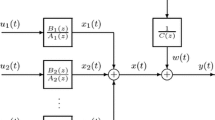
Abstract
A decomposition-based recursive least squares algorithm is developed for Wiener nonlinear systems described by finite impulse response moving average models. After transferring a finite impulse response moving average (FIR-MA) model to a controlled autoregressive model, we compute the parameters by combining the decomposition principle and the least squares method and using the filtering idea. The simulation results validate the proposed algorithm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Ahmad, O. Kukrer, A. Hocanin, Recursive inverse adaptive filtering algorithm. Digit. Signal Process. 21(4), 491–496 (2011)
S.I. Aihara, A. Bagchi, Recursive parameter identification for infinite-dimensional factor model by using particle filter-application to US-Treasury Bonds. Int. J. Innovative Comput. Inf. Control 4(1), 35–52 (2008)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, SSHI methods for solving general linear matrix equations. Eng. Comput. 28(8), 1028–1043 (2011)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, Iterative algorithms for the generalized centro-symmetric and central anti-symmetric solutions of general coupled matrix equations. Eng. Comput. 29(5), 528–560 (2012)
M. Dehghan, M. Hajarian, Fourth-order variants of Newton’s method without second derivatives for solving non-linear equations. Eng. Comput. 29(4), 356–365 (2012)
F. Ding, K.P. Deng, X.M. Liu, Decomposition based Newton iterative identification method for a Hammerstein nonlinear FIR system with ARMA noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. doi: 10.1007/s00034-014-9772-y.
J. Ding, J.X. Lin, Modified subspace identification for periodically non-uniformly sampled systems by using the lifting technique. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. doi:10.1007/s00034-013-9704-2.
F. Ding, T. Chen, Gradient based iterative algorithms for solving a class of matrix equations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(8), 1216–1221 (2005)
F. Ding, T. Chen, Performance analysis of multi-innovation gradient type identification methods. Automatica 43(1), 1–14 (2007)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Auxiliary model based multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient parameter estimation with colored measurement noises. Signal Process. 89(10), 1883–1890 (2009)
F. Ding, X.P. Liu, G. Liu, Multi-innovation least squares identification for linear and pseudo-linear regression models. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 40(3), 767–778 (2010)
F. Ding, Several multi-innovation identification methods. Digit. Signal Process. 20(4), 1027–1039 (2010)
J. Ding, C.X. Fan, J.X. Lin, Auxiliary model based parameter estimation for dual-rate output error systems with colored noise. Appl. Math. Model. 37(6), 4051–4058 (2013)
F. Ding, X.M. Liu, H.B. Chen, G.Y. Yao, Hierarchical gradient based and hierarchical least squares based iterative parameter identification for CARARMA systems. Signal Process. 97(4), 31–39 (2014)
F. Ding, Combined state and least squares parameter estimation algorithms for dynamic systems. Appl. Math. Model. 38(1), 403–412 (2014)
J.L. Figueroa, S.I. Biagiola, O.E. Agamennoni, An approach for identification of uncertain Wiener systems. Math. Comput. Model. 48(1–2), 305–315 (2008)
A. Hagenblad, L. Ljung, A. Wills, Maximum likelihood identification of Wiener models. Automatica 44(11), 2697–2705 (2008)
P.P. Hu, F. Ding, Multistage least squares based iterative estimation for feedback nonlinear systems with moving average noises using the hierarchical identification principle. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(1–2), 583–592 (2013)
P.P. Hu, F. Ding, J. Sheng, Auxiliary model based least squares parameter estimation algorithm for feedback nonlinear systems using the hierarchical identification principle. J. Franklin Inst. 350(10), 3248–3259 (2013)
J.H. Li, Parameter estimation for Hammerstein CARARMA systems based on the Newton iteration. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(1), 91–96 (2013)
Y.J. Liu, Y.S. Xiao, X.L. Zhao, Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for multiple-input single-output systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 215(4), 1477–1483 (2009)
Y.J. Liu, L. Yu, F. Ding, Multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithm and its performance analysis. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 29(4), 649–667 (2010)
Y.J. Liu, F. Ding, Y. Shi, An efficient hierarchical identification method for general dual-rate sampled-data systems. Automatica 50(3), 962–973 (2014)
J.X. Ma, F. Ding, Recursive relations of the cost functions for the least squares algorithms for multivariable systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(1), 83–101 (2013)
B.Q. Mu, H.F. Chen, Recursive identification of errors-in-variables Wiener systems. Automatica 49(9), 2744–2753 (2013)
G.B. Qian, L.P. Li, M.G. Luo, On the blind channel identifiability of MIMO-STBC systems using noncircular complex FastICA algorithm. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. doi:10.1007/s00034-013-9722-0.
M. Schoukens, R. Pintelon, Y. Rolain, Identification of Wiener–Hammerstein systems by a nonparametric separation of the best linear approximation. Automatica 50(2), 628634 (2014)
Y. Shi, F. Ding, T. Chen, 2-Norm based recursive design of transmultiplexers with designable filter length. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 25(4), 447–462 (2006)
Z.Y. Wang, Z.C. Ji, Data filtering based iterative identification methods for nonlinear FIR-MA systems. J. Vib. Control (2013). doi:10.1177/1077546313484048
D.Q. Wang, Recursive extended least squares identification method based on auxiliary models. IET Control Theory Appl. 26(1), 51–56 (2009)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Performance analysis of the auxiliary models based multi-innovation stochastic gradient estimation algorithm for output error systems. Digit. Signal Process. 20(3), 750–762 (2010)
D.Q. Wang, Least squares-based recursive and iterative estimation for output error moving average systems using data filtering. IET Control Theory Appl. 5(14), 1648–1657 (2011)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Hierarchical least squares estimation algorithm for Hammerstein–Wiener systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(12), 825–828 (2012)
D.Q. Wang, F. Ding, Y.Y. Chu, Data filtering based recursive least squares algorithm for Hammerstein systems using the key-term separation principle. Inf. Sci. 222(10), 203–212 (2013)
F. Yu, Z.Z. Mao, M.X. Jia, Recursive identification for Hammerstein–Wiener systems with dead-zone input nonlinearity. J. Process Control 23(8), 1108–1115 (2013)
H. Zhang, Y. Shi, A.S. Mehr, Robust FIR equalization for time-varying communication channels with intermittent observations via an LMI approach. Signal Process. 91(7), 1651–1658 (2011)
H. Zhang, Y. Shi, A.S. Mehr, Robust equalisation for inter symbol interference communication channels. IET Signal Process. 6(2), 73–78 (2012)
H. Zhang, Y. Shi, On energy-to-peak filtering for nonuniformly sampled nonlinear systems: a Markovian jump system approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(1), 212–222 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61174032, 61202473), the Doctoral Foundation of Higher Education Priority Fields of Scientific Research (No. 20110093130001), the Scientific Research Foundation of Jiangnan University (No. 1252050205135110), and by the PAPD of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Wang, Y. & Ji, Z. Decomposition-Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm for Wiener Nonlinear Feedback FIR-MA Systems Using the Filtering Theory. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33, 3649–3662 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-014-9806-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-014-9806-5