Abstract
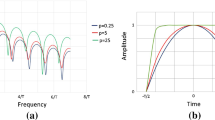
Windowing is a common method to reduce spectral leakage in Fourier analysis. Based on the principle that time domain multiplication corresponds to frequency domain convolution, this paper suggests frequency convolution to implement windowing functions by FIR filter structure. The proposed digital filter has full compatibility for variable length of window and is capable of implementing the three most popular windows, viz. Hanning, Hamming and Blackman. Numerical simulation indicates that the method consumes \(78\,\%\) less area, \(11\,\%\) higher throughput rate than the CORDIC-based (co-ordinate rotation digital computer) method, and achieves \(33\,\%\) lower quantization error for fixed point than the time domain multiplication method. Furthermore, an example of stretch processing in HF radar is shown to reduce the \(99\,\%\) computational complexity because of the segmental frequency points windowing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Aggarwal, K. Khare, CORDIC-based window implementation to minimise area and pipeline depth. IET Signal Process. 7(5), 427–435 (2013)
S. Aggarwal, K. Khare, Efficient window-architecture design using completely scaling-free CORDIC pipeline. in 2013 26th International Conference on VLSI Design and 2013 12th International Conference on Embedded Systems, pp. 60–65 (2013)
T.L.J. Ferris, A.J. Grant, Frequency domain method for windowing in Fourier analysis. Electron. Lett. 28(15), 1440 (1992)
F.I. Harris, On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with discrete Fourier transform. Proc. IEEE 66(1), 51–83 (1978)
S.K. Mitra, Digital Signal Processing a Computer-based Approach, 2nd edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2001)
A.V. Oppenheim, R.W. Schafer, Discrete-Time Signal Processing (Pearson Higher Education, New York City, 2010)
K.C. Ray, A.S. Dhar, CORDIC-based unified VLSI architecture for implementing window functions for real time spectral analysis. IEEE Proc.-Circ. Devices Syst. 153(6), 539–544 (2006)
K.C. Ray, A.S. Dhar, High throughput VLSI architecture for Blackman windowing in real time spectral analysis. J. Comput. 3(5), 54–59 (2008)
J. Tan, B.Y. Wen, Y.W. Tian et al., Design and FPGA implementation of time-frequency transforming for stretch processing. IEICE Electron. Expr. 11, 1–6 (2013)
Xilinx: ’Xilinx logic core product specifications CORDIC v4.0 DS249’, (Xilinx 2011)
L. Yeh, K.T. Wong, H.S. Mir, Viable/inviable polynomial-phase modulations for ’stretch processing. IEEE Trans. Aeros. Electron. Syst. 48(1), 923–926 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported by the National Special Program for Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development of China under Grant 2013YQ160793 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant 2014212020202.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., Wen, B., Tian, Y. et al. Frequency Convolution for Implementing Window Functions in Spectral Analysis. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 2198–2208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0403-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0403-7