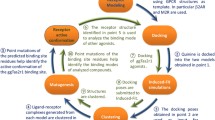
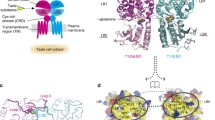
Abstract
Bitter taste receptors (TAS2Rs) are a poorly understood subgroup of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The experimental structure of these receptors has yet to be determined, and key-residues controlling their function remain mostly unknown. We designed an integrative approach to improve comparative modeling of TAS2Rs. Using current knowledge on class A GPCRs and existing experimental data in the literature as constraints, we pinpointed conserved motifs to entirely re-align the amino-acid sequences of TAS2Rs. We constructed accurate homology models of human TAS2Rs. As a test case, we examined the accuracy of the TAS2R16 model with site-directed mutagenesis and in vitro functional assays. This combination of in silico and in vitro results clarifies sequence-function relationships and proposes functional molecular switches that encode agonist sensing and downstream signaling mechanisms within mammalian TAS2Rs sequences.




taken from PDB code 5JQH
Similar content being viewed by others
Code and data availability
The scripts used to generate and analyze the models as well as PDB files of TAS2Rs 3D models with the highest meta-score have been deposited on GitHub. (https://github.com/chemosim-lab/TAS2R_data).
References
Lindemann B (2001) Receptors and transduction in taste. Nature 413(6852):219–225
Meyerhof W (2005) Elucidation of mammalian bitter taste. In: Reviews of physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 37–72
Mueller KL, Hoon MA, Erlenbach I, Chandrashekar J, Zuker CS, Ryba NJ (2005) The receptors and coding logic for bitter taste. Nature 434(7030):225–229
Lee S-J, Depoortere I, Hatt H (2019) Therapeutic potential of ectopic olfactory and taste receptors. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 18(2):116–138
Foster S, Blank K, See Hoe L, Behrens M, Meyerhof W, Peart J, Thomas W (2014) Novel bitter taste receptor ligands elicit G protein-dependent negative inotropic effects in mouse heart (LB572). FASEB J. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.28.1_supplement.lb572
Malki A, Fiedler J, Fricke K, Ballweg I, Pfaffl MW, Krautwurst D (2015) Class I odorant receptors, TAS1R and TAS2R taste receptors, are markers for subpopulations of circulating leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol 97(3):533–545
Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2000) A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell 100(6):693–702
Fredriksson R, Lagerström MC, Lundin L-G, Schiöth HB (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol 63(6):1256–1272
Nordström KJ, Sällman Almén M, Edstam MM, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB (2011) Independent HHsearch, Needleman–Wunsch-based, and motif analyses reveal the overall hierarchy for most of the G protein-coupled receptor families. Mol Biol Evol 28(9):2471–2480
Krishnan A, Almén MS, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB (2012) The origin of GPCRs: identification of mammalian like Rhodopsin, Adhesion, Glutamate and Frizzled GPCRs in fungi. PLoS ONE 7(1):9817
Di Pizio A, Levit A, Slutzki M, Behrens M, Karaman R, Niv MY (2016) Comparing Class A GPCRs to bitter taste receptors: structural motifs, ligand interactions and agonist-to-antagonist ratios. Methods Cell Biol 132:401–427
Cvicek V, Goddard WA III, Abrol R (2016) Structure-based sequence alignment of the transmembrane domains of all human GPCRs: phylogenetic, structural and functional implications. PLoS Comput Biol 12(3):e1004805
Munk C, Isberg V, Mordalski S, Harpsøe K, Rataj K, Hauser A, Kolb P, Bojarski A, Vriend G, Gloriam D (2016) GPCRdb: the G protein-coupled receptor database–an introduction. Br J Pharmacol 173(14):2195–2207
Deupi X, Standfuss J (2011) Structural insights into agonist-induced activation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr Opin Struct Biol 21(4):541–551
Zhou Q, Yang D, Wu M, Guo Y, Guo W, Zhong L, Cai X, Dai A, Jang W, Shakhnovich EI (2019) Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.50279
de March CA, Yu Y, Ni MJ, Adipietro KA, Matsunami H, Ma M, Golebiowski J (2015) Conserved residues control activation of mammalian G protein-coupled odorant receptors. J Am Chem Soc 137(26):8611–8616
Schönegge A-M, Gallion J, Picard L-P, Wilkins AD, Le Gouill C, Audet M, Stallaert W, Lohse MJ, Kimmel M, Lichtarge O (2017) Evolutionary action and structural basis of the allosteric switch controlling β 2 AR functional selectivity. Nat Commun 8(1):1–12
de March CA, Topin J, Bruguera E, Novikov G, Ikegami K, Matsunami H, Golebiowski J (2018) Odorant receptor 7D4 activation dynamics. Angew Chem 130(17):4644–4648
Sakurai T, Misaka T, Ishiguro M, Masuda K, Sugawara T, Ito K, Kobayashi T, Matsuo S, Ishimaru Y, Asakura T (2010) Characterization of the β-d-glucopyranoside binding site of the human bitter taste receptor hTAS2R16. J Biol Chem 285(36):28373–28378
Brockhoff A, Behrens M, Niv MY, Meyerhof W (2010) Structural requirements of bitter taste receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(24):11110–11115
Singh N, Pydi SP, Upadhyaya J, Chelikani P (2011) Structural basis of activation of bitter taste receptor T2R1 and comparison with Class A G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). J Biol Chem 286(41):36032–36041
Karaman R, Nowak S, Di Pizio A, Kitaneh H, Abu-Jaish A, Meyerhof W, Niv MY, Behrens M (2016) Probing the binding pocket of the broadly tuned human bitter taste receptor TAS2R14 by chemical modification of cognate agonists. Chem Biol Drug Des 88(1):66–75
Fierro F, Giorgetti A, Carloni P, Meyerhof W, Alfonso-Prieto M (2019) Dual binding mode of “bitter sugars” to their human bitter taste receptor target. Sci Rep 9(1):1–16
Sandal M, Behrens M, Brockhoff A, Musiani F, Giorgetti A, Carloni P, Meyerhof W (2015) Evidence for a transient additional ligand binding site in the TAS2R46 bitter taste receptor. J Chem Theory Comput 11(9):4439–4449
Di Pizio A, Kruetzfeldt L-M, Cheled-Shoval S, Meyerhof W, Behrens M, Niv MY (2017) Ligand binding modes from low resolution GPCR models and mutagenesis: chicken bitter taste receptor as a test-case. Sci Rep 7(1):1–11
Thomas A, Sulli C, Davidson E, Berdougo E, Phillips M, Puffer BA, Paes C, Doranz BJ, Rucker JB (2017) The Bitter Taste Receptor TAS2R16 Achieves High Specificity and Accommodates Diverse Glycoside Ligands by using a Two-faced Binding Pocket. Sci Rep 7(1):7753
Biarnés X, Marchiori A, Giorgetti A, Lanzara C, Gasparini P, Carloni P, Born S, Brockhoff A, Behrens M, W, (2010) Meyerhof, Insights into the binding of Phenyltiocarbamide (PTC) agonist to its target human TAS2R38 bitter receptor. PLoS ONE 5(8):e12394
Prasad Pydi S, Upadhyaya J, Singh N, Pal Bhullar R, Chelikani P (2012) Recent advances in structure and function studies on human bitter taste receptors. Curr Prot Pept Sci 13(6):501–508
Slack JP, Brockhoff A, Batram C, Menzel S, Sonnabend C, Born S, Galindo MM, Kohl S, Thalmann S, Ostopovici-Halip L (2010) Modulation of bitter taste perception by a small molecule hTAS2R antagonist. Curr Biol 20(12):1104–1109
Wang Y, Zajac AL, Lei W, Christensen CM, Margolskee RF, Bouysset C, Golebiowski J, Zhao H, Fiorucci S, Jiang P (2019) Metal ions activate the human taste receptor TAS2R7. Chem Senses 44(5):339–347
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7(1):539
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DM, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25(9):1189–1191
Lomize MA, Pogozheva ID, Joo H, Mosberg HI, Lomize AL (2012) OPM database and PPM web server: resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1):D370–D376
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W296–W303
Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB (2005) The repertoire of G-protein–coupled receptors in fully sequenced genomes. Mol Pharmacol 67(5):1414–1425
Yang S, Wu Y, Xu T-H, de Waal PW, He Y, Pu M, Chen Y, DeBruine ZJ, Zhang B, Zaidi SA (2018) Crystal structure of the Frizzled 4 receptor in a ligand-free state. Nature 560(7720):666–670
Zhang X, Zhao F, Wu Y, Yang J, Han GW, Zhao S, Ishchenko A, Ye L, Lin X, Ding K (2017) Crystal structure of a multi-domain human smoothened receptor in complex with a super stabilizing ligand. Nat Commun 8(1):1–10
Tsai C-J, Pamula F, Nehmé R, Mühle J, Weinert T, Flock T, Nogly P, Edwards PC, Carpenter B, Gruhl T (2018) Crystal structure of rhodopsin in complex with a mini-Go sheds light on the principles of G protein selectivity. Sci Adv 4(9):eaat7052
Miller-Gallacher JL, Nehme R, Warne T, Edwards PC, Schertler GF, Leslie AG, Tate CG (2014) The 2.1 Å resolution structure of cyanopindolol-bound β1-adrenoceptor identifies an intramembrane Na+ ion that stabilises the ligand-free receptor. PLoS ONE 9(3):e92727
Staus DP, Strachan RT, Manglik A, Pani B, Kahsai AW, Kim TH, Wingler LM, Ahn S, Chatterjee A, Masoudi A (2016) Allosteric nanobodies reveal the dynamic range and diverse mechanisms of G-protein-coupled receptor activation. Nature 535(7612):448–452
Zhang H, Unal H, Gati C, Han GW, Liu W, Zatsepin NA, James D, Wang D, Nelson G, Weierstall U (2015) Structure of the angiotensin receptor revealed by serial femtosecond crystallography. Cell 161(4):833–844
Wu B, Chien EY, Mol CD, Fenalti G, Liu W, Katritch V, Abagyan R, Brooun A, Wells P, Bi FC (2010) Structures of the CXCR4 chemokine GPCR with small-molecule and cyclic peptide antagonists. Science 330(6007):1066–1071
Peng Y, McCorvy JD, Harpsøe K, Lansu K, Yuan S, Popov P, Qu L, Pu M, Che T, Nikolajsen LF (2018) 5-HT2C receptor structures reveal the structural basis of GPCR polypharmacology. Cell 172(4):719-730.e14
Webb B, Sali A (2016) Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinform 54(1):5.6.1-5.6.37
Sandal M, Duy TP, Cona M, Zung H, Carloni P, Musiani F, Giorgetti A (2013) GOMoDo: a GPCRs online modeling and docking webserver. PLoS ONE 8(9):e74092
Gowers RJ, Linke M, Barnoud J, Reddy TJE, Melo MN, Seyler SL, Domanski J, Dotson DL, Buchoux S, Kenney IM (2019) MDAnalysis: a Python package for the rapid analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. Los Alamos National Lab(LANL), Los Alamos
Virtanen P, Gommers R, Oliphant TE, Haberland M, Reddy T, Cournapeau D, Burovski E, Peterson P, Weckesser W, Bright J (2020) SciPy 1.0: fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat Method 17(3):261–272
Harris CR, Millman KJ, van der Walt SJ, Gommers R, Virtanen P, Cournapeau D, Wieser E, Taylor J, Berg S, Smith NJ (2020) Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585(7825):357–362
Mannige RV, Kundu J, Whitelam S (2016) The Ramachandran number: an order parameter for protein geometry. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0160023
Studer G, Biasini M, Schwede T (2014) Assessing the local structural quality of transmembrane protein models using statistical potentials (QMEANBrane). Bioinformatics 30(17):i505–i511
Ueda T, Ugawa S, Yamamura H, Imaizumi Y, Shimada S (2003) Functional interaction between T2R taste receptors and G-protein α subunits expressed in taste receptor cells. J Neurosci 23(19):7376–7380
Di Pizio A, Levit A, Slutzki M, et al (2016) Comparing Class A GPCRs to bitter taste receptors. In: Methods in Cell Biology. Elsevier Ltd, pp 401–427.
Behrens M, Ziegler F (2020) Structure-function analyses of human bitter taste receptors—where do we stand? Molecules 25(19):4423
Pydi SP, Bhullar RP, Chelikani P (2012) Constitutively active mutant gives novel insights into the mechanism of bitter taste receptor activation. J Neurochem 122(3):537–544
Pydi SP, Singh N, Upadhyaya J, Bhullar RP, Chelikani P (2014) The third intracellular loop plays a critical role in bitter taste receptor activation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1838(1):231–236
Pydi SP, Sobotkiewicz T, Billakanti R, Bhullar RP, Loewen MC, Chelikani P (2014) Amino acid derivatives as bitter taste receptor (T2R) blockers. J Biol Chem 289(36):25054–25066
Upadhyaya J, Singh N, Bhullar RP, Chelikani P (2015) The structure–function role of C-terminus in human bitter taste receptor T2R4 signaling. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1848(7):1502–1508
Jaggupilli A, Singh N, De Jesus VC, Gounni MS, Dhanaraj P, Chelikani P (2019) Chemosensory bitter taste receptors (T2Rs) are activated by multiple antibiotics. FASEB J 33(1):501–517
Liu K, Jaggupilli A, Premnath D, Chelikani P (2018) Plasticity of the ligand binding pocket in the bitter taste receptor T2R7. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1860(5):991–999
Dotson CD, Zhang L, Xu H, Shin Y-K, Vigues S, Ott SH, Elson AE, Choi HJ, Shaw H, Egan JM (2008) Bitter taste receptors influence glucose homeostasis. PLoS ONE 3(12):e3974
Born S, Levit A, Niv MY, Meyerhof W, Behrens M (2013) The human bitter taste receptor TAS2R10 is tailored to accommodate numerous diverse ligands. J Neurosci 33(1):201–213
Nowak S, Di Pizio A, Levit A, Niv MY, Meyerhof W, Behrens M (2018) Reengineering the ligand sensitivity of the broadly tuned human bitter taste receptor TAS2R14. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 1862(10):2162–2173
Shaik FA, Jaggupilli A, Chelikani P (2019) Highly conserved intracellular H208 residue influences agonist selectivity in bitter taste receptor T2R14. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1861(12):183057
Soranzo N, Bufe B, Sabeti PC, Wilson JF, Weale ME, Marguerie R, Meyerhof W, Goldstein DB (2005) Positive selection on a high-sensitivity allele of the human bitter-taste receptor TAS2R16. Curr Biol 15(14):1257–1265
Greene TA, Alarcon S, Thomas A, Berdougo E, Doranz BJ, Breslin PA, Rucker JB (2011) Probenecid inhibits the human bitter taste receptor TAS2R16 and suppresses bitter perception of salicin. PLoS ONE 6(5):e20123
Thomas A, Sulli C, Davidson E, Berdougo E, Phillips M, Puffer BA, Paes C, Doranz BJ, Rucker JB (2017) The bitter taste receptor TAS2R16 achieves high specificity and accommodates diverse glycoside ligands by using a two-faced binding pocket. Sci Rep 7(1):1–15
Biarnés X, Marchiori A, Giorgetti A, Lanzara C, Gasparini P, Carloni P, Born S, Brockhoff A, Behrens M, Meyerhof W (2010) Insights into the binding of Phenyltiocarbamide (PTC) agonist to its target human TAS2R38 bitter receptor. PLoS ONE 5(8):e12394
Marchiori A, Capece L, Giorgetti A, Gasparini P, Behrens M, Carloni P, Meyerhof W (2013) Coarse-grained/molecular mechanics of the TAS2R38 bitter taste receptor: experimentally-validated detailed structural prediction of agonist binding. PLoS ONE 8(5):e64675
Charlier L, Topin J, Ronin C, Kim S-K, Goddard WA, Efremov R, Golebiowski J (2012) How broadly tuned olfactory receptors equally recognize their agonists. Human OR1G1 as a test case. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(24):4205–4213
Bushdid C, Claire A, Topin J, Do M, Matsunami H, Golebiowski J (2019) Mammalian class I odorant receptors exhibit a conserved vestibular-binding pocket. Cell Mol Life Sci 76(5):995–1004
Fierro F, Suku E, Alfonso-Prieto M, Giorgetti A, Cichon S, Carloni P (2017) Agonist binding to chemosensory receptors: a systematic bioinformatics analysis. Front Mol Biosci 4:63
Katritch V, Fenalti G, Abola EE, Roth BL, Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2014) Allosteric sodium in class A GPCR signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 39(5):233–244
Miao Y, Nichols SE, Gasper PM, Metzger VT, McCammon JA (2013) Activation and dynamic network of the M2 muscarinic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(27):10982–10987
Venkatakrishnan A, Deupi X, Lebon G, Tate CG, Schertler GF, Babu MM (2013) Molecular signatures of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 494(7436):185–194
Dalton JA, Lans I, Giraldo J (2015) Quantifying conformational changes in GPCRs: glimpse of a common functional mechanism. BMC Bioinformatics 16(1):1–15
Levit A, Beuming T, Krilov G, Sherman W, Niv MY (2014) Predicting GPCR promiscuity using binding site features. J Chem Inf Model 54(1):184–194
Kim D, Cho S, Castaño MA, Panettieri RA, Woo JA, Liggett SB (2019) Biased TAS2R bronchodilators inhibit airway smooth muscle growth by downregulating phosphorylated extracellular signal–regulated kinase 1/2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 60(5):532–540
Flock T, Hauser AS, Lund N, Gloriam DE, Balaji S, Babu MM (2017) Selectivity determinants of GPCR–G-protein binding. Nature 545(7654):317–322
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Xiaojing Cong for fruitful discussion and critical review of the manuscript. This work was funded by the French Ministry of Higher Education and Research [PhD Fellowship to CB], by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) [grant number NRF2020R1A2C2004661], by GIRACT (Geneva, Switzerland) [9th European PhD in Flavor Research Bursaries for first year students to CB], and the Gen Foundation (Registered UK Charity No. 1071026), a charitable trust that primarily funds research in natural sciences, particularly food sciences/technology [grant to CB and JT]. We also benefited from funding by the French government through the UCAJEDI “Investments in the Future” project, managed by the ANR [grant No. ANR-15-IDEX-01 to SF and JG]. Computation for the work described in this paper was supported by the Université Côte d’Azur’s Center for High-Performance Computing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JT†, CB†, and JP performed numerical modeling. YK and MR conducted functional assays. JT, CB, and SF performed data curation. JT, CB, JP, YK, and MR conducted formal analyses. JT, SF, and JG supervised and managed the study and wrote the paper. MR and JG provided resources for this study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topin, J., Bouysset, C., Pacalon, J. et al. Functional molecular switches of mammalian G protein-coupled bitter-taste receptors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 7605–7615 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03968-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03968-7