Abstract
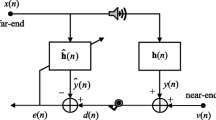
Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation (SAEC) applications of adaptive filters are complex compared to monophonic AEC due to the presence of an additional acoustic channel. In long room impulse response, SAEC is carried out with the help of more than one adaptive filter, each having hundreds to thousands of filter coefficients. A large number of filter weights result in degraded convergence and enhances filter design complexity. Multiple sub-filters (MSF) and variable tap-length (VT) algorithms are independently proposed for SAEC scenarios to address these issues. The MSF-based design improves the convergence; on the other hand, the VT algorithm optimizes the weight requirement for adaptive filters. Pseudo-optimum filter order is a common phenomenon in the VT algorithm, which results in undermodelling in SAEC applications. This paper analyses the convergence, mean-square convergence, and stability of an undermodelled final error VT-MSF-SAEC (FE-MSF-SAEC) and VT-MSF-SAEC. The mathematical analysis and the supported simulation with three variants of inputs represent the effect of pseudo-fractional undermodelling for a VT-MSF-SAEC.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Azarnia, Diffusion fractional tap-length algorithm with adaptive error width and step-size. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 41(1), 321–345 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01778-7
A. Barik, G. Murmu, T.P. Bhardwaj, R. Nath, LMS adaptive multiple sub-filters based acoustic echo cancellation, in: 2010 International Conference on Computer and Communication Technology (ICCCT) (2010), pp. 824–827. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCT.2010.5640392
J. Benesty, Y. Huang, Adaptive Signal Processing: Applications to Real-World Problems (Springer, Berlin, 2013)
J. Benesty, D.R. Morgan, M.M. Sondhi, A better understanding and an improved solution to the specific problems of stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 6(2), 156–165 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/89.661474
C. Breining, P. Dreiscitel, E. Hansler, A. Mader, B. Nitsch, H. Puder, T. Schertler, G. Schmidt, J. Tilp, Acoustic echo control. An application of very-high-order adaptive filters. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 16(4), 42–69 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/79.774933
S. Burra, A. Kar, Nonlinear stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation using sub-filter based adaptive algorithm. Digit. Signal Process. 121, 103323 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103323
M. Djendi, A. Bounif, Performance analysis of under-modelling stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation by adaptive filtering LMS algorithm. Comput. Electr. Eng. 38(6), 1579–1594 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2012.06.008
A. Feuer, E. Weinstein, Convergence analysis of LMS filters with uncorrelated gaussian data. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 33(1), 222–230 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164493
Y. Gong, C.F. Cowan, An LMS style variable tap-length algorithm for structure adaptation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(7), 2400–2407 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2005.849170
Y. Gu, K. Tang, H. Cui, W. Du, Convergence analysis of a deficient-length LMS filter and optimal-length sequence to model exponential decay impulse response. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 10(1), 4–7 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2002.806704
S. Haykin, Adaptive Filter Theory by Simon Haykin (Pearson Education India, New Delhi, 2002)
A. Kar, M. Chandra, Pseudo-fractional tap-length learning based applied soft computing for structure adaptation of LMS in high noise environment, in: Soft Computing Techniques in Engineering Applications (Springer, Berlin, 2014), pp. 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04693-8_8
A. Kar, M. Chandra, An improved variable structure adaptive filter design and analysis for acoustic echo cancellation. Radioengineering 24(1), 252–261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.13164/re.2015.0252
A. Kar, M. Chandra, Performance evaluation of a new variable tap-length learning algorithm for automatic structure adaptation in linear adaptive filters. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69(1), 253–261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2014.09.010
A. Kar, M. Swamy, Convergence and steady state analysis of a tap-length optimization algorithm for linear adaptive filters. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 70(9), 1114–1121 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2016.05.010
A. Kar, M. Swamy, Tap-length optimization of adaptive filters used in stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. Signal Process. 131, 422–433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.09.003
A. Kar, T. Padhi, B. Majhi, M. Swamy, Analysing the impact of system dimension on the performance of a variable-tap-length adaptive algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 150, 207–215 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.02.015
A. Kar, A. Anand, M. Swamy, Analysing the impact of system dimension on the performance of a variable-tap-length adaptive algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 158, 107043 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.107043
R. Nath, Adaptive echo cancellation based on a multipath model of acoustic channel. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(4), 1673–1698 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9529-4
C. Schüldt, F. Lindstrom, H. Li, I. Claesson, Adaptive filter length selection for acoustic echo cancellation. Signal Process. 89(6), 1185–1194 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.12.023
R.N. Sharma, A. Chaturvedi, G. Sharma, Tracking behaviour of acoustic echo canceller using multiple sub-filters, in: 2006 14th European Signal Processing Conference (IEEE, 2006), pp. 1–5
M.M. Sondhi, D.R. Morgan, J.L. Hall, Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation–an overview of the fundamental problem. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2(8), 148–151 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1109/97.404129
R. Vanamadi, A. Kar, Feedback cancellation in digital hearing aids using convex combination of proportionate adaptive algorithms. Appl. Acoust. 182, 108175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108175
R. Vanamadi, A. Kar, A. Anand, B. Majhi, M. Swamy, Analyzing the effects of pseudo-optimum tap-length for an MSF-based acoustic echo canceller. Appl. Acoust. 150, 198–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.02.014
R. Vanamadi, A. Kar, S. Burra, A. Anand, B. Majhi, Convergence performance evaluation of MSF-based LMS adaptive algorithm, in: 2019 16th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON) (2019), pp. 597–600. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTI-CON47248.2019.8955136
Y. Wei, Z. Yan, Variable tap-length LMS algorithm with adaptive step size. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(7), 2815–2827 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0438-9
B. Widrow, S.D. Stearns, Adaptive Signal Processing (Pearson Education, New Delhi, 2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanamadi, R., Kar, A. Convergence Analysis for an Undermodelled Variable Tap-Length MSF-Based Stereophonic Acoustic Echo Canceller. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 5226–5253 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02033-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02033-3