Abstract
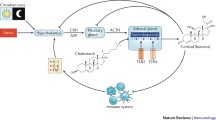
Growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) can modulate the development and function of the immune system. In this chapter, we present data on the expression of receptors for GH and IGFs and the in vitro and in vivo effects of these proteins. We show that expression of GH and IGFs in the immune system opens up the possibility that these proteins are not only involved in endocrine control of the immune system but can also play a role as local growth and differentiation factors (cytokines). Endocrine control of GH could be direct or mediated via endocrine or autocrine/paracrine IGF-I. In addition, GH can act as an autocrine or paracrine factor itself. Furthermore, IGF-I in the immune system has been shown to be regulated by cytokines, such as interleukin-1 and interferon-γ, alluding to a cytokine-like function of IGF-I. In addition to data on the function of GH and IGF-I in the immune system, we present new findings which imply a possible function of IGF-II and IGF-binding proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Buul-Offers, S., Kooijman, R. The role of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factors in the immune system. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 54, 1083–1094 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050237
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050237