Abstract
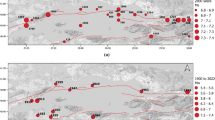
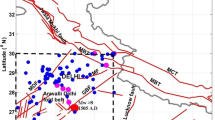
In this paper, ground motion during the Independence Day earthquake of August 15, 1950 (Mw 8.6, Ben-Menahem et al., 1974) in the northeastern part of India is estimated by seismological approaches. A hybrid simulation technique which combines the low frequency ground motion simulated from an analytical source mechanism model with the stochastically simulated high-frequency components is used for obtaining the acceleration time histories. A series of ground motion simulations are carried out to estimate the peak ground acceleration (PGA) and spectral accelerations at important cities and towns in the epicentral region. One sample PGA distribution in the epicentral region encompassing the epicenter is also obtained. It is found that PGA in the epicentral region has exceeded 1 g during this earthquake. The estimated PGA’s are validated to the extent possible using the MMI values. The simulated acceleration time histories can be used for the assessment of important engineering structures in northeastern India.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghukanth, S.T.G. Simulation of Strong Ground Motion During the 1950 Great Assam Earthquake. Pure appl. geophys. 165, 1761–1787 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-008-0403-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-008-0403-z