequency delay in impulsive noise using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(1), 2669–2687 (1996)
M. Meller, K. Stawiarski, On DOA estimation for rotating arrays using stochastic maximum likelihood approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 68, 5219–5229 (2020)
P. Pal, P.P. Vaidyanathan, Nested arrays: a novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(8), 4167–4181 (2010)
P. Pal, P.P. Vaidyanathan, Coprime sampling and the music algorithm, in 2011 Digital Signal Processing and Signal Processing Education Meeting (DSP/SPE), pp. 289–294 (2011)
P. Pal, P.P. Vaidyanathan, Multiple level nested array: an efficient geometry for \(2q\)th order cumulant based array processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(3), 1253–1269 (2012)
R.K. Patra, A.S. Dhar, A novel nested array for real-valued sources exploiting array motion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1375–1379 (2021)
C. Peng, Z. Yang, Z. Chen, Z. Guo, Reconfigurable intelligent surface aided sparse DOA estimation method with non-ULA. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 2023–2027 (2021)
M.H. Qais, H.M. Hasanien, S. Alghuwainem, Transient search optimization: a new meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Appl. Intell. 50, 3926–3941 (2020)
R. Roy, T. Kailath, ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 37(7), 984–995 (1989)
I. Santamaria, P.P. Pokharel, J.C. Principe, Generalized correlation function: definition, properties, and application to blind equalization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(6), 2187–2197 (2006)
O. Schmidt, Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 34(3), 276–280 (1986)
Q. Si, Y. Zhang, M.G. Amin, Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(6), 1377–1390 (2015)
P. Stoica, A.B. Gershman, Maximum-likelihood DOA estimation by data-supported grid search. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 6(10), 273–275 (1999)
A. Swindlehurst, M. Viberg, Subspace fitting with diversely polarized antenna arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 41(12), 1687–1694 (2002)
Z. Tian, Beamspace iterative quadratic WSF for DOA estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 10(6), 176–179 (2003)
P. Tsakalides, C.L. Nikias, The robust covariation-based MUSIC (ROC-MUSIC) algorithm for bearing estimation in impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(7), 1623–1633 (1996)
P.P. Vaidyanathanand, P. Pal, Sparse sensing with co-prime samplers and arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(2), 573–586 (2011)
M. Wagner, Y. Park, P. Gerstoft, Gridless DOA estimation and root-MUSIC for non-uniform linear arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 69, 2144–2157 (2021)
L. Wan, K. Liu, Y. Liang, T. Zhu, DOA and polarization estimation for non-circular signals in 3-D millimeter wave polarized massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 20(5), 3152–3167 (2021)
C. Wang, L. Ai, F. Wen et al., An improved PARAFAC estimator for 2D-DOA estimation using EMVS array. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 41, 147–165 (2022)
Z. Wang, D. Wang, B. Bai et al., Direction finding algorithm of correlated interferometer based on genetic algorithm with high degree of stretching. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 40(1), 39–44 (2018)
X. Wang, M. Lu, S. Wei et al., Multi-objective optimization based optimal setting control for industrial double-stream alumina digestion process. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 173–185 (2022)
F. Wen, G. Gui, H. Gacanin, H. Sari, Compressive sampling framework for 2D-DOA and polarization estimation in mmWave polarized massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2022.3215965
Z. Weng, P.M. Djuri, A search-free DOA estimation algorithm for coprime arrays. Digit. Signal Process. 24, 27–33 (2014)
X. Yan, G. Liu, H. Wu et al., Robust modulation classification over \(\alpha \)-stable noise using graph-based fractional lower-order cyclic spectrum analysis. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(3), 2836–2849 (2020)
G. Yang, J. Wang, G. Zhang et al., Joint estimation of timing and carrier phase offsets for MSK signals in alpha-stable noise. IEEE Commun. Lett. 22(1), 89–92 (2018)
G. You, T. Qiu, Y. Zhu, A novel extended fractional lower order cyclic MUSIC algorithm in impulsive noise. ICIC Express Lett. 6(9), 2371–2376 (2012)
Z. Zheng, Y. Huang, W. Wang et al., Direction-of-arrival estimation of coherent signals via coprime array interpolation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 27(99), 585–589 (2020)
Z. Zheng, Y. Huang, W.-Q. Wang, H.C. So, Augmented covariance matrix reconstruction for DOA estimation using difference coarray. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 69, 5345–5358 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 62073093), the postdoctoral science research developmental fund of in Heilongjiang Province (Grant LBH-Q19098), and the Heilongjiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant LH2020F017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
To prove the boundness of the complex matrix \(\mathbf{{R}}\) with the component \({R_{ij}}\) \((i,j = 1,2, \ldots ,M)\), we can prove the boundness of \({{\text {Re}}} \{ {R_{ij}}\} \) and \({{\text {Im}}} \{ {R_{ij}}\} \) as follows:
Thus, \(- 1 \le {{\text {Re}}} \{ {R_{ij}}\} \le 1\). Similarly, \(- 1 \le {{\text {Im}}} \{ {R_{ij}}\} \le 1\). In this case, \(\mathbf{{R}}\) is also bounded.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Gao, H., Liu, Y. et al. A Sparse Array Direction-Finding Approach Under Impulse Noise. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 5579–5601 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02377-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02377-4