Abstract
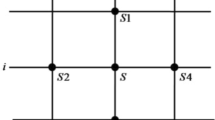
Surface wave tomography based on continuous regionalization of model parameters is widely used to invert for 2-D phase or group velocity maps. An inevitable problem is that the distribution of ray paths is far from homogeneous due to the spatially uneven distribution of stations and seismic events, which often affects the spatial resolution of the tomographic model. We present an improved tomographic method with a spatially varying smoothing scheme that is based on the continuous regionalization approach. The smoothness of the inverted model is constrained by the Gaussian a priori model covariance function with spatially varying correlation lengths based on ray path density. In addition, a two-step inversion procedure is used to suppress the effects of data outliers on tomographic models. Both synthetic and real data are used to evaluate this newly developed tomographic algorithm. In the synthetic tests, when the contrived model has different scales of anomalies but with uneven ray path distribution, we compare the performance of our spatially varying smoothing method with the traditional inversion method, and show that the new method is capable of improving the recovery in regions of dense ray sampling. For real data applications, the resulting phase velocity maps of Rayleigh waves in SE Tibet produced using the spatially varying smoothing method show similar features to the results with the traditional method. However, the new results contain more detailed structures and appears to better resolve the amplitude of anomalies. From both synthetic and real data tests we demonstrate that our new approach is useful to achieve spatially varying resolution when used in regions with heterogeneous ray path distribution.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abers, G. A., & Roecker, S. W. (1991). Deep structure of an arc-continent collision: Earthquake relocation and inversion for upper mantle P and S wave velocities beneath Papua New Guinea. Journal Geophysical Research, 96(B4), 6379–6401.
An, M., Feng, M., & Zhao, Y. (2009). Destruction of lithosphere within the north China craton inferred from surface wave tomography. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(8), Q08016.
Bao, X., Sun, X., Xu, M., Eaton, D. W., Song, X., Wang, L., et al. (2015). Two crustal low-velocity channels beneath SE Tibet revealed by joint inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion and receiver functions, Earth planet. Science Letters, 415, 16–24.
Barmin, M. P., Ritzwoller, M. H., & Levshin, A. L. (2001). A fast and reliable method for surface wave tomography. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 158, 1351–1375.
Bodin, T., & Sambridge, M. (2009). Seismic tomography with the reversible jump algorithm. Geophysical Journal International, 178(3), 1411–1436.
Böhm, G., Galuppo, P., & Vesnaver, A. (2000). 3D adaptive tomography using Delaunay triangles and Voronoi polygons. Geophysical Prospecting, 48(4), 723–744.
Boschi, L., & Ekström, G. (2002). New images of the Earth’s upper mantle from measurements of surface wave phase velocity anomalies. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 107(B4), 2059.
Chiao, L. Y., & Kuo, B. Y. (2001). Multiscale seismic tomography. Geophysical Journal International, 145(2), 517–527.
Chiao, L. Y., & Liang, W. T. (2003). Multiresolution parameterization for geophysical inverse problems. Geophysics, 68(1), 199–209.
Debayle, E., Kennett, B., & Priestley, K. (2005). Global azimuthal seismic anisotropy and the unique plate-motion deformation of Australia. Nature, 433(7025), 509–512.
Debayle, E., & Sambridge, M. (2004). Inversion of massive surface wave data sets: Model construction and resolution assessment. Journal Geophysical Research, 109, B02316.
Delost, M., Virieux, J., & Operto, S. (2008). First arrival traveltime tomography using second generation wavelets. Geophysical Prospecting, 56(4), 505–526.
Ditmar, P. G., & Yanovskaya, T. B. (1987). Generalization of the Backus–Gilbert method for estimation of the horizontal variations of surface wave velocity. Izvestiya of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR Physics of the Solid Earth, English Translation, 23(6), 470–477.
Ekström, G., Tromp, J., & Larson, E. W. (1997). Measurements and global models of surface wave propagation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 102(B4), 8137–8157.
Fang, H., Yao, H., Zhang, H., Huang, Y. C., & van der Hilst, R. D. (2015). Direct inversion of surface wave dispersion for three-dimensional shallow crustal structure based on ray tracing: methodology and application. Geophysical Journal International, 201(3), 1251–1263.
Fang, H., & Zhang, H. (2014). Wavelet-based double-difference seismic tomography with sparsity regularization. Geophysical Journal International, 199(2), 944–955.
Gelman, A., Carlin, J. B., Stern, H. S., & Rubin, D. B. (2004). Bayesian data analysis. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Hawkins, R., & Sambridge, M. (2015). Geophysical imaging using trans-dimensional trees. Geophysical Journal International, 203(2), 972–1000.
Hung, S. H., Chen, W. P., & Chiao, L. Y. (2011). A data-adaptive, multiscale approach of finite-frequency, traveltime tomography with special reference to P and S wave data from central Tibet. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 116(B6), B06307. doi:10.1029/2010JB008190.
Lévêque, J. J., Rivera, L., & Wittlinger, G. (1993). On the use of the checker-board test to assess the resolution of tomographic inversions. Geophysical Journal International, 115, 313–318.
Levshin, A. L., Yanovskaya, T. B., Lander, A. V., Bukchin, B. G., Barmin, M. P., Ratnikova, L. I., et al. (1989). Seismic surface waves in a laterally inhomogeneous Earth. Norwell: Kluwer Academic.
Lin, F.-C., Moschetti, M. P., & Ritzwoller, M. H. (2008). Surface wave tomography of the western United States from ambient seismic noise: Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocity maps. Geophysical Journal International, 173(1), 281–298.
Lin, F.-C., & Ritzwoller, M. H. (2011). Helmholtz surface wave tomography for isotropic and azimuthally anisotropic structure. Geophysical Journal International, 186(3), 1104–1120.
Lin, F.-C., Ritzwoller, M. H., & Snieder, R. (2009). Eikonal tomography: Surface wave tomography by phase front tracking across a regional broadband seismic array. Geophysical Journal International, 177(3), 1091–1110.
Liu, Q. Y., van der Hilst, R. D., Li, Y., Yao, H. J., Chen, J. H., Guo, B., et al. (2014). Eastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau by crustal flow and strain partitioning across faults. Nature Geoscience, 7(5), 361–365.
Loris, I., Nolet, G., Daubechies, I., & Dahlen, F. A. (2007). Tomographic inversion using 1-norm regularization of wavelet coefficients. Geophysical Journal International, 170(1), 359–370.
Montagner, J.-P. (1986). Regional three-dimensional structures using long period surface waves. Annales Geophysicae, 4, 283–294.
Montagner, J.-P., & Tanimoto, T. (1991). Global upper mantle tomography of seismic velocities and anisotropies. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 96(B12), 20337–20351.
Pollitz, F., & Snoke, J. A. (2010). Rayleigh-wave phase-velocity maps and three-dimensional shear velocity structure of the western US from local non-plane surface wave tomography. Geophysical Journal International, 180(3), 1153–1169.
Rawlinson, N., & Spakman, W. (2016). On the use of sensitivity tests in seismic tomography. Geophysical Journal International, 205(2), 1221–1243.
Ritzwoller, M. H., & Levshin, A. L. (1998). Eurasian surface wave tomography: Group velocities. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 103(B3), 4839–4878.
Ritzwoller, M. H., Shapiro, N. M., Barmin, M. P., & Levshin, A. L. (2002). Global surface wave diffraction tomography. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 107(B12), ESE-4.
Ritzwoller, M. H., Shapiro, N. M., Levshin, A. L., & Leahy, G. M. (2001). Crustal and upper mantle structure beneath Antarctica and surrounding oceans. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 106(B12), 30645–30670.
Sambridge, M., & Gumundsson, Ó. (1998). Tomographic systems of equations with irregular cells. Journal Geophysical Research, 103(B1), 773–781.
Saygin, E., Cummins, P. R., Cipta, A., Hawkins, R., Pandhu, R., Murjaya, J., et al. (2016). Imaging architecture of the Jakarta Basin, Indonesia with transdimensional inversion of seismic noise. Geophysical Journal International, 204(2), 918–931.
Shapiro, N. M., & Ritzwoller, M. H. (2002). Monte-Carlo inversion for a global shear-velocity model of the crust and upper mantle. Geophysical Journal International, 151(1), 88–105.
Shapiro, N. M., Ritzwoller, M. H., Molnar, P., & Levin, V. (2004). Thinning and flow of Tibetan crust constrained by seismic anisotropy. Science, 305(5681), 233–236.
Shen, Z.-K., Lü, J., Wang, M., & Bürgmann, R. (2005). Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan plateau. Journal Geophysical Research, 106(B4), 6793–6816.
Silveira, G., & Stutzmann, E. (2002). Anisotropic tomography of the Atlantic Ocean. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 132(4), 237–248.
Simons, F. J., Loris, I., Nolet, G., Daubechies, I. C., Voronin, S., Judd, J. S., et al. (2011). Solving or resolving global tomographic models with spherical wavelets, and the scale and sparsity of seismic heterogeneity. Geophysical Journal International, 187(2), 969–988.
Simons, F. J., van der Hilst, R. D., Montagner, J. P., & Zielhuis, A. (2002). Multimode Rayleigh wave inversion for heterogeneity and azimuthal anisotropy of the Australian upper mantle. Geophysical Journal International, 151, 738–754.
Spakman, W., & Bijwaard, H. (2001). Optimization of cell parameterizations for tomographic inverse problems. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 158(8), 1401–1423.
Spetzler, J., & Snieder, R. (2001). The effect of small scale heterogeneity on the arrival time of waves. Geophysical Journal International, 145(3), 786–796.
Tarantola, A., & Nercessian, A. (1984). Three-dimensional inversion without blocks. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 76, 299–306.
Tarantola, A., & Valette, B. (1982). Generalized nonlinear inverse problem solved using the least squares criterion. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 20(2), 219–232.
Wang, E., & Burchfiel, B. C. (2000). Late Cenozoic to Holocene deformation in southwestern Sichuan and adjacent Yunnan, China, and its role in formation of the southeastern part of the Tibetan plateau. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 112(3), 413–423.
Wang, E., Burchfiel, B. C., Royden, L. H., Chen, L., Chen, J., Li, W., et al. (1998). Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang, Red River and Dali fault systems of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China. Special Papers - Geological Society of America, 327, 1–108.
Yang, Y., Ritzwoller, M. H., Levshin, A. L., & Shapiro, N. M. (2007). Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography across Europe. Geophysical Journal International, 168(1), 259–274.
Yang, Y., Ritzwoller, M. H., Zheng, Y., Shen, W., Levshin, A. L., & Xie, Z. (2012) A synoptic view of the distribution and connectivity of the mid-crustal low velocity zone beneath Tibet. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 117(B4), B04303. doi:10.1029/2011JB008810.
Yanovskaya, T. B., & Ditmar, P. G. (1990). Smoothness criteria in surface wave tomography. Geophysical Journal International, 102(1), 63–72.
Yao, H., Beghein, C., & Van Der Hilst, R. D. (2008). Surface wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis—II. Crustal and upper-mantle structure. Geophysical Journal International, 173(1), 205–219.
Yao, H., van der Hilst, R. D., & Montagner, J.-P. (2010). Heterogeneity and anisotropy of the lithosphere of SE Tibet from surface wave array tomography. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 115(B12), B12307. doi:10.1029/2009JB007142.
Yao, H., Xu, G., Zhu, L., & Xiao, X. (2005). Mantle structure from interstation Rayleigh wave dispersion and its tectonic implication in western China and neighboring regions. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 148, 39–54.
Yoshizawa, K., & Kennett, B. (2004). Multimode surface wave tomography for the Australian region using a three-stage approach incorporating finite frequency effects. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978–2012), 109(B2), B02310. doi:10.1029/2002JB002254.
Zhang, H., & Thurber, C. H. (2005). Adaptive mesh seismic tomography based on tetrahedral and Voronoi diagrams: Application to Parkfield, California. Journal Geophysical Research, 110(B4), B04303. doi:10.1029/2004JB003186.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments, which help to significantly improve the original manuscript. Most figures are made from the Generic Mapping Tools (GMT) (http://gmt.soest.hawaii.edu/). This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41574034, 41222028), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in China (WK2080000053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Yao, H. Surface Wave Tomography with Spatially Varying Smoothing Based on Continuous Model Regionalization. Pure Appl. Geophys. 174, 937–953 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-016-1434-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-016-1434-5