Abstract.
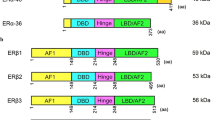
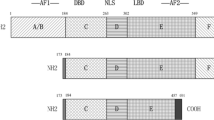
In the last decades, substances with estrogenic activity have been dispersed into the environment. Xenoestrogens act by binding to estrogen receptors, ligand-regulated transcription factors, for which two subtypes have been described, Er-α and Er-β, which are often coexpressed at variable amounts in different tissues. We investigated variations in the expression of Er-α and Er-β mRNAs following treatment with four xenoestrogens (bisphenol A, 4-tert octylphenol, 2-hydroxybiphenyl, 4-hydroxybiphenyl) and with 17β-estradiol in estrogen-sensitive (T47D) and estrogen-insensitive (BT20) breast cancer cell lines. Although to a variable extent, both estradiol and the tested xenoestrogens increased the expression of Er-β mRNA, whereas a slight effect on Er-α was observed only in T47D cells. Upregulation of Er-β expression by estradiol and xenoestrogens was observed only in the presence of detectable Er-α protein levels. These findings indicate a regulatory role for ER-β in ER-α-mediated transcription and a role for ER-β in mediating xenoestrogen toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 5 November 2002; received after revision 12 December 2002; accepted 23 January 2003
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappelletti, V., Saturno, G., Miodini, P. et al. Selective modulation of ER-β by estradiol and xenoestrogens in human breast cancer cell lines. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60, 567–576 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180300048
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180300048