Abstract
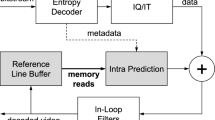
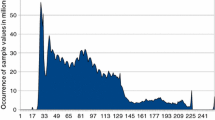
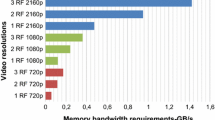
In this paper, an autocorrelation-based lossless recompression (ABLR) algorithm is proposed. The ABLR can save the memory bandwidth of video coding systems and preserves the visual quality. The ABLR consists of two core techniques: (1) a correlation-based prediction technique and (2) a correlation-adaptive Golomb-Rice code. Furthermore, dual-mode memory addressing (DMMA) is also proposed to provide ABLR with memory random access functionality. The word-length utilization rate (WLUR) of DMMA is as high as 92.34 % on average. The experimental results reveal that the ABLR exhibits a lossless compression ratio of 2.05 on average for 1080p test sequences. This indicates that the memory bandwidth can be saved up to 50 %. The VLSI architecture of ABLR is designed with three-stage pipelining and is realized in 0.18 μm 1P6M CMOS technology with a cell-based design flow. The logic gate count is about 28 K and the core area is 0.69×0.68 mm2. The encoding capability can reach full HD (1920×1080)@30 fps at a clock rate of 62.5 MHz. The power dissipation is 9.35 mW at a clock rate of 62.5 MHz.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Bahari, T. Arslan, A.T. Erdogan, Low-power H.264 video compression architectures for mobile communication. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 19(9), 1251–1261 (2009)
X. Bao, D. Zhou, S. Goto, A lossless frame recompression scheme for reducing DRAM power in video encoding, in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Circuits Syst. (ISCAS), (2010), pp. 677–680
A. Beric, J. van Meerbergen, G. de Haan, R. Sethuraman, Memory-centric video processing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 18(4), 439–452 (2008)
H.-C. Chang, J.-W. Chen, B.-T. Wu, C.-L. Su, J.-S. Wang, J.-I. Guo, A dynamic quality-adjustable H.264 video encoder for power-aware video applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 19(12), 1739–2009 (2009)
Y.-H. Chen, C.-C. Cheng, T.-D. Chuang, C.-Y. Chen, S.-Y. Chien, L.-G. Chen, Efficient architecture design of motion-compensated temporal filtering/motion compensated prediction engine. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 18(1), 98–109 (2008)
T.-D. Chuang, P.-K. Tsung, P.-C. Lin, L.-M. Chang, T.-C. Ma, Y.-H. Chen, L.-G. Chen, Low bandwidth decoder framework for H.264/AVC scalable extension, in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Circuit. Syst, (2004), pp. 2960–2963
A. Eisner, When will 4K make your HDTV obsolete? LCD-TV Matters 4(3), 39–40 (2012)
D.F. Finchelstein, V. Sze, A.P. Chandrakasan, Multicore processing and efficient on-chip caching for H.264 and future video decoders. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 19(1), 1704–1713 (2009)
P.G. Howard, J.S. Vitter, Fast and efficient lossless image compression, in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Data Compression, (1993), pp. 501–510
ISO/IEC FDIS15 444-1, JPEG 2000 Part 1 Final Draft International Standard (2000)
ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29 WG1 ITU-T SG8, Lossless and Near-Lossless Coding of Continuous Still Images (JPEG-LS) (JPEG/JBIG) (1998)
ISO/IEC 11172-2, Coding of Moving Pictures and Associated Audio for Digital Storage Media at up to 1.5 Mbit/s (1992)
ISO/IEC 13818, Information Technology-Generic Coding of Moving Pictures and Associated Audio Information: Parts 13 (2000)
ISO/IEC 14496-2, Information Technology-Coding of Audio-Visual Objects—Part 2: Visual (1999)
ITU Rec. T.81 ISO/IEC 10918-1, Digital Compression and Coding of Continuous Tone Still Images: Requirements and Guidelines (1993)
ITU-T Recommendation H.264 & ISO/IEC 14496-10, Advanced Video Coding for Generic Audiovisual Services (2005)
K. Iwata et al., A 342 mW mobile application processor with Full-HD multi-standard video codec and tile-based address-translation circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 45(1), 59–68 (2010)
Y. Kikuchi et al., A 40 nm 222 mW H.264 Full-HD decoding, 25 power domains, 14-core application processor with × 512b stacked DRAM. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46(1), 32–41 (2011)
H.-S. Kim, J. Lee, H. Kim, S. Kang, C. Park, A lossless color image compression architecture using a parallel Golomb-Rice hardware CODEC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 21(11), 1581–1587 (2011)
M. Kimura et al., A Full HD multistandard video codec for mobile applications. IEEE MICRO 29(6), 18–27 (2009)
Z. Li et al., HDTV1080p H.264/AVC encoder chip design and performance analysis. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(2), 594–608 (2009)
C.-C. Lin et al., A 160K gates/4.5 KB SRAM H.264 video decoder for HDTV applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(1), 170–182 (2007)
T.-M. Liu, T.-A. Lin, S.-Z. Wang, W.-P. Lee, J.-Y. Yang, K.-C. Hou, C.-Y. Lee, A 125 μW, fully scalable MPEG-2 and H.264AVC video decoder for mobile applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(1), 161–169 (2007)
A. Netravali, J.O. Limb, Picture coding: a review. Proc. IEEE 68, 366–406 (1980)
L. Song, D. Zhou, X. Jin, S. Goto, An adaptive bandwidth reduction scheme for video coding, in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Circuits Syst. (ISCAS), (2010), pp. 404–410
T. Song, T. Shimamoto, Reference frame data compression method for H.264/AVC. IEICE Electron. Express 4(3), 121–126 (2007)
V. Sze, D.F. Finchelstein, M.E. Sinangil, A.P. Chandrakasan, A 0.7-V 1.8-mW H.264/AVC 720p video decoder. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(11), 2943–2956 (2009)
N.H.E. Weste, K. Eshraghian, Principles of CMOS VLSI Design: A Systems Perspective, 2nd edn. (Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, 1993)
J.-H. Woo, J.-H. Sohn, H. Kim, H.-J. Yoo, A 195 mW/152 mW mobile multimedia SoC with fully programmable 3-D graphics and MPEG4/H.264/JPEG. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43(9), 2047–2056 (2008)
J.-H. Woo, H. Kim, H.-J. Yoo, J.-H. Sohn, A low-power multimedia SoC with fully programmable 3D graphics for mobile devices. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 29(5), 82–90 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Science Council (NSC), R.O.C., under grants NSC 101-2221-E-155-072.
This research was supported in part by IC-Design tools services from the National Chip Implementation Center (CIC), Taiwan, R.O.C. The authors express many thanks for the reviewer’s precious comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YH., Chen, CC. & You, YL. Design of VLSI Architecture of Autocorrelation-Based Lossless Recompression Engine for Memory-Efficient Video Coding Systems. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33, 459–482 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9648-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9648-6