Abstract
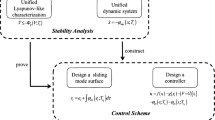
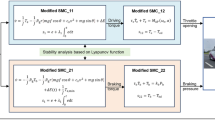
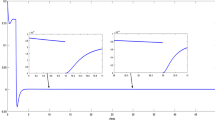
This paper investigates the problem of sliding mode control (SMC) for a class of discrete-time stochastic systems subject to hybrid cyber attacks. Both stochastic nonlinearities and norm-bounded parameter uncertainties are introduced into the system, which occur according to mutually independent Bernoulli-distributed white noise sequences. Moreover, hybrid cyber attacks consisting of denial-of-service attack and deception attack are considered in the transmission channel. By employing the Lyapunov stability theory, sufficient conditions are established for guaranteeing the stability of the state trajectory in the specified sliding surface. Meanwhile, an SMC law is given to ensure the reachability of the specified sliding surface. Finally, a simulation example is put forward to verify the effectiveness of the proposed theoretical results.






Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
All MATLAB codes used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
S. Amin, G.A. Schwartz, S. Shankar Sastry, Security of interdependent and identical networked control systems. Automatica 49(1), 186–192 (2013)
G.K. Befekadu, V. Gupta, P.J. Antsaklis, Risk-sensitive control under Markov modulated denial-of-service (DoS) attack strategies. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(12), 3299–3304 (2015)
B. Chen, Y. Niu, Y. Zou, Security control for Markov jump system with adversarial attacks and unknown transition rates via adaptive sliding mode technique. J. Frankl. Inst. 356(6), 3333–3352 (2019)
B. Chen, Y. Niu, Y. Zou, Sliding mode control for stochastic Markovian jumping systems subject to successive packet losses. J. Frankl. Inst. 351(4), 2169–2184 (2014)
P. Derler, E.A. Lee, A.S. Vincentelli, Modeling cyber-physical systems. Proc. IEEE 100(1), 13–28 (2012)
D. Ding, Q. Han, Z. Wang, X. Ge, A survey on model-based distributed control and filtering for industrial cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 15(5), 2483–2499 (2019)
D. Ding, Z. Wang, B. Shen, G. Wei, Event-triggered consensus control for discrete-time stochastic multi-agent systems: the input-to-state stability in probability. Automatica 62, 284–291 (2015)
D. Ding, Z. Wang, Q. Han, G. Wei, Security control for discrete-time stochastic nonlinear systems subject to deception attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 48(5), 779–789 (2018)
D. Ding, Z. Wang, J. Lam, B. Shen, Finite-horizon \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) control for discrete time-varying systems with randomly occurring nonlinearities and fading measurements. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(9), 2488–2493 (2015)
H. Dong, Z. Wang, S. Ding, H. Gao, Finite-horizon estimation of randomly occurring faults for a class of nonlinear time-varying systems. Automatica 50(12), 3182–3189 (2014)
X. Fan, Q. Zhang, J. Ren, Event-triggered sliding mode control for discrete-time singular system. IET Control Theory Appl. 12(17), 2390–2398 (2018)
W. Gao, Y. Wang, A. Homaifa, Discrete-time variable structure control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 42(2), 117–122 (1995)
X. Ge, Q. Han, Consensus of multiagent systems subject to partially accessible and overlapping Markovian network topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(8), 1807–1819 (2017)
X. Ge, F. Yang, Q. Han, Distributed networked control systems: a brief overview. Inf. Sci. 380, 117–131 (2017)
X. Guan, B. Yang, C. Chen, W. Dai, Y. Wang, A comprehensive overview of cyber-physical systems: from perspective of feedback system. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 3(1), 1–14 (2016)
J. Hu, Z. Wang, D. Chen, F.E. Alsaadi, Estimation, filtering and fusion for networked systems with network-induced phenomena: new progress and prospects. Inf. Fusion 31, 65–75 (2016)
J. Hu, Z. Wang, H. Gao, L.K. Stergioulas, Robust sliding mode control for discrete stochastic systems with mixed time delays, randomly occurring uncertainties, and randomly occurring nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(7), 3008–3015 (2012)
M. Hu, J. Cao, A. Hu, Mean square exponential stability for discrete-time stochastic switched static neural networks with randomly occurring nonlinearities and stochastic delay. Neurocomputing 129, 476–481 (2014)
C. Hua, J. Chen, X. Guan, Fractional-order sliding mode control of uncertain QUAVs with time-varying state constraints. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 1347–1360 (2019)
T.H. Lee, J.H. Park, Z.G. Wu, S.C. Lee, D.H. Lee, Robust \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) decentralized dynamic control for synchronization of a complex dynamical network with randomly occurring uncertainties. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(1), 559–570 (2012)
J. Liu, L. Wei, X. Xie, E. Tian, S. Fei, Quantized stabilization for T-S fuzzy systems with hybrid-triggered mechanism and stochastic cyber-attacks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(6), 3820–3834 (2018)
J. Liu, Y. Gu, X. Xie, D. Yue, J.H. Park, Hybrid-driven-based \(\cal{H} _{\infty }\) control for networked cascade control systems with actuator saturations and stochastic cyber attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(12), 2452–2463 (2019)
J. Liu, Y. Gu, L. Zha, Y. Liu, J. Cao, Event-triggered \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) load frequency control for multiarea power systems under hybrid cyber attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(8), 1665–1678 (2019)
L. Liu, L. Ma, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Bo, Sliding mode control for nonlinear Markovian jump systems under denial-of-service attacks. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 7(6), 1638–1648 (2020)
S. Liu, G. Wei, Y. Song, Y. Liu, Extended Kalman filtering for stochastic nonlinear systems with randomly occurring cyber attacks. Neurocomputing 207, 708–716 (2016)
S. Liu, Y. Liu, S. Li, B. Xu, \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) control for time-varying cyber-physical system under randomly occurring hybrid attacks: the output feedback case. IEEE Access 8, 60780–60789 (2020)
Y. Liu, A. Liu, X. Liu, M. Ma, A trust-based active detection for cyber-physical security in industrial environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 15(12), 6593–6603 (2019)
Z. Liu, L. Zhao, H. Xiao, C. Gao, Adaptive \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) integral sliding mode control for uncertain singular time-delay systems based on observer. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36, 4365–4387 (2017)
Y. Mo, B. Sinopoli, On the performance degradation of cyber-physical systems under stealthy integrity attacks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 61(9), 2618–2624 (2016)
Y. Mo, B. Sinopoli, Secure control against replay attacks, in 47th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton). (IEEE, Monticello, 2009), pp. 911–918
Y. Niu, D.W.C. Ho, X. Wang, Robust \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) control for nonlinear stochastic systems: a sliding-mode approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 53(7), 1695–1701 (2008)
Y. Niu, D.W.C. Ho, Design of sliding mode control subject to packet losses. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(11), 2623–2628 (2010)
Z. Pang, G. Liu, Z. Dong, Secure networked control systems under denial of service attacks. IFAC Proc. 44(1), 8908–8913 (2011)
C.D. Persis, P. Tesi, Input-to-state stabilizing control under denial-of-service. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(11), 2930–2944 (2015)
I.R. Petersen, B.D.O. Anderson, E.A. Jonckheere, A first principles solution to the non-singular \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) control problem. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 1(3), 171–185 (1991)
A. Pisano, E. Usai, Sliding mode control: a survey with applications in math. Math. Comput. Simul. 81(5), 954–979 (2011)
W. Qi, X. Yang, C.K. Ahn, J. Cao, J. Cheng, Input–output finite-time sliding-mode control for T-S fuzzy systems with application. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2954854
H. Shen, Z. Wu, J.H. Park, Reliable mixed passive and filtering for semi-Markov jump systems with randomly occurring uncertainties and sensor failures. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 25(17), 3231–3251 (2015)
B. Tang, L.D. Alvergue, G. Gu, Secure networked control systems against replay attacks without injecting authentication noise, in American Control Conference (ACC). (IEEE, Chicago, 2015), pp. 6028–6033
J. Wang, Y. Song, S. Liu, S. Zhang, Security in \(\cal{H}_{2}\)-sense for polytopic uncertain systems with attacks based on model predictive control. J. Frankl. Inst. 353(15), 3769–3785 (2016)
Y. Wang, J. Lu, J. Liang, Security control of multiagent systems under denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3026083
Z. Wang, L. Li, H. Sun, C. Zhu, X. Xu, Dynamic output feedback control of cyber-physical systems under DoS attacks. IEEE Access 7, 181032–181040 (2019)
Z. Wang, B. Shen, X. Liu, \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) filtering with randomly occurring sensor saturations and missing measurements. Automatica 48(3), 556–562 (2012)
C. Wu, L. Wu, J. Liu, Z. Jiang, Active defense-based resilient sliding mode control under denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensic Secur. 15, 237–249 (2020)
C. Yang, J. Xia, J. Park, H. Shen, J. Wang, Sliding mode control for uncertain active vehicle suspension systems: an event-triggered \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) control scheme. Nonlinear Dyn. 103, 3209–3221 (2020)
F. Yang, Z. Wang, Y.S. Hung, M. Gani, \(\cal{H}_{\infty }\) control for networked systems with random communication delays. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 51(3), 511–518 (2006)
D. Yao, M. Liu, H. Li, H. Ma, Robust adaptive sliding mode control for nonlinear uncertain neutral Markovian jump systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35, 2741–2761 (2016)
Y. Yuan, H. Yuan, D.W.C. Ho, L. Guo, Resilient control of wireless networked control system under denial-of-service attacks: a cross-layer design approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(1), 48–60 (2020)
X. Zhao, C. Liu, E. Tian, Finite-horizon tracking control for a class of stochastic systems subject to input constraints and hybrid cyber attacks. ISA Trans. 104, 93–100 (2020)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61973137 (by Jing Chen and Manfeng Hu) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20181342 (by Aihua Hu and Manfeng Hu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC and MH contributed to the conception of the study; JC and JZ performed the MATLAB experiment; JC, JC, AH and MH contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; JC and MH performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; JZ, JC and AH helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Zhou, J., Chen, J. et al. Sliding Mode Control for Discrete-Time Systems with Randomly Occurring Uncertainties and Nonlinearities Under Hybrid Cyber Attacks. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 5864–5885 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01744-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01744-3