Abstract
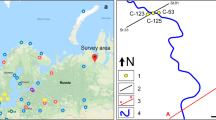
Controlled source radiomagnetotellurics (CSRMT) is a relatively new geophysical method for near-surface applications. A rectangular signal with base frequencies between 0.1 and 150 kHz is injected through a grounded electric dipole which is used as a transmitter. Electric and magnetic field components are observed at these frequencies and at their subharmonics, usually in the far-field zone so that apparent resistivities and impedance phases can be obtained in a broad frequency range between 1 and 1000 kHz. Inline or broadside configuration can be used for measurements. Similar to the controlled source audiomagnetotelluric method, tensor measurements are also possible when locating two transmitters perpendicular to each other. A scalar CSRMT survey was carried out on the buried faults in the Vuoksa region, 110 km north of St. Petersburg to test the applicability of this method to the mapping of near-surface faults. A 700 m electric dipole with base frequencies of 0.5, 11.3, 30 and 105 kHz was used as a transmitter. Smooth apparent resistivity and phase values as a function of frequency from 1 kHz to 1 MHz were observed in the far-field zone for the inline configuration at 57 stations using a station distance of 20 m. Electric fields observed in the direction of the transmitter were perpendicular to the assumed strike direction of the buried faults so that they could be associated with the TM mode. The observed apparent resistivity and phase TM mode data were interpreted using the 2D inversion algorithm, and a good data fitting could be obtained. The resistivity structure beneath the survey area (down to a depth of 80 m) could be derived and the buried faults could be mapped successfully. In addition to the CSRMT observations, a conventional radiomagnetotelluric (RMT) survey was also carried out on the same profile. An excellent correlation of the observed RMT and CSRMT transfer functions and 2D conductivity models was achieved.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastani, M. (2001). EnviroMT—a new controlled source/radio magnetotelluric system. PhD thesis, Uppsala University, Sweden.
Bastani, M., & Pedersen, L. P. (2001). Estimation of magnetotelluric transfer functions from radio transmitters. Geophysics, 66, 1038–1051.
Bastani, M., Persson, L., Mehta, S., & Malehmir, A. (2015). Boat-towed radiomagnetotellurics (RMT)—a new technique and case study from the city of Stockholm. Geophysics, 80, B193–B202.
Bastani, M., Savvaidis, A., Pedersen, L., & Kalscheuer, T. (2011). CSRMT measurements in the frequency range of 1–250 kHz to map a normal fault in the Volvi basin Greece. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 75, 180–195.
Candansayar, M. E., & Tezkan, B. (2008). Two-dimensional joint inversion of radiomagnetotelluric and direct current resistivity data. Geophysical Prospecting, 56, 737–749. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.2008.00695.x.
Chave, A. D., Thomson, D. J., & Ander, M. E. (1987). On the robust estimation of power spectra, coherences and transfer functions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 92(B1), 633–648.
Hansen, P. C. (1992). Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of L-curve. SIAM Reviews, 34, 561–580.
Hansen, P., & O’Leary, D. (1993). The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 14, 1487–1503.
Kalscheuer, T., Pedersen, L. P., & Siripunvaraporn, W. (2008). Radiomagnetotelluric two dimensional forward and inverse modelling accounting for displacement currents. Geophysical Journal International, 175, 486–514.
Linde, N., & Pedersen, L. B. (2004). Characterization of a fractured granite using radio magnetotelluric (RMT) data. Geophysics, 69, 1155–1165.
Mackie, R., Rieven, S., & Rodi, W. (1997). User manual and software documentation for two-dimensional of magnetotelluric data. Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.
Martin, R. (2009). Development and application of 2D and 3D transient electromagnetic inverse solutions based on adjoint Green functions: A feasibility study for the spatial reconstruction of conductivity distributions by means of sensitivities. PhD thesis, University of Cologne.
Mehta, G., Bastani, M., Malehmir, A., & Pedersen, L. P. (2017). Resolution and sensitivity boat-towed RMT data to deliniate fracture tones—Examples of the Stockholm, bypass multi-lane tunnel. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 139, 131–143.
Müller, I. (1983). Anisotropic properties of rocks detected with electromagnetic VLF (pp. 273–282). Zürich: International Symposium Field Measurements in Geomechanics.
Özyıldırım, Ö., Candansayar, M. E., Demirci, İ., & Tezkan, B. (2017). Two-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric/radiomagnetotelluric data by using unstructured mesh. Geophysics, 82(4), E197–E210.
Pedersen, L. B., Bastani, M., & Dynesius, L. (2005). Groundwater exploration using combined controlled-source and radiomagnetotelluric techniques. Geophysics, 70, G8–G15.
Recher, (2002). Dreidimensionale Erkundung von Altlasten mit Radio-Magnetotellurik-Vergleiche mit geophysikalische, geochemischen und geologischen Analysen an Bodenproben aus Rammkernsondierungen, PhD thesis, University of Cologne.
Rodi, W. L., & Mackie, R. L. (2001). Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion. Geophysics, 66, 174–187. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1444893.
Saraev, A., Simakov, A., Shylkov, A., & Tezkan, B. (2017). Controlled source radiomagnetotellurics: a tool for near surface investigations in remote regions. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 146, 228–237.
Saraev, A. K., Simakov, A. E., Tezkan, B. (2011). Foot, mobile and controlled source modifications of the radiomagnetotelluric method. Near surface 2011—17th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Leicester, UK, 12–14 September 2011.
Schwalenberg, K., Rath, V., & Haak, V. (2002). Sensitivity studies applied to a two dimensional resistivity model from the Central Andes. Geophysical Journal International, 150, 673–686.
Sidorenko, A., Selivanova, V., & Sokolova, T. (1971). Geology of USSR. Leningrad, Pskov and Novgorod regions. Description of geology (Vol. 1, p. 504). Moscow: Nedra (Annex 1. Geological map of the Sub Quaternary sediments).
Smith, J. T., & Booker, J. R. (1991). Rapid inversion of two and three dimensional magnetotelluric data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 96, 3905–3922.
Tarasov, G. A., Somov, G. M., Eliseev, A. A., & Antonov, G. K. (1973). Method of alternating natural electric field (User’s guide) (p. 128). Leningrad: Nedra.
Tezkan, B. (1999). A review of environmental applications of quasi-stationary electromagnetic techniques. Surveys In Geophysics, 20, 279–308.
Tezkan, B. (2009). Radiomagnetotellurics. In R. Kirsch (Ed.), Groundwater geophysics—a tool for hydrogeology (2nd ed., pp. 295–317). Berlin: Springer.
Tezkan, B., Georgescu, P., & Fauzi, U. (2005). A radiomagnetotelluric survey on an oil-contaminated area near the Brazi Refinery, Romania. Geophysical Prospecting, 53, 311–323.
Tezkan, B., Goldman, M., Greinwald, S., Hördt, A., Müller, I., Neubauer, F. M., et al. (1996). A joint application of radiomagnetotellurics and transient electromagnetics to the investigation of a waste deposit in Cologne (Germany). Journal of Applied Geophysics, 31, 133–143.
Tezkan, B., Hördt, A., & Gobashy, M. (2000). Two dimensional inversion of radiomagnetotelluric data: selected case histories for waste site exploration. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 44, 237–256.
Tezkan, B., & Saraev, A. (2008). A new broadband radiomagnetotelluric instrument application to near surface investigation: near surface. Geophysics, 6, 243–250.
Turberg, P., Müller, I., & Flury, F. (1994). Hydrogeological investigation of porous environments by radio magnetotelluric resistivity (RMT-R 12-240 kHz). Journal of Applied Geophysics, 31, 133–143.
Vozoff, K. (1972). The magnetotelluric method in the exploration of sedimentary basins. Geophysics, 37, 98–141.
Wang, S., Malehmir, A., & Bastani, M. (2016). Geophysical characterization of areas prone to quick-clay landslides using radio-magnetotelluric and seismic methods. Tectonophysics, 677, 248–260.
Ward, S. H., Donnell, J. O., Rivera, R., Ware, G. H., & Fraser, D. C. (1966). AFMAG—applications and limitations. Geophysics, 31(3), 576–605.
Yogeshwar, P., Tezkan, B., Israil, M., & Candansayar, M. E. (2012). Groundwater contamination in the Roorkee area, India: 2D joint inversion of radiomagnetotelluric and direct current resistivity data. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 76, 127–135.
Zacher, G., Tezkan, B., Neubauer, F. M., Hördt, A., & Müller, I. (1996). Radiomagnetotellurics: a powerful tool for waste-site exploration. European Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 1, 139–159.
Zonge K.L., Hughes L.J. (1991). Controlled source audio-frequency magnetotellurics. Electromagnetic methods in applied geophysics. vol. 2—Applications. Series: Investigations in geophysics, No. 3, pp. 713–809.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the BMBF, German Science Foundation and by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project No 18-505-12033. We also thank the two unknown reviewers for their suggestions to improve the manuscript. I.M. thanks the Indonesian Government for the MORA fellowship and the GSGS fellowship Grant of the Graduate School of Geoscience of the University of Cologne.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tezkan, B., Muttaqien, I. & Saraev, A. Mapping of buried faults using the 2D modelling of far-field controlled source radiomagnetotelluric data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 176, 751–766 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1980-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1980-0