Abstract
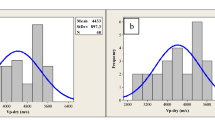
Petrophysical properties and ultrasonic P- and S-wave attenuation measurements on 35 Deccan basalt core specimens, recovered from Killari borehole site in western India, provide unique reference data-sets for a lesser studied Deccan Volcanic Province. These samples represent 338-m-thick basaltic column, consisting four lava flows each of Ambenali and Poladpur Formations, belonging to Wai Subgroup of the Deccan volcanic sequence. These basalt samples are found to be iron-rich (average FeOT: 13.4 wt%), but relatively poor in silica content (average SiO2: 47.8 wt%). The saturated massive basalt cores are characterized by a mean density of 2.91 g/cm3 (range 2.80–3.01 g/cm3) and mean P- and S-wave velocities of 5.89 km/s (range 5.01–6.50 km/s) and 3.43 km/s (range 2.84–3.69 km/s), respectively. In comparison, saturated vesicular basalt cores show a wide range in density (2.40–2.79 g/cm3) as well as P-wave (3.28–4.78 km/s) and S-wave (1.70–2.95 km/s) velocities. Based on the present study, the Deccan volcanic sequence can be assigned a weighted mean density of 2.74 g/cm3 and a low Vp and Vs of 5.00 and 3.00 km/s, respectively. Such low velocities in Deccan basalts can be attributed mainly to the presence of fine-grained glassy material, high iron contents, and hydrothermally altered secondary mineral products, besides higher porosity in vesicular samples. The measured Q values in saturated massive basalt cores vary enormously (Qp: 33–1960 and Qs: 35–506), while saturated vesicular basalt samples exhibit somewhat lesser variation in Qp (6–46) as well as Qs (5–49). In general, high-porosity rocks exhibit high attenuation, but we observed the high value of attenuation in some of the massive basalt core samples also. In such cases, energy loss is mainly due to the presence of fine-grained glassy material as well as secondary alteration products like chlorophaeite, that could contribute to intrinsic attenuation. Dominance of weekly bound secondary minerals might also be responsible for the generation of microcracks, which may generate squirt flow in saturated samples. Hence, we argue that the Deccan basalts attenuate seismic energy significantly, where its composition plays a major role.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beane, J. E., Turner, C. A., Hooper, P. R., Subbarao, K. V., & Walsh, J. N. (1986). Stratigraphy, composition and form of the Deccan Basalts, Western Ghats, India. Bulletin Volcanology, 48, 61–83.
Birch, F. (1960). The velocity of compressional waves in rocks to 10 Kilobars, part 1. Journal of Geophysical Research, 65, 1083–1102.
Birch, F. (1961a). Composition of the earth’s mantle. Geophysical Journal of Royal Astronomical Society, 4, 295–311.
Birch, F. (1961b). The velocity of compressional waves in rocks to 10 kilobars, part 2. Journal of Geophysical Research, 66, 2199–2224.
Brown, E. T. (1981). Rock characterization testing and monitoring: ISRM suggested methods. Oxford, New York: International Society of Rock Mechanics.
Carlson, R. L., & Herrick, C. N. (1990). Densities and porosities in the oceanic crust and their variation with depth and age. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95, 9153–9170.
Cerney, B., & Carlson, R. L. (1999). The effect of cracks on the seismic velocities of Basalt from site 990, SE Greenland margin. Proceeding of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 163, 29–35.
Chatterjee, N., & Bhattacharji, S. (2008). Trace elements variation in Deccan basalts: Role of mantle melting, fractional crystallization and crustal assimilation. Journal of Geological Society of India, 71, 171–188.
Christensen, N. I. (1968). Compressional wave velocities in basic rocks. Pacific Science, XXII, 41–44.
Christensen, N. I., Blair, S. C., Wilkens, R. H., & Salisbury, M. H. (1980). Compressional wave velocities, densities, and porosities of basalts from Holes 417A, 417 D, and 418 A. Deep Sea Drilling Project Legs 51–53. In: T. Donnelly et al. (Eds.), Init. Reports DSDP, 51,52,53 (part 2, pp. 1467–1471).
Christensen, N. I., & Mooney, W. D. (1995). Seismic velocity structure and composition of the continental crust: A global view. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100, 9761–9788.
Courtillot, V., Feraud, G., Maluski, H., Vandamme, D., Moreau, M. G., & Besse, J. (1988). Deccan flood basalts and the cretaceous/tertiary boundary. Nature, 333, 843–846.
Cox, K. G., & Hawkesworth, C. J. (1985). Geochemical Stratigraphy of the Deccan Traps at Mahabaleshwar, Western Ghats, India, with implications for open system magmatic process. Journal of Petrology, 26, 355–377.
Cox, K. G., & Mitchell, C. (1988). Importance of crystal settling in the differentiation of Deccan Trap basaltic magmas. Nature, 333, 447–449.
Dixit, M. M., Tewari, H. C., & Visweswara Rao, C. (2010). Two-dimensional velocity model of the crust beneath the South Cambay Basin, India from refraction and wide-angle reflection data. Geophysical Journal International, 181, 635–652.
Goldberg, D., & Sun, Y. F. (1997). Attenuation differences in layer 2A in intermediate- and slow-spreading oceanic crust. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 150, 221–231.
Goldberg, D., & Yin, C. S. (1994). Attenuation of p-waves in oceanic crust: Multiple scattering from observed heterogeneities. Geophysical Research Letters, 21, 2311–2314.
Gradstein, F. M., Ogg, J. G., Schmitz, M. D., & Ogg, G. M. (2012). The Geologic Time Scale 2012. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Gupta, H. K., & Dwivedi, K. K. (1996). Drilling at Latur earthquake region exposes a peninsular gneiss basement. Journal of Geological Society of India, 47, 129–131.
Gupta, H. K., & Gupta, G. D. (2003). Earthquake studies in Peninsular India since 1993. Memoir Geological Society of India, 54, 254.
Gupta, H. K., Mohan, I., Rastogi, B. K., Rao, C. V. K., & Rao, G. V., et al. (1993). Investigation of Latur earthquakes of September 30, 1993. In: Abstract Volume, Workshop on 30 September 1993 Maharashtra Earthquake, December 24, 1993, Hyderabad, pp. 2–3
Gupta, H. K., Srinivasan, R., Rao, R. U. M., Rao, G. V., Reddy, G. K., Roy, S., et al. (2003). Borehole investigations in the surface rupture zone of the 1993 Latur SCR earthquake, Maharashtra, India: Overview of results. Memoir Geological Society of India, 54, 1–22.
Ivankina, T. I., Kern, H. M., & Nikitin, A. N. (2005). Directional dependence of P- and S-wave propagation and polarization in foliated rocks from Kola superdeep well: Evidence from laboratory measurements and calculations based on TOF neutron diffraction. Tectonophysics, 407, 25–42.
Jay, A. E., & Widdowson, M. (2008). Stratigraphy, structure and volcanology of the SE Deccan continental flood basalt province: Implications for eruptive extent and volumes. Journal Geological Society of London, 165, 177–188.
Ji, S., Wang, Q., & Salisbury, M. H. (2009). Composition and tectonic evolution of the Chinese continental crust constrained by Poissons’ ratio. Tectonophysics, 463, 15–30.
Kern, H., Megjel, K., Strauss, K. W., Ivankina, T. I., Nikitin, A. N., & Kukkonen, I. T. (2009). Elastic wave velocities, chemistry and modal mineralogy of crustal rocks sampled by the Outokumpu scientific drill hole: Evidence from lab measurements and modeling. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 175, 151–166.
Kern, H., Walther, C. H., Fluh, E. R., & Marker, M. (1993). Seismic properties of rocks exposed in the POLAR profile region—Constraints on the interpretation of the refraction data. Precambrian Research, 64, 169–187.
Krishna, A. K., & Govil, P. K. (2007). Soil contamination due to heavy metals from an Industrial area of Surat, Gujarat, Western India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 124, 263–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9224-7.
Lewis, B. T. R., & Jung, H. (1989). Attenuation of refracted seismic waves in young oceanic crust. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 79, 1070–1088.
Lightfoot, P. C., Hawkesworth, C. J., Devey, C. W., Rogers, N. W., & Van Calsteren, P. W. C. (1990). Source and differentiation of Deccan trap lavas: Implications of geochemical and mineral chemical variations. Journal of Petrology, 31, 1165–1200.
Mahoney, J. J. (1988). Deccan traps. In J. D. Macdougall (Ed.), Continental flood basalts (pp. 151–194). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Mitchell, C. H., & Widdowson, M. (1991). A geological map of the southern Deccan, India and its structural implications. Journal of Geological Society of London, 148, 495–505.
Moose, D., & Zoback, M. D. (1983). In situ studies of velocity in fractured crystallined rock. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88(B3), 2345–2358.
Murphy, W. F. (1982). Effects of partial water saturation on attenuation in Massilon sandstone and Vycor porous glass. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 71(6), 1458–1468. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.387843.
Murty, A. S. N., Koteswara Rao, P., Dixit, M. M., Kesava Rao, G., Reddy, M. S., Prasad, B. R., et al. (2011). Basement configuration of the Jhagadia-Rajpipla profile in the western part of Deccan syneclise, India from travel-time inversion of seismic refraction and wide-angle reflection data. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40, 40–51.
Murty, A. S. N., Rajendra Prasad, B., Rao, Koteswara, Raju, S., & Sateesh, T. (2010). Delineation of subtrappean Mesozoic sediments in Deccan syneclise, India, using travel-time inversion of seismic refraction and wide-angle reflection data. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 167, 233–251.
Pandey, O. P. (2008). Deccan Trap volcanic eruption affected the Archean Dharwar craton of southern India: Seismic evidences. Journal of Geological Society of India, 72, 510–514.
Pandey, O. P. (2009). Shallowing of mafic crust and seismic instability in the high velocity Indian shield. Journal of Geological Society of India, 74, 615–624.
Pandey, O. P. (2016). Deep Scientific drilling results from Koyna and Killari earthquake regions reveal why Indian shield lithosphere is unusual, thin and warm. Geoscience Frontiers, 7, 851–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.08.010.
Pandey, O. P., Chandrakala, K., Parthasarathy, G., Reddy, P. R., & Koti Reddy, G. (2009). Upwarped high-velocity mafic crust, subsurface tectonics and causes of intraplate Latur-Killari (M 6.2) and Koyna (M 6.3) earthquakes, India—A comparative study. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34, 781–795.
Pandey, O. P., Tripathi, P., Parthasarathy, G., Rajagopalan, V., & Sreedhar, B. (2014). Geochemical and mineralogical studies of chlorine-rich amphibole and biotite from the 2.5 Ga mid-crustal basement beneath the 1993 Killari earthquake region, Maharashtra, India: Evidence for mantle metasomatism beneath the Deccan Traps. Journal of Geological Society of India, 83, 599–612.
Pandey, O. P., Tripathi, P., Vedanti, M., & SrinivasaSarma, D. (2016). Anomalous seismic velocity drop in iron and biotite rich amphibolite to granulite facies transitional rocks from Deccan volcanic covered 1993 Killari earthquake region, Maharashtra (India): A case study. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 173, 2455–2471.
Parthasarathy, G. (2006). Zeolite zonation and amygdaloidal minerals from the Killari borehole of Deccan traps, Maharashtra, India. Journal of Applied Geochemistry, 8, 546–557.
Parthasarathy, G., Choudary, B. M., Sreedhar, B., Kunwar, A. C., & Srinivasan, R. (2003). Ferrous saponite from Deccan Trap, India, and its application in adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium. American Mineralogist, 88, 1983–1988.
Prasanna Lakshmi, K. J., Senthil Kumar, P., Vijayakumar, K., Ravinder, S., Seshunarayana, T., & Sen, M. K. (2014). Petrophysical properties of the Deccan basalts exposed in the Western Ghats escarpment around Mahabaleshwar and Koyna, India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 84, 176–187.
Ramana, Y. V., & Rao, M. V. M. S. (1974). Q by pulse broadening in rocks under pressure. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 8(4), 337–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9201(74)90042-9.
Rao, M. V. M. S., & Prasanna Lakshmi, K. J. (2003). Shear-wave propagation in rocks and other lossy media: An experimental study. Current Science, 85, 1221–1225.
Rao, M. V. M. S., Prasanna Lakshmi, K. J., Sarma, L. P., & Chary, K. B. (2006). Elastic properties of granulite facies rocks of Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu,India. Journal of Earth System Science, 115(6), 673–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-006-0005-z.
Reddy, G. K., Rao, G. V., & Rao, R. U. M. (1998). Low density of Deccan traps: Evidence from boreholes at Killari, Latur earthquake site and implications for geophysical modeling. In: Abstract volume, Chapman Conference on Stable Continental Region (SCR) earthquakes, Hyderabad, 25–29 January, p. 31.
Renne, P. R., Sprain, C. J., Richards, M. A., Self, S., Vanderkluysen, L., & Pande, K. (2015). State shift in Deccan volcanism at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary, possibly induced by impact. Science, 350(Issue 6256), 76–78.
Rudnick, R. L., & Fountain, D. M. (1995). Nature and composition of the continental crust: A lower crustal perspective. Reviews of Geophysics, 33, 267–309.
Sano, T., Fujii, T., Deshmukh, S. S., Fukuoka, T., & Aramaki, S. (2001). Differentiation process of Deccan trap basalts: Contribution from geochemistry and experimental petrology. Journal of Petrology, 42, 2175–2195.
Schoene, B., Samperton, K. M., Eddy, M. P., Keller, G., Adatte, T., et al. (2015). U-Pb geochronology of the Deccan Traps and relation to the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. Science, 347(6218), 182–184.
Sen, G. (2001). Generation of Deccan trap magmas. Proceedings of Indian Academy of Sciences (Earth Planet Sci.), 110, 409–431.
Sen, G., Borges, M., & Marsh, B. D. (2006). A case for short duration of Deccan Trap eruption. EOS, 87(20), 197–204.
Sen, G., & Chandrasekharam, D. (2011). Deccan trap flood basalt province: An evaluation of the thermochemical plume model. In: J. Ray, et al. (Eds.), Topics in igneous petrology. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9600-5_2.
Shrivastava, J. P., Duncan, R. A., & Kashyap, M. (2015). Post-K/PB younger 40Ar–39Ar ages of the Mandla lavas: Implications for the duration of the Deccan volcanism. Lithos, 224, 214–224.
Shrivastava, J. P., Kumar, R., & Rani, N. (2017). Feeder and post Deccan Trap dyke activities in the northern slope of the Satpura Mountain: Evidence from new 40Ar-39Ar ages. Geoscience Frontier, 8, 483–492.
Shrivastava, J. P., Mahoney, J. J., & Kashyap, M. R. (2014). Trace elemental and Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic compositional variation in 37 lava flows of the Mandla lobe and their chemical relation to the western Deccan stratigraphic succession, India. Mineralogy and Petrology, 108, 801–817.
Sun, S., Ji, S., Wang, Q., Xu, Z., Salisbury, M., & Long, C. (2012). Seismic velocities and anisotropy of core samples from the Chinese continental scientific drilling borehole in the Sulu UHP terrane, Eastern China. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117, B01206. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008672.
Tisato, N., & Quintal, B. (2014). Laboratory measurements of seismic attenuation in sandstone: Strain versus fluid saturation effects. Geophysics, 79(5), WB9–WB14. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2013-0419.1.
Tompkins, M. J., & Christensen, N. I. (2001). Ultrasonic P-and S-wave attenuation in Oceanic Basalt. Geophysical Journal International, 145, 172–186.
Tripathi, P. (2015). Nature and composition of crystalline basement below Deccan volcanic covered 1993 Latur-Killari earthquake region, Maharashtra (India). Ph.D. thesis, Osmania University, Hyderabad, India, p. 164.
Tripathi, P., Pandey, O. P., Rao, M. V. M. S., & Koti Reddy, G. (2012a). Elastic properties of amphibolite and granulite facies mid-crustal basement rocks of the Deccan volcanic covered 1993 Latur-Killari earthquake region, Maharashtra (India) and mantle metasomatism. Tectonophysics, 554–557, 159–168.
Tripathi, P., Parthasarathy, G., Masood Ahmed, S. M., & Pandey, O. P. (2012b). Mantle-derived fluids in the basement of the Deccan trap: Evidence from stable carbon and oxygen isotopes of carbonates from the Killari borehole basement, Maharashtra, India. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 101, 1385–1395.
Ullemeyer, K., Nikolayev, D. I., Christensen, N. I., & Behrmann, J. H. (2011). Evaluation of Intrinsic velocity–pressure trends from low-pressure P-wave velocity measurements in rocks containing microcracks. Geophysical Journal International, 185, 1312–1320.
Vedanti, N., Lakshmi, K. J. P., Dutta, S., Malkoti, A., & Pandey, O. P. (2015). Investigation of petrophysical properties and ultrasonic P-and S-wave attenuation in Deccan Flood Basalts, India. In: SEG technical program expanded abstracts, pp. 3274–3278, https://doi.org/10.1190/segam2015-5858683.1
Vijaya Kumar, K., Chavan, C., Sawant, S., Naga Raju, K., et al. (2010). Geochemical investigation of a semi-continuous extrusive basaltic section from the Deccan volcanic province, India: Implications for the mantle and magma chamber processes. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 159, 839–862.
Volarovitch, M. P., & Gurvitch, A. S. (1957). Investigation of dynamic moduli of elasticity for rocks in relation to temperature. Bulletin Academy of Sciences, USSR Geophysics Series, 4, 1–9.
Walker, G. P. (1993). Basaltic-volcano systems. In: H. M. Richard, T. Alabaster, N. B. W. Harris, & C. R. Neary (Eds.), Magmatic processes and plate tectonics (pp. 3–38). Geological Society Special Publication no. 76.
Weiner, A. T., Manghnani, M. H., & Raj, R. (1987). Internal friction in tholeiitic basalts. Journal of Geophysics Research, 92(11), 635–643.
Wepfer, W. W. (1989). Application of laboratory velocities and attenuation data to the Earth’s crust. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN.
Wepfer, W. W., & Christensen, N. I. (1990). Compressional wave attenuation in oceanic basalts. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95, 431–439.
Wepfer, W. W., & Christensen, N. I. (1991). Q-structure of the oceanic crust. Marine Geophysical Researches, 13(3), 227–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369151.
White, D. J., & Clowes, R. M. (1994). Seismic attenuation structure beneath the Juan de Fuca ridge from tomographic inversion of amplitudes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99, 3043–3056.
Winkler, K. W., & Nur, A. (1982). Seismic attenuation: Effects of pore fluids and frictional sliding. Geophysics, 47, 1–15.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. K.J.P. Lakshmi, Kesav Krishna and M. Satyanarayanan for petrophysical and geochemical analysis and Drs. D. V. Subbarao and Dinesh Pandit for petrological examination of the thin sections and many useful discussions. We are also thankful to Prof. Mrinal K. Sen, Ex-Director, CSIR-National Geophysical Research Institute, Hyderabad, for making available the samples for the analysis. This study has been supported by CSIR project SHORE PSC 0205. Dr. O.P. Pandey is thankful to CSIR for emeritus scientist position at CSIR-NGRI. One of the authors (AM) acknowledges UGC for providing Senior Research Fellowship. Further, highly constructive suggestions made by the anonymous reviewer and Prof. Y. Gueguen, Editor, Pure and Applied Geophysics, have been very helpful in improving the manuscript. Permission accorded by the Director CSIR-NGRI to publish this work, is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vedanti, N., Malkoti, A., Pandey, O.P. et al. Ultrasonic P- and S-Wave Attenuation and Petrophysical Properties of Deccan Flood Basalts, India, as Revealed by Borehole Studies. Pure Appl. Geophys. 175, 2905–2930 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1817-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1817-x