Abstract
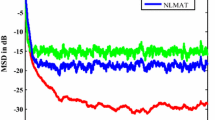
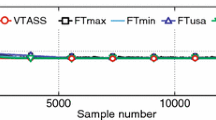
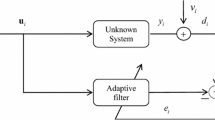
To solve the problem that the least mean square (LMS) algorithm cannot balance the convergence rate and steady-state mean square error (MSE) well and require excessive manual adjustment of parameters, this paper proposes a parameter-free variable step-size LMS algorithm based on the hyperbolic tangent function. First, the algorithm uses the hyperbolic tangent function to establish a nonlinear relationship between the error and the step size. Based on this, the average value of the error signal is used to update the step size. Further, the accumulated error value is multiplied by its average value and added to the input signal energy. Then, the algorithm is normalized by using this value to prevent the algorithm divergence due to the sudden increase in the signal power. The convergence proof of the proposed algorithm is provided in this paper. The simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithm can automatically adjust the parameters. The convergence rate and the steady-state MSE are better than those of other algorithms for both high and low signal-to-noise ratios.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
W.P. Ang, B.F. Boroujeny, A new class of gradient adaptive step-size LMS algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(4), 805–810 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.912925
F. Albu, J. Kadlec, N. Coleman, A. Fagan, The Gauss–Seidel Fast Affine Projection Algorithm. in Signal Processing Systems, (SIPS '02). IEEE Workshop on 16-18 Oct, 2002, pp. 109–114
F. Albu, C. Paleologu, S. Ciochina, New Variable Step Size Affine Projection Algorithms, in 2012 9th International Conference on Communications, COMM 2012–Conference Proceedings, (IEEE, 2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICComm.2012.6262602
T. Aboulnasr, K. Mayyas, A robust variable step-size LMS-type algorithm: analysis and simulations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(3), 631–631 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.558478
A. Benveniste, M. Metivier, P. Priouret, Adaptive Algorithms and Stochastic Approximation (Springer, New York, 2012)
J. Benesty, H. Rey, L.R. Vega et al., A nonparametric VSS NLMS algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 13(10), 581–584 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2006.876323
H.H. Chang, L. Junghsi, A new variable step-size NLMS algorithm and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(4), 2055–2060 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/tsp.2011.2181505
Y.R. Chien, W.J. Tseng, Switching-based variable step-size approach for partial update LMS algorithms. Electron. Lett. 49, 1081–1083 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2013.1762
J.M. Górriz, J. Ramírez, S. Cruces-Alvarez et al., Speech enhancement in discontinuous transmission systems using the constrained-stability least-mean-squares algorithm. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124(6), 36693683 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.3003933
S.L. Gay, S. Tavathia, The fast affine projection algorithm. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 5, 3023–3026 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8644-3_2
S. Guan, Z. Li, Z.H. Ru, New Variable Step-size of l1-LMS Algorithm, in International Conference on Signal Processing Systems, (ACM, 2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/3015166.3015198
L.Y. Jin, Y.R. Chien, Y. Tsao, Rapid converging M-Max partial update least mean square algorithms with new variable step-size methods. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 98(12), 2650–2657 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1587/transfun.e98.a.2650
B. Jalal, X. Yang, Q. Liu, T. Long et al., Fast and robust variable-step-size lms algorithm for adaptive beamforming. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 19(7), 1206–1210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2020.2995244
R.H. Kwong, E.W. Johnston, A variable step-size LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40(7), 1633–1642 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcs.1986.1085982
Z.S. Kui, M.Z. Hong, K.S. Yang, A fast variable step-size LMS algorithm with system identification. IEEE Conf. Ind. Electron. Appl. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/iciea.2007.4318828
K. Kumar, N.V. George, Weibull M-transform least mean square algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107488
E.M. Lobato, O.J. Tobias, R. Seara, Stochastic modeling of the transform-domain εLMS algorithm for correlated Gaussian data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56, 1840–1852 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITS.2006.4433401
M. Li, L. Li, H.M. Tai, Variable step size LMS algorithm based on function control. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 32(6), 3121–3130 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9598-z
W. Mikhael, F. Wu et al., Adaptive filters with individual adaptation of parameters. Circ. Syst. IEEE Trans. (1986). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCS.1986.1085982
V.H. Nascimento, The Normalized LMS Algorithm with Dependent Noise, in Anais do 19° Simpòsio Brasileiro de Telecomunicações Fortaleza, (Brazil, 2001)
S.H. Pauline, D. Samiappan, R. Kumar et al., Variable tap-length non-parametric variable step-size NLMS adaptive filtering algorithm for acoustic echo cancellation. Appl. Acoust. 159, 107074 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.107074
D.T.M. Slock, On the convergence behavior of the LMS and the normalized LMS algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41, 2811–2825 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.236504
K. Shi, X. Ma, A variable-step-size NLMS algorithm using statistics of channel response. Signal Process. 90(6), 2107–2111 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.01.015
B.C. Widrow, M.E. Hoff, Adaptive switching circuits, 1988
G. Wang, H. Zhao, P. Song, Robust variable step-size reweighted zero-attracting least mean M-Estimate algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Exp. Briefs 67(6), 1149–1153 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2019.2928322
K. Zou, X. Zhao, A New Modified Robust Variable Step-Size LMS Algorithm, in 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, 2009, pp 2699–2703. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEA.2009.5138654
J. Zhang, H. Yu, Q. Zhang, Improved variable step-size LMS algorithm based on hyperbolic tangent function. J. Commun. 41(11), 116–123 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review, as well as MJEditor (www.mjeditor.com) for providing English editing services during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
No funding agency is associated with the work mentioned in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Zhao, X. Variable Step-size LMS Algorithm Based on Hyperbolic Tangent Function. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 4415–4431 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02303-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02303-8