Abstract
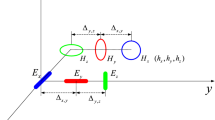
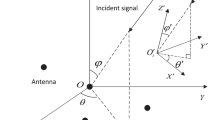
The problem of DOA and polarization parameter estimation is considered in this paper from a perspective of sparse reconstruction. We present a novel off-grid hierarchical block-sparse Bayesian method for DOA and polarization parameter estimation to improve the estimation accuracy. Firstly, an off-grid model is formulated via the first-order Taylor expansion of the source steering vector. Then, a block-sparse vector is constructed based on sparse Bayesian inference, on which a two-layer hierarchical prior is imposed to promote block sparsity and internal sparsity simultaneously. Finally, the variables and model parameters are updated alternately by adopting the variational Bayesian approximation. In addition, the Cramer–Rao bound for DOA and polarization estimation, the convergence property and the computational complexity analysis of the proposed method are derived. Compared with the existing sparse reconstruction methods and the traditional subspace-based methods, the proposed method can achieve higher estimation accuracy. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness and notable performance of the proposed method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Beizuo, X. Xiong, Z. Xiaofei, DOA and polarization estimation with reduced-dimensional MUSIC algorithm for L-shaped electromagnetic vector sensor array, IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), pp. 61-64 (2019)
H. Chen, W. Wang, W. Liu, Joint DOA, range, and polarization estimation for rectilinear sources with a COLD array. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 8(5), 1398–1401 (2019)
W. Dong, M. Diao, The resolving power analysis of a distributed polarization-sensitive array. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(9), 4040–4055 (2019)
Y.C. Eldar, P. Kuppinger, H. Bolcskei, Block-sparse signals: uncertainty relations and efficient recovery. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(6), 3042–3054 (2010)
S. Ghofrani, M.G. Amin, Y.D. Zhang, High-resolution direction finding of non-stationary signals using matching pursuit. Sig. Process. 93(12), 3466–3478 (2013)
J. He, Z. Zhang, T. Shu et al., Direction finding of multiple partially polarized signals with a nested cross-diople array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 16, 1679–1682 (2017)
J. He, Z. Zhang, T. Shu et al., Joint angle–frequency estimation with spatiotemporal nested sampling. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 11(9), 1373–1378 (2017)
Y. Hua, A pencil-MUSIC algorithm for finding two-dimensional angles and polarizations using crossed dipoles. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 41(3), 370–376 (1993)
T.S. Jaakkola, Y. Qi, Parameter expanded variational Bayesian methods. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 19, 1097–1104 (2007)
G.Z. Karabulut, T. Kurt, A. Yongaçoglu, Estimation of directions of arrival by matching pursuit (EDAMP). EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2, 197–205 (2005)
H. Krim, M. Viberg, Two decades of array signal processing research: the parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 13, 67–94 (1992)
B. Li, W. Bai, G. Zheng et al., BSBL-based DOA and polarization estimation with linear spatially separated polarization sensitive array. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 109(3), 2051–2065 (2019)
C.H. Lin, W.H. Fang, Efficient estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance technique-based algorithm with automatic pairing for two-dimensional angle and polarisation estimation using crossed dipoles. IET Signal Proc. 8(4), 309–319 (2013)
Z. Liu, DOA and polarization estimation via signal reconstruction with linear polarization-sensitive arrays. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 28(6), 1718–1724 (2015)
Z.Q. Luo, P. Tseng, On the convergence of the coordinate descent method for convex differentiable minimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 72(1), 7–35 (1992)
S. Miron, N. Le Bihan, J.I. Mars, Vector-sensor MUSIC for polarized seismic sources localization. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. 2005, 74–84 (2005)
S. Miron, N. Le Bihan, J.I. Mars, Quaternion-MUSIC for vector-sensor array processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(4), 1218–1229 (2006)
A. Nehorai, E. Paldi, Vector-sensor array processing for electromagnetic source localization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 42(2), 376–398 (1994)
P. Stoica, A. Nehorai. MUSIC, maximum likelihood and Cramer-Rao bound, in International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing ICASSP-88, IEEE, pp. 2296–2299 (1988)
X. Sun, R. Zhou, K. Su, et al, Bayesian compressive spectrum sensing joint DOA estimation and polarization signal processing, in 2017 20th International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC). IEEE, pp. 579–584 (2017)
J.W. Tao, Performance analysis for interference and noise canceller based on hypercomplex and spatio-temporal-polarisation processes. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 7(3), 277–286 (2013)
Y. Tian, X. Sun, S. Zhao, DOA and power estimation using a sparse representation of second-order statistics vector and ℓ0-norm approximation. Sig. Process. 105, 98–108 (2014)
Y. Tian, H. Xu, DOA, power and polarization angle estimation using sparse signal reconstruction with a COLD array. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69(11), 1606–1612 (2015)
Y. Tian, X. Sun, S. Zhao, Sparse-reconstruction-based direction of arrival, polarisation and power estimation using a cross-dipole array. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 9(6), 727–731 (2015)
M.E. Tipping, Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 1(6), 211–244 (2001)
W. Wang, H. Chen, J. Jin et al., Quaternion-MUSIC for near-field strictly noncircular sources with large-scale polarization array. Digit. Signal Proc. 94, 137–145 (2019)
X. Xu, X. Wei, Z. Ye, DOA estimation based on sparse signal recovery utilizing weighted l1-norm penalty. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(3), 155–158 (2012)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, C. Zhang, Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(1), 38–43 (2013)
P. Zhao, W. Si, G. Hu et al., DOA Estimation for a mixture of uncorrelated and coherent sources based on hierarchical sparse Bayesian inference with a Gauss-Exp-Chi2 Prior. Int. J. Antennas Propag. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3505918
P. Zhao, G. Hu, Z. Qu et al., Enhanced nested array configuration with hole-free co-array and increasing degrees of freedom for DOA estimation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 23(12), 2224–2228 (2019)
G. Zheng, Two-dimensional DOA estimation for polarization sensitive array consisted of spatially spread crossed-dipole. IEEE Sens. J. 18(12), 5014–5023 (2018)
M.D. Zoltowski, K.T. Wong, ESPRIT-based 2-D direction finding with a sparse uniform array of electromagnetic vector sensors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48(8), 2195–2204 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Doctoral Scientific Research Startup Foundation of Jinling Institute of Technology (Grant No. jit-b-201724), Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Province (Project No. BK20161104) and the Six Talent Peaks Project of the Jiangsu Province (Project No. DZXX-022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, P., Hu, G. & Zhou, H. An Off-Grid Block-Sparse Bayesian Method for Direction of Arrival and Polarization Estimation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 4378–4398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01372-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01372-3