Abstract
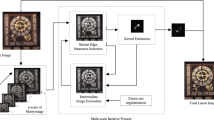
Salient edge selection is a crucial technique to warrant the success of image deblurring. Current edge-based methods mainly focus on the single salient edge without exploiting the rich structural information of different levels of the image. With this in mind, we propose an effective mixed-order salient edge selection for blind image deblurring, i.e., besides the salient edge based on first-order gradient, we further consider combining zero- and second-order information. We find that the finer image structure inscribed at zero-order repairs the important structure missing in the latent image, while the strong structure of salient edges depicted at second-order further enhances the latent image. The union of these three increases the robustness of the intermediate latent image, which leads to an accurate estimation of the kernel. Also, the inclusion of the gradient L0-norm improves the quality of the recovery by preserving the favorable edges and removing the detrimental details. Experimental results show that the proposed method is much faster than the prior-based ones, and it provides more satisfactory recovery than the single salient edge-based approaches (e.g., in terms of error ratio, PSNR, SSIM, SSDE). Compared with state-of-the-art works, our method achieves better results on quantitative datasets and real-world images.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
N. Apostoloff, A. Fitzgibbon, Bayesian video matting using learnt image priors, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2004), pp. 407–414
L. Alvarez, L. Mazorra, Signal and image restoration using shock filters and anisotropic diffusion. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31(4), 590–605 (1994)
L. Chen, F. Fang, T. Wang, G. Zhang, Blind image deblurring with local maximum gradient prior, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019), pp. 1742–1750
L. Chen, F. Fang, J. Zhang, J. Liu, G. Zhang, OID: outlier identifying and discarding in blind image deblurring, in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2020), pp. 598–613
S. Cho, S. Lee, Fast motion deblurring. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(5), 1–8 (2009)
T.F. Chan, C.-K. Wong, Total variation blind deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 7(3), 370–375 (1998)
S. Cho, J. Wang, S. Lee, Handling outliers in non-blind image deconvolution, in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2011), pp. 495–502
W. Cai, L. Zuo, Zhang, Dark and bright channel prior embedded network for dynamic scene deblurring. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 6885–6897 (2020)
R. Fergus, B. Singh, A. Hertzmann, S.T. Roweis, W.T. Freeman, Removing camera shake from a single photograph. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(3), 787–794 (2006)
X. Guo, Y. Li, J. Ma, H. Ling, Mutually guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(3), 694–707 (2020)
X. Ge, J. Tan, L. Zhang, Blind image deblurring using a non-linear channel prior based on dark and bright channels. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 6970–6984 (2021)
X. Ge, J. Tan, L. Zhang, Y. Qian, Blind image deconvolution via salient edge selection and mean curvature regularization. Signal Process. 190, 108336 (2022)
Z. Hu, S. Cho, J. Wang, M.-H. Yang, Deblurring low-light images with light streaks, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014), pp. 3382–3389
Z. Hu, M.H. Yang, Good regions to deblur, in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2012), pp. 59–72
N. Joshi, R. Szeliski, D. J. Kriegman, PSF estimation using sharp edge prediction, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2008), pp. 1–8
O. Kupyn, V. Budzan, M. Mykhailych, D. Mishkin, J. Matas, DeblurGAN: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018), pp. 8183–8192
D. Krishnan, R. Fergus, Fast image deconvolution using hyper-Laplacian priors, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) (2009), pp. 1033–1041.
R. Köhler, M. Hirsch, B. Mohler, B. Schölkopf, S. Harmeling, Recording and playback of camera shake: benchmarking blind deconvolution with a real-world database, in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2012), pp. 27–40
T. H. Kim, K. M. Lee, Segmentation-free dynamic scene deblurring, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014), pp. 2766–2773
D. Krishnan, T. Tay, R. Fergus, Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2011), pp. 233–240
W.-S. Lai, J.-J. Ding, Y.-Y. Lin, Y.-Y. Chuang, Blur kernel estimation using normalized color-line prior, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2015), pp. 64–72
W.S. Lai, J.B. Huang, Z. Hu, N. Ahuja, M.H. Yang, A comparative study for single image blind deblurring, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2016), pp. 1701–1709
L. Li, J. Pan, W.-S. Lai, C. Gao, N. Sang, M.-H. Yang, Blind image deblurring via deep discriminative priors. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 127(8), 1025–1043 (2019)
A. Levin, Y. Weiss, F. Durand, W. T. Freeman, Understanding and evaluating blind deconvolution algorithms, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2009), pp. 1964–1971
A. Levin, Y. Weiss, F. Durand, W. T. Freeman, Efficient marginal likelihood optimization in blind deconvolution, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2011), pp. 2657–2664
J. Liu, M. Yan, T. Zeng, Surface-aware blind image deblurring. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(3), 1041–1055 (2021)
J. Mairal, F. Bach, J. Ponce, G. Sapiro, A. Zisserman, Non-local sparse models for image restoration, in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2009), pp. 2272–2279
T. Michaeli, M. Irani, Blind deblurring using internal patch recurrence, in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2014), pp. 783–798
S. Nah, T. H. Kim, K. M. Lee, Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017), pp. 3883–3891
S. Osher, L.I. Rudin, Feature-oriented image enhancement using shock filters. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27(4), 919–940 (1990)
D. Perrone, P. Favaro, Total variation blind deconvolution: The devil is in the details, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014), pp. 2909–2916
J. Pan, Z. Hu, Z. Su, Deblurring face images with exemplars, in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2014), pp. 47–62
J. Pan, Z. Hu, Z. Su, M.-H. Yang, Deblurring text images via L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014), pp. 2901–2908
J. Pan, Z. Hu, Z. Su, M.H. Yang, L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior for deblurring text images and beyond. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(2), 342–355 (2017)
J. Pan, R. Liu, Z. Su, X. Gu, Kernel estimation from salient structure for robust motion deblurring. Signal Process. Image Commun. 28(9), 1156–1170 (2013)
J. Pan, D. Sun, H. Pfister, M.-H. Yang, Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2016), pp. 1628–1636
S. Roth, M. J. Black, Fields of experts: a framework for learning image priors, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2005), pp. 860–867
W. Ren, X. Cao, J. Pan, X. Guo, W. Zuo, M.-H. Yang, Image deblurring via enhanced low-rank prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(7), 3426–3437 (2016)
R. M. Rameshan, S. Chaudhuri, R. Velmurugan, Joint MAP estimation for blind deconvolution: when does it work? ACM Int. Conf. Proc. Ser. 50 (2012)
Y. Romano, M. Elad, P. Milanfar, The little engine that could: regularization by denoising (RED). SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 10(4), 1804–1844 (2017)
L. Sun, S. Cho, J. Wang, J. Hays, Edge-based blur kernel estimation using patch priors, in IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP) (2013), pp. 1–8
J. Sun, W. Cao, Z. Xu, J. Ponce, Learning a convolutional neural network for non-uniform motion blur removal, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2015), pp. 769–777
C.J. Schuler, M. Hirsch, S. Harmeling, B. Schölkopf, Learning to deblur. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(7), 1439–1451 (2016)
X. Tao, H. Gao, X. Shen, J. Wang, J. Jia, Scale-recurrent network for deep image deblurring, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2018), pp. 8174–8182
M. F. Tappen, B. C. Russell, W. T. Freeman, Exploiting the sparse derivative prior for super-resolution, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2003
Y. Tang, Y. Xue, Y. Chen, L. Zhou, Blind deblurring with sparse representation via external patch priors. Digit. Signal Proc. 78, 322–331 (2018)
S.V. Venkatakrishnan, C.A. Bouman, B. Wohlberg, Plug-and play priors for model-based reconstruction, in IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP) (2013).
F. Wen, R. Ying, Y. Liu, P. Liu, T.-K. Truong, A simple local minimal intensity prior and an improved algorithm for blind image deblurring. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 31(8), 2923–2937 (2021)
Z. Xu, H. Chen, Z. Li, Blind image deblurring using group sparse representation. Digit. Signal Proc. 102, 102736 (2020)
L. Xu, J. Jia, Two-phase kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring, in European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2010), pp. 157–170
L. Xu, C. Lu, Y. Xu, J. Jia, Image smoothing via L0 gradient minimization. ACM Trans. Graph. 30(6), 1–12 (2011)
L. Xu, S. Zheng, J. Jia, Unnatural L0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2013), pp. 1107–1114
Y. Yan, W. Ren, Y. Guo, R. Wang, X. Cao, Image deblurring via extreme channels prior, in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017), pp. 4003–4011
Y. Zhang, W. Li, Z. Li, T. Ning, Dual attention per-pixel filter network for spatially varying image deblurring. Digit. Signal Proc. 113, 103008 (2021)
W. Zuo, D. Ren, D. Zhang, S. Gu, L. Zhang, Learning iteration wise generalized shrinkage–thresholding operators for blind deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(4), 1751–1764 (2016)
D. Zoran, Y. Weiss, From learning models of natural image patches to whole image restoration, in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2011), pp. 479–486
H. Zhang, J. Yang, Y. Zhang, N. M. Nasrabadi, T. S. Huang, Close the loop: joint blind image restoration and recognition with sparse representation prior, in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (2011), pp. 770–777
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the reviewers for their helpful suggestions which greatly improve the clarity of the paper. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62172135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, D., Tan, J. & Ge, X. Image Deconvolution Using Mixed-Order Salient Edge Selection. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 3902–3925 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02283-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02283-1