Abstract
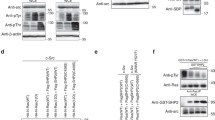
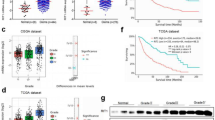
Activation of the Ras signaling pathway promotes the growth of malignant human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Mutations in Ras are rare in GBM, elevated levels of activated Ras are prevalently observed in GBM. However, the potential mechanism of how Ras is activated in GBM remains unclear. In this study, we screened a new interacted protein of Ras, PHLDA1. Our findings confirmed that PHLDA1 acted as an oncogene and promoted glioma progression and recurrence. We demonstrated that PHLDA1 was upregulated in GBM tissues and cells. PHLDA1 overexpression promoted cell proliferation and tumor growth. In terms of mechanism, PHLDA1 promoted cell proliferation by regulating Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk signaling pathway. Moreover, Src promotes GTPase activity of Ras via tyrosine 32 phosphorylation. PHLDA1 and Src competed for binding with Ras, inhibiting Ras phosphorylation by Src and rescuing Ras activity. This study may provide a new idea of the molecular mechanism underlying glioma progression and a novel potential therapeutic target for comprehensive glioblastoma treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data sets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Louis DN, Holland EC, Cairncross JG (2001) Glioma classification: a molecular reappraisal. Am J Pathol 159(3):779–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61750-6
Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (1999) Primary and secondary glioblastomas: from concept to clinical diagnosis. Neuro Oncol 1(1):44–51. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/1.1.44
Holland EC (2001) Gliomagenesis: genetic alterations and mouse models. Nat Rev Genet 2(2):120–129. https://doi.org/10.1038/35052535
Jiang BH, Aoki M, Zheng JZ, Li J, Vogt PK (1999) Myogenic signaling of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase requires the serine-threonine kinase Akt/protein kinase B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(5):2077–2081. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.5.2077
Mattingly RR (2013) Activated ras as a therapeutic target: constraints on directly targeting ras isoforms and wild-type versus mutated proteins. ISRN Oncol 2013:536529. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/536529
DeClue JE, Papageorge AG, Fletcher JA, Diehl SR, Ratner N, Vass WC, Lowy DR (1992) Abnormal regulation of mammalian p21ras contributes to malignant tumor growth in von Recklinghausen (type 1) neurofibromatosis. Cell 69(2):265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90407-4
Haslam RJ, Koide HB, Hemmings BA (1993) Pleckstrin domain homology. Nature 363(6427):309–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/363309b0
Ingley E, Hemmings BA (1994) Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains in signal transduction. J Cell Biochem 56(4):436–443. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.240560403
Saraste M, Hyvonen M (1995) Pleckstrin homology domains: a fact file. Curr Opin Struct Biol 5(3):403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-440x(95)80104-9
Nagai MA, Fregnani JH, Netto MM, Brentani MM, Soares FA (2007) Down-regulation of PHLDA1 gene expression is associated with breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9475-6
Neef R, Kuske MA, Prols E, Johnson JP (2002) Identification of the human PHLDA1/TDAG51 gene: down-regulation in metastatic melanoma contributes to apoptosis resistance and growth deregulation. Cancer Res 62(20):5920–5929
Gomes I, Xiong W, Miki T, Rosner MR (1999) A proline- and glutamine-rich protein promotes apoptosis in neuronal cells. J Neurochem 73(2):612–622. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730612.x
Hossain GS, van Thienen JV, Werstuck GH, Zhou J, Sood SK, Dickhout JG, de Koning AB, Tang D, Wu D, Falk E, Poddar R, Jacobsen DW, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ, Austin RC (2003) TDAG51 is induced by homocysteine, promotes detachment-mediated programmed cell death, and contributes to the cevelopment of atherosclerosis in hyperhomocysteinemia. J Biol Chem 278(32):30317–30327. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M212897200
Hayashida N, Inouye S, Fujimoto M, Tanaka Y, Izu H, Takaki E, Ichikawa H, Rho J, Nakai A (2006) A novel HSF1-mediated death pathway that is suppressed by heat shock proteins. EMBO J 25(20):4773–4783. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601370
Oberst MD, Beberman SJ, Zhao L, Yin JJ, Ward Y, Kelly K (2008) TDAG51 is an ERK signaling target that opposes ERK-mediated HME16C mammary epithelial cell transformation. BMC Cancer 8:189. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-8-189
Hinz T, Flindt S, Marx A, Janssen O, Kabelitz D (2001) Inhibition of protein synthesis by the T cell receptor-inducible human TDAG51 gene product. Cell Signal 13(5):345–352
Zhao P, Lu Y, Liu L (2015) Correlation of decreased expression of PHLDA1 protein with malignant phenotype of gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(5):5230–5235
Sakthianandeswaren A, Christie M, D’Andreti C, Tsui C, Jorissen RN, Li S, Fleming NI, Gibbs P, Lipton L, Malaterre J, Ramsay RG, Phesse TJ, Ernst M, Jeffery RE, Poulsom R, Leedham SJ, Segditsas S, Tomlinson IP, Bernhard OK, Simpson RJ, Walker F, Faux MC, Church N, Catimel B, Flanagan DJ, Vincan E, Sieber OM (2011) PHLDA1 expression marks the putative epithelial stem cells and contributes to intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 71(10):3709–3719. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2342
Murata T, Sato T, Kamoda T, Moriyama H, Kumazawa Y, Hanada N (2014) Differential susceptibility to hydrogen sulfide-induced apoptosis between PHLDA1-overexpressing oral cancer cell lines and oral keratinocytes: role of PHLDA1 as an apoptosis suppressor. Exp Cell Res 320(2):247–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.10.023
Wang R, Zhang L, Yin D, Mufson RA, Shi Y (1998) Protein kinase C regulates Fas (CD95/APO-1) expression. J Immunol 161(5):2201–2207
Carlisle RE, Heffernan A, Brimble E, Liu L, Jerome D, Collins CA, Mohammed-Ali Z, Margetts PJ, Austin RC, Dickhout JG (2012) TDAG51 mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human proximal tubular epithelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 303(3):F467-481. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00481.2011
Chen Y, Takikawa M, Tsutsumi S, Yamaguchi Y, Okabe A, Shimada M, Kawase T, Sada A, Ezawa I, Takano Y, Nagata K, Suzuki Y, Semba K, Aburatani H, Ohki R (2018) PHLDA1, another PHLDA family protein that inhibits Akt. Cancer Sci 109(11):3532–3542. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13796
Avruch J, Khokhlatchev A, Kyriakis JM, Luo Z, Tzivion G, Vavvas D, Zhang XF (2001) Ras activation of the Raf kinase: tyrosine kinase recruitment of the MAP kinase cascade. Recent Prog Horm Res 56:127–155. https://doi.org/10.1210/rp.56.1.127
Bunda S, Heir P, Srikumar T, Cook JD, Burrell K, Kano Y, Lee JE, Zadeh G, Raught B, Ohh M (2014) Src promotes GTPase activity of Ras via tyrosine 32 phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(36):E3785-3794. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1406559111
Bunda S, Burrell K, Heir P, Zeng L, Alamsahebpour A, Kano Y, Raught B, Zhang ZY, Zadeh G, Ohh M (2015) Inhibition of SHP2-mediated dephosphorylation of Ras suppresses oncogenesis. Nat Commun 6:8859. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9859
Simanshu DK, Nissley DV, McCormick F (2017) RAS proteins and their regulators in human disease. Cell 170(1):17–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.009
Iversen L, Tu HL, Lin WC, Christensen SM, Abel SM, Iwig J, Wu HJ, Gureasko J, Rhodes C, Petit RS, Hansen SD, Thill P, Yu CH, Stamou D, Chakraborty AK, Kuriyan J, Groves JT (2014) Molecular kinetics. Ras activation by SOS: allosteric regulation by altered fluctuation dynamics. Science 345(6192):50–54. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1250373
Hai J, Liu S, Bufe L, Do K, Chen T, Wang X, Ng C, Li S, Tsao MS, Shapiro GI, Wong KK (2017) Synergy of WEE1 and mTOR inhibition in mutant KRAS-driven lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res 23(22):6993–7005. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1098
Saturno G, Lopes F, Niculescu-Duvaz I, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Zambon A, Davies L, Johnson L, Preece N, Lee R, Viros A, Holovanchuk D, Pedersen M, McLeary R, Lorigan P, Dhomen N, Fisher C, Banerji U, Dean E, Krebs MG, Gore M, Larkin J, Marais R, Springer C (2021) The paradox-breaking panRAF plus SRC family kinase inhibitor, CCT3833, is effective in mutant KRAS-driven cancers. Ann Oncol 32(2):269–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.10.483
Johnson EO, Chang KH, de Pablo Y, Ghosh S, Mehta R, Badve S, Shah K (2011) PHLDA1 is a crucial negative regulator and effector of Aurora A kinase in breast cancer. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 16):2711–2722. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.084970
Li G, Wang X, Hibshoosh H, Jin C, Halmos B (2014) Modulation of ErbB2 blockade in ErbB2-positive cancers: the role of ErbB2 Mutations and PHLDA1. PLoS ONE 9(9):e106349. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106349
Coutinho-Camillo CM, Lourenco SV, Nonogaki S, Vartanian JG, Nagai MA, Kowalski LP, Soares FA (2013) Expression of PAR-4 and PHLDA1 is prognostic for overall and disease-free survival in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch 463(1):31–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-013-1438-9
Chiu ST, Hsieh FJ, Chen SW, Chen CL, Shu HF, Li H (2005) Clinicopathologic correlation of up-regulated genes identified using cDNA microarray and real-time reverse transcription-PCR in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(2):437–443. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0396
Ren L, Mendoza A, Zhu J, Briggs JW, Halsey C, Hong ES, Burkett SS, Morrow J, Lizardo MM, Osborne T, Li SQ, Luu HH, Meltzer P, Khanna C (2015) Characterization of the metastatic phenotype of a panel of established osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget 6(30):29469–29481. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5177
Liu L, Shi Y, Shi J, Wang H, Sheng Y, Jiang Q, Chen H, Li X, Dong J (2019) The long non-coding RNA SNHG1 promotes glioma progression by competitively binding to miR-194 to regulate PHLDA1 expression. Cell Death Dis 10(6):463. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1698-7
Buday L, Vas V (2020) Novel regulation of Ras proteins by direct tyrosine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Cancer Metastasis Rev 39(4):1067–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09918-2
Buday L, Downward J (2008) Many faces of Ras activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1786(2):178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.05.001
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan (162300410336); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82073075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD and KL designed and supervised the experiments; JW prepared the manuscript; JW, NY, YH, MW, LY, performed experiments; JW, ML, SP and XL performed data analysis and interpretation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval was obtained by the Ethics Review Commission of Zhengzhou University (CUHCI2020001).
Consent to participate
As no human subjects were involved, consent to participate is not relevant to this manuscript submission.
Consent for publication
All authors have given consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yao, N., Hu, Y. et al. PHLDA1 promotes glioblastoma cell growth via sustaining the activation state of Ras. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 520 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04538-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04538-1