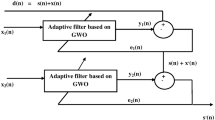
Abstract
Electromyogram (EMG) signal is the electrical form of muscular activity that could be used to diagnose myopathy and neuropathy disorders. Several artefacts are getting imposed on the EMG during the recording process, affecting its performance. This paper proposes a novel noise clampdown method for surface electromyogram signals to employ powerful evolutionary algorithms such as cat swarm optimisation (CSO), binary gravitational search algorithm (BGSA) and spotted hyena optimisation (SHO) for the optimisation purpose of the adaptive filter. The proposed technique has been appraised on records from the standard database, corrupted by baseline wander, electrode motion, power-line noise and different additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) levels. The potency of the proposed method is studied in terms of standard metrics, namely signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), normalised root mean square error, mean squared error (MSE), peak reconstruction error, mean difference and maximum error. Results exemplify that the proposed scheme outpaces the benchmark algorithm-based techniques with an average SNR of 87.618 dB and MSE of 3.91E−10, across different datasets, in contrast to the recently employed noise reduction algorithms at 10 dB AWGN.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Ahirwal, A. Kumar, G.K. Singh, EEG/ERP adaptive noise canceller design with controlled search space (CSS) approach in cuckoo and other optimisation algorithms. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 10(6), 1491–1504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcbb.2013.119
M.K. Ahirwal, A. Kumar, G.K. Singh, Adaptive filtering of EEG/ERP through bounded range artificial bee colony (BR-ABC) algorithm. Digit. Signal Process. 25(1), 164–172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2013.10.019
R.H. Chowdhury, M.B.I. Reaz, M.A.B.M. Ali, A.A.A. Bakar, K. Chellappan, T.G. Chang, Surface electromyography signal processing and classification techniques. Sensors 13, 12431–12466 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/s130912431
L. Demanet, L. Ying, Wave atoms and sparsity of oscillatory patterns. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 23(3), 368–387 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acha.2007.03.003
B. Derrick, P. White, Comparing two samples from an individual likert question. Int. J. Math. Stat. 18(3), 1–13 (2017)
G. Dhiman, V. Kumar, Spotted hyena optimiser: a novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Adv. Eng. Softw. 114, 48–70 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.05.014
C. Elisei-Iliescu, C. Stanciu, C. Paleologu, J. Benesty, C. Anghel, S. Ciochină, Efficient recursive least-squares algorithms for the identification of bilinear forms. Digit. Signal Process. 83, 280–296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2018.09.005
D. Farina, F. Negro, Accessing the neural drive to muscle and translation to neurorehabilitation technologies. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 5, 3–14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/rbme.2012.2183586
A.L. Goldberger, L.A.N. Amaral, L. Glass, J.M. Hausdorff, PCh. Ivanov, R.G. Mark, J.E. Mietus, G.B. Moody, C.-K. Peng, H.E. Stanley, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23), e215–e220 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215
T. Grujic, A. Kuzmanic, Denoising of surface EMG signals: A comparison of wavelet and classical digital filtering procedures. Technol. Healthc. 12(2), 130–135 (2004)
A. Jafarifarmand, M.-A. Badamchizadeh, S. Khanmohammadi, M.A. Nazari, B.M. Tazehkand, Real-time ocular artifacts removal of EEG data using a hybrid ICA-ANC approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 31, 199–210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2016.08.006
S. Jain, M.K. Ahirwal, A. Kumar, V. Bajaj, G.K. Singh, QRS detection using adaptive filters: a comparative study. ISA Trans. 66, 362–375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2016.09.023
L. Janjanam, S.K. Saha, R. Kar, D. Mandal, An efficient identification approach for highly complex nonlinear systems using the evolutionary computing-based Kalman filter. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 138, 153–890 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2021.153890
R.K. Joseph, G. Titus, M.S. Sudhakar, Effective EMG denoising using a hybrid model based on WAT and GARCH. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 45, 305–312 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.05.040
S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis, Adaptive gbest-guided gravitational search algorithm. Neural. Comput. Appl. 25, 1569–1584 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1640-y
P.K. Mohapatra, P.K. Jena, S.K. Bisoi, S.K. Rout, S.P. Panigrahi, Channel equalisation as an optimisation problem, in International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication, Power and Embedded System (SCOPES) (2016), pp. 1158–1163. https://doi.org/10.1109/scopes.2016.7955623
G.B. Moody, W.E. Muldrow, R.G. Mark, A noise stress test for arrhythmia detectors. Comput. Cardiol. 11, 381–384 (1984). https://doi.org/10.13026/c2hs3t
B. Nagasirisha, V.V.K.D.V. Prasad, Noise removal from EMG signal using adaptive enhanced squirrel search algorithm. Fluct. Noise Lett. 19(4), 2050039 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/s021947752050039x
G.R. Naik, S.E. Selvan, H.T. Nguyen, Single-channel EMG classification with ensemble-empirical-mode-decomposition-based ICA for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 24(7), 734–743 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2015.2454503
H.S. Pal, A. Kumar, A. Vishwakarma, M.K. Ahirwal, Electrocardiogram signal compression using tunable-Q wavelet transform and meta-heuristic optimisation techniques. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 78, 103932 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103932
J. Piskorowski, Time-efficient removal of power-line noise from EMG signals using IIR notch filters with non-zero initial conditions. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 33(3), 171–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2013.07.006
M. Rakshit, S. Das, An efficient ECG denoising methodology using empirical mode decomposition and adaptive switching mean filter. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 40, 140–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.09.020
S.K. Saha, S.P. Ghoshal, R. Kar, D. Mandal, Design and simulation of FIR bandpass and bandstop filters using gravitational search algorithm. Memet. Comput. 5(4), 311–321 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-013-0122-6
S.K. Saha, S.P. Ghoshal, R. Kar, D. Mandal, Cat swarm optimisation algorithm for optimal linear phase FIR filter design. ISA Trans. 52(6), 781–794 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2013.07.009
I.-M. Skavhaug, K.R. Lyons, A. Nemchuk, S.D. Muroff, S.S. Joshi, Learning to modulate the partial powers of a single sEMG power spectrum through a novel human-computer interface. Hum. Mov. Sci. 47, 60–69 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2015.12.003
P. Sutha, V. Jayanthi, Fetal electrocardiogram extraction and analysis using adaptive noise cancellation and wavelet transformation techniques. J. Med. Syst. 42, 21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0868-3
N.V. Thakor, Y.-S. Zhu, Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 38(8), 785–794 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1109/10.83591
S. Thongpanja, A. Phinyomark, F. Quaine, Y. Laurillau, C. Limsakul, P. Phukpattaranont, Probability density functions of stationary surface EMG signals in noisy environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 65(7), 1547–1557 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2016.2534378
M.H. Trabuco, M.V.C. Costa, B. Macchiavello, F.A.D.O. Nascimento, S-EMG signal compression in one-dimensional and two-dimensional approaches. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 22(4), 1104–1113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2017.2765922
A.R. Verma, Y. Singh, B. Gupta, Adaptive filtering method for EMG signal using bounded range artificial bee colony algorithm. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 8, 231–238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-017-0056-x
S. Yadav, S.K. Saha, R. Kar, D. Mandal, Optimised adaptive noise canceller for denoising cardiovascular signal using SOS algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 69, 102–830 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102830
S. Yadav, S.K. Saha, R. Kar, D. Mandal, EEG/ERP signal enhancement through an optimally tuned adaptive filter based on marine predators’ algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 73, 103–427 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103427
Y. Zheng, X. Hu, Interference removal from electromyography based on independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 27(5), 887–894 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2019.2910387
Funding
The authors declare that there is no institute/agency funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S., Saha, S.K., Kar, R. et al. Noise Confiscation from sEMG Through Enhanced Adaptive Filtering Based on Evolutionary Computing. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 4096–4128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02302-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02302-9