Abstract
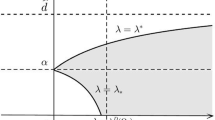
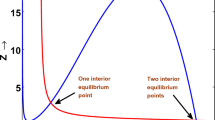
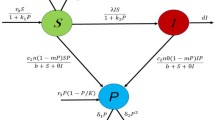
This paper deals with the global boundedness and asymptotic stability of the solution of the two-predator and one-prey systems with density-dependent motion in a n-dimensional bounded domain with Neumann boundary conditions. In a previous paper, Qiu et al. (J Dyn Differ Equ, 1–25, 2021) proved the global existence and uniform boundedness of classical solution by limiting the conditions on motility functions and the coefficients of logistic source. By contrast, we relax the limitation conditions in Qiu et al. (2021) by constructing the weight function. Moreover, under diverse competition circumstances, the global stabilities of nonnegative spatially homogeneous equilibria for the special model are established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann, H.: Dynamic theory of quasilinear parabolic equations. II. Reaction–diffusion systems. Differ. Integral Equ. 3(1), 13–75 (1990)
Amann, H.: Dynamic theory of quasilinear parabolic systems. III. Math. Z. 202(2), 219–250 (1989)
Ahn I., Yoon C.: Global well-posedness and stability analysis of prey–predator model with indirect prey-taxis. J. Differ. Equ. 268(8) (2019)
Ahn, J., Yoon, C.: Global well-posedness and stability of constant equilibria in parabolic-elliptic chemotaxis systems without gradient sensing. Nonlinearity 32, 1327–1351 (2019)
Bai, X., Winkler, M.: Equilibration in a fully parabolic two-species chemotaxis system with competitive kinetics. Indiana Univ. Math. J. 65, 553–583 (2016)
Chesson, P.L., Murdoch, W.W.: Aggregation of risk: relationships among host-parasitoid models. Am. Nat. 127(5), 696–715 (1986)
Desvillettes, L., Kim, Y.J., Trescases, A., Yoon, C.: A logarithmic chemotaxis model featuring global existence and aggregation. Nonlin. Anal. Real World Appl. 50, 562–582 (2019)
Fuest, M.: Global solutions near homogeneous steady states in a multidimensional population model with both predator-and prey-taxis. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 52(6), 5865–5891 (2020)
Fujie, K., Jiang, J.: Boundedness of classical solutions to a degenerate Keller–Segel type model with signal-dependent motilities. Acta Appl. Math. 176, 3 (2021)
Fujie, K., Senba, T.: Global existence and infinite time blow-up of classical solutions to chemotaxis systems of local sensing in higher dimensions. Nonlinear Anal.: Int. Multidiscip. J. 222, 112987 (2022)
He, X., Zheng, S.: Global boundedness of solutions in a reaction–diffusion system of predator–prey model with prey-taxis. Appl. Math. Lett. 49, 73–77 (2015)
Hsiao, L., Xin, Z.P.: On the asymptotic behavior of solutions of a reacting-diffusing system: a two predators-one prey model. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 18(3), 647–669 (1987)
Jie, J., Hao, W., Zheng, S.: Blow-up for a Three dimensional Keller–Segel model with consumption of chemoattractant. J. Differ. Equ. 264(8), 5432–5464 (2018)
Jin, H.Y., Wang, Z.A.: Global dynamics and spatio-temporal patterns of predator–prey systems with density-dependent motion. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 32(4), 652–682 (2021)
Jin, H.Y., Wang, Z.A.: Global stability of prey-taxis systems. J. Differ. Equ. 262(3), 1257–1290 (2017)
Kareiva, P., Odell, G.: Swarms of predators exhibit “preytaxis’’ if individual predators use area-restricted search. Am. Nat. 130(2), 233–270 (1987)
Keller, E.F., Segel, L.A.: Initiation of slime mold aggregation viewed as an instability. J. Theor. Biol. 26, 399–415 (1970)
Kozono, H., Sugiyama, Y.: Global strong solution to the semi-linear Keller–Segel system of parabolic-parabolic type with small data in scale invariant spaces. J. Differ. Equ. 247, 1–32 (2009)
Ladyzenskaja, O.A., Solonnikov, V.A., Ural’ceva, N.N.: Linear and Quasilinear Equations of Parabolic Type. AMS, Providence, RI (1968)
Lankeit, J.: A new approach toward boundedness in a two-dimensional parabolic chemotaxis system with singular sensitivity. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 39, 394–404 (2015)
Lankeit, J.: Locally bounded global solutions to a chemotaxis consumption model with singular sensitivity and nonlinear diffusion. J. Differ. Equ. 262(7), 4052–4084 (2016)
Li, C., Wang, X., Shao, Y.: Steady states of a predator-prey model with prey-taxis. Nonlinear Anal. 97, 155–168 (2014)
Li, G., Winkler, M.: Refined regularity analysis for a Keller-Segel-consumption system involving signal-dependent motilities. arXiv:2206.13327
Li, G., Winkler, M.: Relaxation in a Keller–Segel-consumption system involving signal-dependent motilities. arXiv:2206.13292
Lin, J.J., Wang, W., Zhao, C., Yang, T.H.: Global dynamics and traveling wave solutions of two predators-one prey models. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B. 20(4), 1135–1154 (2015)
Liu, D.: Global classical solution to a chemotaxis consumption model with singular sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 41, 497–508 (2018)
Liu, Y., Tao, Y.: Dynamics in a parabolic-elliptic two-species population competition model with cross-diffusion for one species. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 456(1), 1–15 (2017)
Loladze, I., Kuang, Y., Elser, J.J., Fagan, W.F.: Competition and stoichiometry: coexistence of two predators on one prey. Theor. Popul. Biol. 65(1), 1–15 (2004)
Mu, C., Wang, L., Zheng, P., Zhang, Q.: Global existence and boundedness of classical solutions to a parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis system. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14, 1634–1642 (2013)
Nagai, T.: Global existence and blow-up of solutions to a chemotaxis system. Nonlinear Anal. 47, 777–787 (2001)
Okubo, A., Levin, S.A.: Diffusion and Ecological Problems: Modern Perspectives. Springer, New York (2001)
Pang, P.Y.H., Wang, M.: Strategy and stationary pattern in a three-species predator–prey model. J. Differ. Equ. 200(2), 245–273 (2004)
Porzio, M.M., Vespri, V.: Hölder estimates for local solutions of some doubly nonlinear degenerate parabolic equations. J. Differ. Equ. 103(1), 146–178 (1993)
Qiu, S., Mu, C., Tu, X.: Dynamics for a three-species predator–prey model with density-dependent motilities. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 1–25 (2021)
Sapoukhina, N., Tyutyunov, Y., Arditi, R.: The role of prey taxis in biological control: a spatial theoretical model. Am. Nat. 162(1), 61–76 (2003)
Stinner, C., Winkler, M.: Global weak solutions in a chemotaxis system with large singular sensitivity. Nonlin. Anal. RWA 12(6) (2011)
Tao, Y.: Boundedness in a chemotaxis model with oxygen consumption by bacteria. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 381(2), 521–529 (2011)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: A fully cross-diffusive two-component evolution system: existence and qualitative analysis via entropy-consistent thin-film-type approximation. J. Funct. Anal. 281(4), 109069 (2021)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Boundedness in a quasilinear parabolic-parabolic Keller–Segel system with subcritical sensitivity. J. Differ. Equ. 252(1), 692–715 (2012)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Effects of signal-dependent motilities in a Keller–Segel-type reaction–diffusion system. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. Sci. 27, 1645–1683 (2017)
Tao, Y., Winkler, M.: Eventual smoothness and stabilization of large-data solutions in a three-dimensional chemotaxis system with consumption of chemoattractant. J. Differ. Equ. 252(3), 2520–2543 (2012)
Tello, J.I., Wrzosek, D.: Predator–prey model with diffusion and indirect prey-taxis. Math. Models Meth. Appl. Sci. 26(11), 2129–2162 (2016)
Ton, T.V., Hieu, N.T.: Dynamics of species in a model with two predators and one prey. Nonlinear Anal. 74(14), 4868–4881 (2011)
Tsyganov, M.A., Brindley, J., Holden, A.V., Biktashev, V.N.: Quasi-soliton interaction of pursuit-evasion waves in a predator–prey system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 218102 (2003)
Wang, J., Wang, M.: Boundedness and global stability of the two-predator and one-prey models with nonlinear prey-taxis. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 69(3), 1–24 (2018)
Wang, J., Wang, M.: Global solution of a diffusive predator-prey model with prey-taxis. Comput. Math. Appl. 77(10), 2676–2694 (2019)
Wang, Q., Song, Y., Shao, L.: Nonconstant positive steady states and pattern formation of 1D prey-taxis systems. J. Nonlinear Sci. 27(1), 71–97 (2017)
Winkler, M.: Absence of collapse in a parabolic chemotaxis system with signal-dependent sensitivity. Math. Nachr. 283(2), 1664–1673 (2011)
Winkler, M.: Aggregation vs. global diffusive behavior in the higher-dimensional Keller–Segel model. J. Differ. Equ. 248, 2889–2905 (2010)
Winkler, M.: Application of the Moser–Trudinger inequality in the construction of global solutions to a strongly degenerate migration model. Bull. Math. Sci. 2250012 (2022)
Winkler, M.: A quantitative strong parabolic maximum principle and application to a taxis-type migration-consumption model involving signal-dependent degenerate diffusion. arXiv:2209.12724
Winkler, M.: Asymptotic homogenization in a three-dimensional nutrient taxis system involving food-supported proliferation. J. Differ. Equ. 263(8), 4826–4869 (2017)
Winkler, M.: Chemotactic cross-diffusion in complex frameworks. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. Sci. 26(11) (2016)
Winkler, M.: Renormalized radial large-data solutions to the higher-dimensional Keller–Segel system with singular sensitivity and signal absorption. J. Differ. Equ. 264, 2310–2350 (2018)
Winkler, M.: Stabilization in a two-dimensional chemotaxis-Navier–Stokes system. Arch. Ration. Mech. An. 211(2), 455–487 (2014)
Winkler, M.: The two-dimensional Keller–Segel system with singular sensitivity and signal absorption: global large-data solutions and their relaxation properties. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 26, 987–1024 (2016)
Wu, S., Shi, J., Wu, B.: Global existence of solutions and uniform persistence of a diffusive predator–prey model with prey-taxis. J. Differ. Equ. 260(7), 5847–5874 (2016)
Xiang, T.: Global dynamics for a diffusive predator–prey model with prey-taxis and classical Lotka–Volterra kinetics. Nonlinear Anal. RWA. 39, 278–299 (2018)
Xu, H., Wang, L.: Global existence and asymptotic stability of solutions to a forager-exploiter model with logistic source. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 74(4) (2023)
Yan, J., Li, Y.: Global generalized solutions to a Keller–Segel system with nonlinear diffusion and singular sensitivity. Nonlinear Anal. 176, 288–302 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to referees for their valuable comments, which greatly improved the exposition of the paper. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 1771062) and Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. cstc2017jcyjXB0037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Hu, X. Dynamics in two-predator and one-prey models with signal-dependent motility. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 74, 75 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-023-01967-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-023-01967-1