Abstract
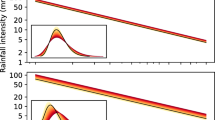
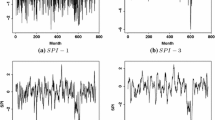
Several bimodal complex processes having great socio-economic impact exist in nature, yet more often than not it is non-trivial to find prediction rules for their regime change. Generic prediction rules for regime transition and duration of subsequent regime are given for several two-regime models. It is demonstrated that prediction rules are a universal property of a large class of bimodal processes. An effort is made to explore the applicability of generic prediction rules to real-world bimodal processes, namely the Indian summer monsoon rainfall and the Indian Ocean Dipole event. Time series representative of these phenomena are analyzed to establish their bimodality and to show that prediction rules hold well for these time series also.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arneodo, A., Coullet, P., and Tresser, C. (1981) A possible new mechanism for the onset of turbulence, Phys. Lett. A 81, 197–201.
Corti, S., Molteni, F., and Palmer, T.N. (1999) Signature of recent climate change in frequencies of natural atmospheric circulation regimes, Nature 398, 799–802.
Dwivedi, S., Mittal, A.K., and Goswami, B.N. (2006) An empirical rule for extended range prediction of duration of Indian summer monsoon breaks, Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L18801, doi:10.1029/2006GL027035.
Dwivedi, S., and Mittal, A.K. (2007) Forecasting the duration of active and break spells in intrinsic mode functions of Indian monsoon intraseasonal oscillations, Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L16827, doi:10.1029/2007GL030540.
Evans, E., Bhatti, N., Kinney, J., Pann, L., Pena, M., Yang, S.-C., Kalnay, E., and Hansen, J. (2004) RISE undergraduates find that regime changes in Lorenz’s model are predictable, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 85, 520–524.
Goswami, B.N., and Xavier, P.K. (2003) Potential predictability and extended range prediction of Indian summer monsoon breaks, Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, doi:10.1029/2003GL017810.
Kalnay, E. Atmospheric Modeling, Data Assimilation and Predictability (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 2003).
Kaufman, L. and Rousseeuw, P.J. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis (Wiley-Interscience, 1990).
Lorenz, E.N. (1963) Deterministic non-periodic flows, J. Atmos. Sci. 20, 130–141.
Mittal, A.K., Dwivedi, S. and Pandey, A.C. (2003) A study of the forced Lorenz model of relevance to monsoon predictability, Ind. J. Radio & Space Phys. 32, 209–216.
Mittal, A.K., Dwivedi, S. and Pandey, A.C. (2005) Bifurcation analysis of a paradigmatic model of monsoon prediction, Nonlin. Proc. Geophys. 12, 707–715.
Mittal, A.K., Dwivedi, S. and Yadav, R.S. (2007) Probability distribution for number of cycles between successive regime transitions for the Lorenz model, Physica D 233, 14–20, doi:10.1016/j.physd.2007.06.014.
Palmer, T.N. (1993) Extended-range atmospheric prediction and the Lorenz Model, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 74, 49–66.
Palmer, T.N. (1994) Chaos and predictability in forecasting the monsoons, Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 60A, 57–66.
Palmer, T.N. (1999) A nonlinear dynamical perspective on climate prediction, J. Clim. 12, 575–591.
Rayner, N.A., Brohan, P., Parker, D.E., Folland, C.K., Kennedy, J.J., Vanicek, M., Ansell, T., and Tett, S.F.B. (2006) Improved analyses of changes and uncertainties in sea surface temperature measured in situ since the mid-nineteenth century: the HadSST2 data set, J. Clim. 19, 446–469.
Rucklidge, A.M. (1992) Chaos in models of double convection, J. Fluid Mech. 237, 209–229.
Waliser, D.E., Lau, K.M., Stern, W. and Jones, C. (2003a) Potential predictability of the Madden-Julian oscillation, Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 84, 33–50.
Waliser, D.E., Stern, W., Schubert, S. and Lau, K.M. (2003b) Dynamic predictability of intraseasonal variability associated with the Asian summer monsoon, Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 129, 2897–2925.
Xavier, P.K., and Goswami, B.N. (2007) An analog method for real-time forecasting of summer monsoon subseasonal variability, Mon. Wea. Rev. 135, 4149–4160.
Xie, P., and Arkin, P.A. (1996) Analyses of global monthly precipitation using gauge observations, satellite estimates and numerical predictions, J. Clim. 9, 840–858.
Yadav, R.S., Dwivedi, S., and Mittal, A.K. (2005), Prediction rules for regime changes and length in a new regime for the Lorenz model, J. Atmos. Sci. 62, 2316–2321.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Prof. B. N. Goswami for providing the rainfall dataset. Authors also thank ISRO/NCAOR/DST for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, S., Mittal, A.K. Generic Prediction Rules for Regime Change in Bimodal Processes. Pure Appl. Geophys. 169, 755–761 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-011-0346-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-011-0346-7