Abstract
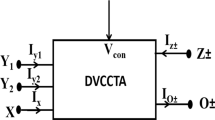
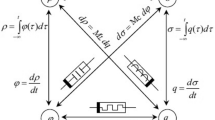
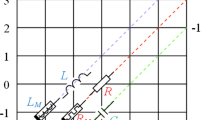
The aim of this work is to report a very compact floating memelement emulator that can realize two memelements (memristor and meminductor). Both realized memelements can be used in incremental as well as the decremental mode of operation. The presented emulator is based on a single dual-output operational transconductance amplifier and a voltage differencing inverted buffered amplifier along with two grounded passive elements and two external MOS transistors only. The desired memelement function can be achieved by just selecting a grounded impedance Z1 as C1 and R1. Overall CMOS implementation of the proposed circuit requires just twenty CMOS transistors. The emulator has a fully symmetric floating structure (incoming and outgoing currents are exactly equal and opposite in magnitude) and provides complete electronic control over the realized memelements behavior (over both time-dependent and time-independent parts). The developed circuit can be validated through presented simulation results generated in PSPICE using the 0.18 µm CMOS technology. The results verify that behavior of both the realized memelements can be obtained satisfactorily up to MHz range of frequency. The applicability of the realized meminductor behavior is shown in the electrical equivalent network designed for mimicking an Amoeba response for the temperature change, while the emulated memristor function has been validated by employing it in the exhibition of associative learning behavior using the depicted circuit. The given simulator circuit is also implemented using commercial ICs and simulation results are presented.



































Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Y. Babacan, An operational transconductance amplifier-based memcapacitor and meminductor. Istanbul Univ. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 18, 36 (2018)
H. Bao, A. Hu, W. Liu, B. Bao, Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 31, 502 (2020)
K. Bhardwaj, M. Srivastava, Floating memristor and inverse memristor emulation configurations with electronic/resistance controllability. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 14, 1065 (2020)
K. Bhardwaj, M. Srivastava, Wide-band compact floating memristor emulator configuration with electronic/resistive adjustability. Microelectron. J. 117, 105284 (2021)
K. Bhardwaj, M. Srivastava, New electronically adjustable memelement emulator for realizing the behavior of fully floating meminductor and memristor. Microelectron. J. 114, 105126 (2021)
D. Biolek, R. Senani, V. Biolkova, Z. Kolka, Active elements for analog signal processing: classification, review and new proposals. Radioengineering 17, 15–32 (2008)
K. Bhardwaj, M. Srivastava, New grounded passive elements-based external multiplier-less memelement emulator to realize the floating meminductor and memristor. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 110, 409 (2022)
K. Bhardwaj, M. Srivastava, New multiplier-less compact tunable charge-controlled memelement emulator using grounded passive elements, circuits. Syst. Signal Process. 41, 2429 (2022)
Y. Babacan, F. Kacar, FCS based memristor emulator with associative learning circuit application. Istanbul Univ. J. Elect. Electron. Eng. 17, 3433–3437 (2017)
L. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit elementI. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507 (1971)
Z.G. Çam Taşkıran, M. Sağbaş, U.E. Ayten, H. Sedef, A new universal mutator circuit for memcapacitor and meminductor elements. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 119, 153180 (2020)
M. Chen, M. Sun, H. Bao, Y. Hu, B. Bao, Flux-charge analysis of two-memristor-based Chua’s circuit: dimensionality decreasing model for detecting extreme multistability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67, 2197 (2020)
M. Di Ventra, Y.V. Pershin, L.O. Chua, Circuit elements with memory: memristors, memcapacitors, and meminductors. Proc. IEEE 97, 1717 (2009)
S. Gupta, S.K. Rai, New grounded and floating decremental/incremental memristor emulators based on CDTA and its application. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 113, 773 (2020)
M. Gupta, R. Srivastava, U. Singh, Low-voltage low-power FGMOS based VDIBA and its application as universal flter. Microelectron. J. 46, 125 (2015)
M. Itoh, L.O. Chua, Duality of memristor circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23, 1330001 (2013)
H. Kim, M.P. Sah, C. Yang, S. Cho, L.O. Chua, Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 59, 2422 (2012)
K. Kumar, B.C. Nagar, New tunable resistorless grounded meminductor emulator. J. Comput. Electron. 20, 1452 (2021)
M. Konal, F. Kacar, Electronically tunable meminductor based on OTA. AEU - Int. J. Electron. Commun. 126, 153391 (2020)
Y. Liu, H.H.-C. Iu, Novel floating and grounded memory interface circuits for constructing mem-elements and their applications. IEEE Access 8, 114761 (2020)
Y.V. Pershin, M. Di Ventra, Emulation of floating memcapacitors and meminductors using current conveyors. Electron. Lett. 47, 243 (2011)
I. Pal, V. Kumar, N. Aishwarya, A. Nayak, A. Islam, A VDTA-based robust electronically tunable memristor emulator circuit. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 104, 47 (2020)
P.B. Petrović, Tunable flux-controlled floating memristor emulator circuits. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 13, 479 (2019)
P.B. Petrović, Simple flux-controlled grounded memristor emulator circuits based on current follower. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 108, 215 (2021)
S.S. Prasad, P. Kumar, R.K. Ranjan, Resistorless memristor emulator using CFTA and its experimental verification. IEEE Access 9, 64065 (2021)
Y. Pershin, S. La Fontaine, M. Di Ventra, Memristive model of amoeba learning. Nat. Preced. 80, 021926-1 (2008)
F.J. Romero, M. Escudero, A. Medina-Garcia, D.P. Morales, N. Rodriguez, Meminductor emulator based on a modified Antoniou’s gyrator circuit. Electronics 9, 1407 (2020)
N. Raj, R.K. Ranjan, F. Khateb, M. Kumngern, Mem-elements emulator design with experimental validation and its application. IEEE Access 9, 69860 (2021)
R.K. Ranjan, S. Sagar, S. Roushan, B. Kumari, N. Rani, F. Khateb, High frequency floating memristor emulator and its experimental results. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 13, 292 (2019)
A. Raj, S. Singh, P. Kumar, Dual mode, high frequency and power efficient grounded memristor based on OTA and DVCC. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 110, 81 (2022)
M.P. Sah, R.K. Budhathoki, C. Yang, H. Kim, Mutator-based meminductor emulator for circuit applications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33, 2363 (2014)
M.P. Sah, R.K. Budhathoki, C. Yang, H. Kim, Charge controlled meminductor emulator. JSTS J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 14, 750 (2014)
H. Sozen, U. Cam, A novel floating/grounded meminductor emulator. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 29, 2050247 (2020)
A. Singh, S.K. Rai, Novel meminductor emulators using operational amplifiers and their applications in chaotic oscillators. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 30 (2021)
A. Singh, S.K. Rai, VDCC-based memcapacitor/meminductor emulator and its application in adaptive learning circuit. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 45, 1151 (2021)
O.G. Sokmen, S.A. Tekin, H. Ercan, M. Alci, A novel design of low-voltage VDIBA and filter application. Elektron. Ir Elektrotechnika 22, 1151 (2016)
P. Thongdit, S. Chunchay, K. Angkeaw, A meminductor emulator based on flux-controlled model using field programmable analog array, in 2020 17th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (IEEE, 2020), pp. 51–54
W. Tangsrirat, Synthetic grounded lossy inductance simulators using single VDIBA. IETE J. Res. 63, 134 (2017)
J. Vista, A. Ranjan, High frequency meminductor emulator employing VDTA and its application. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 39, 2020 (2020)
F.Z. Wang, L.O. Chua, X. Yang, N. Helian, R. Tetzlaff, T. Schmidt, C. Li, J.M.G. Carrasco, W. Chen, D. Chu, Adaptive neuromorphic architecture neural networks. Neural Netw. 45, 111 (2013)
B. Xu, G. Wang, H.H.-C. Iu, S. Yu, F. Yuan, A memristor–meminductor-based chaotic system with abundant dynamical behaviors. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 765 (2019)
Z.Y. Yin, H. Tian, G.H. Chen, L.O. Chua, What are Memristor, Memcapacitor, and Meminductor? IEEE Trans Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 62, 402 (2015)
F. Yuan, Y. Deng, Y. Li, A multistable generalized meminductor with coexisting stable pinched hysteresis loops. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 30, 2050023 (2020)
D. Yu, X. Zhao, T. Sun, H.H.C. Iu, T. Fernando, A simple floating mutator for emulating memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67, 1334 (2020)
F. Yuan, Y. Deng, Y. Li, G. Wang, The amplitude, frequency and parameter space boosting in a memristor–meminductor-based circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 389 (2019)
N. Yadav, S.K. Rai, R. Pandey, New grounded and floating memristor emulators using OTA and CDBA. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 48, 1154 (2020)
A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, F. Kacar, An electronically controllable, fully floating memristor based on active elements: DO-OTA and DVCC. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 123, 153315 (2020)
N. Yadav, S.K. Rai, R. Pandey, Novel memristor emulators using fully balanced VDBA and grounded capacitor. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 45, 229 (2021)
Q. Zhao, C. Wang, X. Zhang, A universal emulator for memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor and its chaotic circuit. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 29, 013141 (2019)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhardwaj, K., Srivastava, M. Compact Floating Dual Memelement Emulator Employing VDIBA and OTA: A Novel Realization. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 5933–5967 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02067-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02067-7