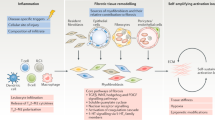
Abstract
Gremlin-1 is part of the TGF-β superfamily and is a BMP antagonist that blocks BMP signalling to precisely control BMP gradients. Gremlin-1 is primarily involved in organogenesis and limb patterning however, has recently been described as being involved in fibrotic diseases. Initially described as a key factor involved in diabetic kidney fibrosis due to being induced by high glucose, it has now been described as being associated with lung, liver, eye, and skin fibrosis. This suggests that it is a key conserved molecule mediating fibrotic events irrespective of organ. It appears that Gremlin-1 may have effects mediated by BMP-dependent and independent pathways. The aim of this review is to evaluate the role of Gremlin-1 in fibrosis, its mechanisms and if this can be targeted therapeutically in fibrotic diseases, which currently have very limited treatment options and are highly prevalent.



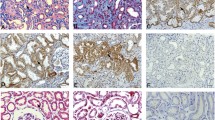
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
NA.
References
Brazil DP et al (2015) BMP signalling: agony and antagony in the family. Trends Cell Biol 25(5):249–264
Sneddon JB et al (2006) Bone morphogenetic protein antagonist gremlin 1 is widely expressed by cancer-associated stromal cells and can promote tumor cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(40):14842–14847
McMahon R et al (2000) IHG-2, a Mesangial Cell Gene induced by high glucose, is human gremlin: regulation by extracellular glucose concentration, cyclic mechanical strain, and transforming growth factor-β1. J Biol Chem 275(14):9901–9904
Koli K et al (2006) Bone morphogenetic protein-4 inhibitor gremlin is overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 169(1):61–71
Boers W et al (2006) Transcriptional profiling reveals novel markers of liver fibrogenesis: gremlin and insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 281(24):16289–16295
O’Reilly S et al (2014) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) trans signaling drives a STAT3-dependent pathway that leads to hyperactive transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling promoting SMAD3 activation and fibrosis via Gremlin protein. J Biol Chem 289(14):9952–9960
Topol LZ et al (1997) Identification of drm, a novel gene whose expression is suppressed in transformed cells and which can inhibit growth of normal but not transformed cells in culture. Mol Cell Biol 17(8):4801–4810
Church RH et al (2015) Gremlin1 preferentially binds to bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and BMP-4 over BMP-7. Biochem J 466(1):55–68
Allendorph GP, Vale WW, Choe S (2006) Structure of the ternary signaling complex of a TGF-beta superfamily member. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(20):7643–7648
Zeller R, López-Ríos J, Zuniga A (2009) Vertebrate limb bud development: moving towards integrative analysis of organogenesis. Nat Rev Genet 10(12):845–858
Roxburgh SA et al (2009) Allelic depletion of grem1 attenuates diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes 58(7):1641–1650
Khokha MK et al (2003) Gremlin is the BMP antagonist required for maintenance of Shh and Fgf signals during limb patterning. Nat Genet 34(3):303–307
Michos O et al (2004) Gremlin-mediated BMP antagonism induces the epithelial-mesenchymal feedback signaling controlling metanephric kidney and limb organogenesis. Development 131(14):3401–3410
Zhang Q et al (2010) In vivo delivery of Gremlin siRNA plasmid reveals therapeutic potential against diabetic nephropathy by recovering bone morphogenetic protein-7. PLoS ONE 5(7):e11709
Mitola S et al (2010) Gremlin is a novel agonist of the major proangiogenic receptor VEGFR2. Blood 116(18):3677–3680
Park SA et al (2020) Gremlin-1 augments the oestrogen-related receptor α signalling through EGFR activation: implications for the progression of breast cancer. Br J Cancer 123(6):988–999
Dutton LR et al (2019) No evidence of Gremlin1-mediated activation of VEGFR2 signaling in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 294(48):18041–18045
Ji C et al (2016) Gremlin inhibits UV-induced skin cell damages via activating VEGFR2-Nrf2 signaling. Oncotarget 7(51):84748–84757
Müller I et al (2013) Gremlin-1 is an inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and attenuates atherosclerotic plaque growth in ApoE-/- Mice. J Biol Chem 288(44):31635–31645
Worthley DL et al (2015) Gremlin 1 identifies a skeletal stem cell with bone, cartilage, and reticular stromal potential. Cell 160(1–2):269–284
Clark KC et al (2020) Targeted disruption of bone marrow stromal cell-derived Gremlin1 limits multiple myeloma disease progression in vivo. Cancers 12(8):2149
Hinz B, Lagares D (2020) Evasion of apoptosis by myofibroblasts: a hallmark of fibrotic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16(1):11–31
Hinchcliff M, O’Reilly S (2020) Current and potential new targets in systemic sclerosis therapy: a new hope. Curr Rheumatol Rep 22(8):42
Henderson J, Distler J, O’Reilly S (2019) The role of epigenetic modifications in systemic sclerosis: a druggable target. Trends Mol Med 25(5):395–411
Dolan V et al (2005) Expression of gremlin, a bone morphogenetic protein antagonist, in human diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 45(6):1034–1039
McKnight AJ et al (2010) A GREM1 gene variant associates with diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(5):773–781
Walsh DW et al (2008) Co-regulation of Gremlin and Notch signalling in diabetic nephropathy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Mol Basis Dis 1782(1):10–21
Church RH et al (2017) Gremlin1 plays a key role in kidney development and renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 312(6):F1141–F1157
Marchant V et al (2015) Tubular overexpression of Gremlin in transgenic mice aggravates renal damage in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 309(6):F559–F568
Murphy M et al (2008) IHG-1 amplifies TGF-beta1 signaling and is increased in renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(9):1672–1680
Marquez-Exposito L et al (2018) Gremlin regulates tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition via VEGFR2: potential role in renal fibrosis. Front Pharmacol 9:1195
Rodrigues-Diez R et al (2014) Gremlin activates the Smad pathway linked to Epithelial Mesenchymal Transdifferentiation in cultured Tubular Epithelial cells. BioMed Res Int 2014:802841
Lavoz C et al (2015) Gremlin regulates renal inflammation via the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 pathway. J Pathol 236(4):407–420
Myllärniemi M et al (2008) Gremlin localization and expression levels partially differentiate idiopathic interstitial pneumonia severity and subtype. J Pathol 214(4):456–463
Myllärniemi M et al (2008) Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177(3):321–329
Farkas L et al (2011) Transient overexpression of Gremlin results in Epithelial activation and reversible fibrosis in rat lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44(6):870–878
Murphy N et al (2016) Altered expression of bone morphogenetic protein accessory proteins in murine and human pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 186(3):600–615
Epstein Shochet G et al (2020) TGF-β pathway activation by idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) fibroblast derived soluble factors is mediated by IL-6 trans-signaling. Respir Res 21(1):56
Duffy L et al (2021) Bone Morphogenetic Protein Antagonist Gremlin-1 Increases Myofibroblast Transition in Dermal Fibroblasts: implications for systemic sclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:1451
Oreilly S (2021) Circulating Gremlin-1 is elevated in systemic sclerosis patients. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. https://doi.org/10.1177/23971983211036571
Zeng X-Y et al (2016) Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation through downregulation of gremlin1 expression by the miR-23b/27b cluster. Oncotarget 7(52):86198–86210
O’Reilly S (2016) MicroRNAs in fibrosis: opportunities and challenges. Arthritis Res Ther 18(1):11
Yang T et al (2012) Bone morphogenetic protein 7 suppresses the progression of hepatic fibrosis and regulates the expression of gremlin and transforming growth factor β1. Mol Med Rep 6(1):246–252
Staloch D et al (2015) Gremlin is a key pro-fibrogenic factor in chronic pancreatitis. J Mol Med 93(10):1085–1093
Yang Y et al (2021) Targeting Gremlin 1 prevents Intestinal Fibrosis Progression by inhibiting the fatty acid oxidation of fibroblast cells. Front Pharmacol 12:663774
Lee H et al (2007) The role of gremlin, a BMP antagonist, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48(9):4291–4299
Qin D, Jin X, Jiang Y (2020) Gremlin mediates the TGF-β-induced induction of profibrogenic genes in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Ther Med 19(3):2353–2359
Li D et al (2019) Gremlin-1: An endogenous BMP antagonist induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and interferes with redifferentiation in fetal RPE cells with repeated wounds. Mol Vis 25:625–635
Rowan SC et al (2018) EXPRESS: Gremlin1 blocks vascular endothelial growth factor signalling in the pulmonary microvascular endothelium. Pulm Circ 10(1):2045894018807205
Tamminen JA et al (2013) Gremlin-1 associates with fibrillin microfibrils in vivo and regulates mesothelioma cell survival through transcription factor slug. Oncogenesis 2(8):e66–e66
Chen B et al (2004) Cutting edge: bone morphogenetic protein Antagonists Drm/Gremlin and Dan interact with Slits and act as negative regulators of Monocyte Chemotaxis. J Immunol 173(10):5914
Sung NJ et al (2020) Gremlin-1 promotes metastasis of breast cancer cells by activating STAT3-MMP13 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 21(23):9227
Meng L et al (2020) Vital roles of Gremlin-1 in pulmonary arterial hypertension induced by systemic-to-pulmonary shunts. J Am Heart Assoc 9(15):e016586
Ciuclan L et al (2013) Treatment with anti-gremlin 1 antibody ameliorates chronic hypoxia/SU5416-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in mice. Am J Pathol 183(5):1461–1473
Bond MJ, Crews CM (2021) Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) come of age: entering the third decade of targeted protein degradation. RSC Chem Biol 2(3):725–742
Schapira M et al (2019) Targeted protein degradation: expanding the toolbox. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 18(12):949–963
Bai L et al (2019) A potent and selective small-molecule degrader of STAT3 achieves complete tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Cell 36(5):498-511.e17
Wynn TA (2004) Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol 4(8):583–594
Funding
No funding was provided for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SOR designed, conceived and wrote this work solely.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
NA.
Consent for publication
NA.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Reilly, S. Gremlin: a complex molecule regulating wound healing and fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 7917–7923 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03964-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03964-x