Abstract
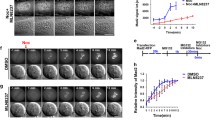
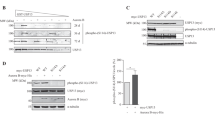
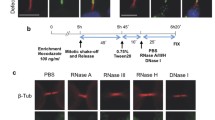
Aurora B activation is triggered at the mitotic entry and required for proper microtubule-kinetochore attachment at mitotic phase. Therefore, Aurora B should be in inactive form in interphase to prevent aberrant cell cycle progression. However, it is unclear how the inactivation of Aurora B is sustained during interphase. In this study, we find that IK depletion-induced mitotic arrest leads to G2 arrest by Aurora B inhibition, indicating that IK depletion enhances Aurora B activation before mitotic entry. IK binds to Aurora B, and colocalizes on the nuclear foci during interphase. Our data further show that IK inhibits Aurora B activation through recruiting PP2A into IK and Aurora B complex. It is thus believed that IK, as a scaffold protein, guides PP2A into Aurora B to suppress its activity in interphase until mitotic entry.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IK:
-
Inhibitor K562
- PP2A:
-
Protein phosphatase 2A
References
Krief P, Augery-Bourget Y, Plaisance S, Merck MF, Assier E, Tanchou V, Billard M, Boucheix C, Jasmin C, Azzarone B (1994) A new cytokine (IK) down-regulating HLA class II: monoclonal antibodies, cloning and chromosome localization. Oncogene 9(12):3449–3456
Willers J, Haffner A, Zepter K, Storz M, Urosevic M, Burg G, Dummer R (2001) The interferon inhibiting cytokine IK is overexpressed in cutaneous T cell lymphoma derived tumor cells that fail to upregulate major histocompatibility complex class II upon interferon-gamma stimulation. J Invest Dermatol 116(6):874–879. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01339.x (jid1339 [pii])
Cao LXLB-KM, Clay D, Oshevski S, Jasmin C, Krief P (1997) Implication of a new molecule IK in CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Blood 89(10):3615–3623
Muraoka M, Hasegawa H, Kohno M, Inoue A, Miyazaki T, Terada M, Nose M, Yasukawa M (2006) IK cytokine ameliorates the progression of lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum 54(11):3591–3600. doi:10.1002/art.22172
Shao R, Liu X, Ding Y, Chen X, Gao R, He J, Wang Y (2012) Characterization of IK cytokine expression in mouse endometrium during early pregnancy and its significance on implantation. Int J Mol Med 30(3):615–621. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2012.1019
Lee S, Han S, Jeong AL, Park JS, Yang Y (2014) Depletion of IK causes mitotic arrest through aberrant regulation of mitotic kinases and phosphatases. FEBS Lett 588(17):2844–2850. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.06.046 (S0014-5793(14)00508-0 [pii])
Hu L, Yang F, Liu X, Xu D, Dai W (2013) Nuclear protein IK undergoes dynamic subcellular translocation and forms unique nuclear bodies during the cell cycle. Biomark Res 1(1):1
Assier E, Bouzinba-Segard H, Stolzenberg MC, Stephens R, Bardos J, Freemont P, Charron D, Trowsdale J, Rich T (1999) Isolation, sequencing and expression of RED, a novel human gene encoding an acidic-basic dipeptide repeat. Gene 230(2):145–154 (S0378111999000669 [pii])
Kimura M, Matsuda Y, Yoshioka T, Okano Y (1999) Cell cycle-dependent expression and centrosome localization of a third human aurora/Ipl1-related protein kinase, AIK3. J Biol Chem 274(11):7334–7340
Sasai K, Katayama H, Stenoien DL, Fujii S, Honda R, Kimura M, Okano Y, Tatsuka M, Suzuki F, Nigg EA, Earnshaw WC, Brinkley WR, Sen S (2004) Aurora-C kinase is a novel chromosomal passenger protein that can complement Aurora-B kinase function in mitotic cells. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 59(4):249–263. doi:10.1002/cm.20039
Tang CJ, Lin CY, Tang TK (2006) Dynamic localization and functional implications of Aurora-C kinase during male mouse meiosis. Dev Biol 290(2):398–410. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.11.036 (S0012-1606(05)00866-3 [pii])
Fu J, Bian M, Jiang Q, Zhang C (2007) Roles of Aurora kinases in mitosis and tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res 5(1):1–10. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0208 (5/1/1 [pii])
Katayama H, Brinkley WR, Sen S (2003) The Aurora kinases: role in cell transformation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22(4):451–464
Hannak E, Kirkham M, Hyman AA, Oegema K (2001) Aurora-A kinase is required for centrosome maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Biol 155(7):1109–1116. doi:10.1083/jcb.200108051 (jcb.200108051 [pii])
Berdnik D, Knoblich JA (2002) Drosophila Aurora-A is required for centrosome maturation and actin-dependent asymmetric protein localization during mitosis. Curr Biol 12(8):640–647 (S0960982202007662 [pii])
Dodson CA, Bayliss R (2012) Activation of Aurora-A kinase by protein partner binding and phosphorylation are independent and synergistic. J Biol Chem 287(2):1150–1157. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.312090 (M111.312090 [pii])
Eyers PA, Erikson E, Chen LG, Maller JL (2003) A novel mechanism for activation of the protein kinase Aurora A. Curr Biol 13(8):691–697 (S0960982203001660 [pii])
Eyers PA, Maller JL (2004) Regulation of Xenopus Aurora A activation by TPX2. J Biol Chem 279(10):9008–9015. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312424200 (M312424200 [pii])
Adams RR, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC (2001) Chromosomal passengers and the (aurora) ABCs of mitosis. Trends Cell Biol 11(2):49–54 (S0962-8924(00)01880-8 [pii])
Murata-Hori M, Tatsuka M, Wang YL (2002) Probing the dynamics and functions of aurora B kinase in living cells during mitosis and cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell 13(4):1099–1108. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-09-0467
Bolton MA, Lan W, Powers SE, McCleland ML, Kuang J, Stukenberg PT (2002) Aurora B kinase exists in a complex with survivin and INCENP and its kinase activity is stimulated by survivin binding and phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 13(9):3064–3077. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-02-0092
Honda R, Korner R, Nigg EA (2003) Exploring the functional interactions between Aurora B, INCENP, and survivin in mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 14(8):3325–3341. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-11-0769 (E02-11-0769 [pii])
Yasui Y, Urano T, Kawajiri A, Nagata K, Tatsuka M, Saya H, Furukawa K, Takahashi T, Izawa I, Inagaki M (2004) Autophosphorylation of a newly identified site of Aurora-B is indispensable for cytokinesis. J Biol Chem 279(13):12997–13003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311128200 (M311128200 [pii])
Bishop JD, Schumacher JM (2002) Phosphorylation of the carboxyl terminus of inner centromere protein (INCENP) by the Aurora B Kinase stimulates Aurora B kinase activity. J Biol Chem 277(31):27577–27580. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200307200 (C200307200 [pii])
Sessa F, Mapelli M, Ciferri C, Tarricone C, Areces LB, Schneider TR, Stukenberg PT, Musacchio A (2005) Mechanism of Aurora B activation by INCENP and inhibition by hesperadin. Mol Cell 18(3):379–391. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.03.031 (S1097-2765(05)01224-4 [pii])
Sugiyama K, Sugiura K, Hara T, Sugimoto K, Shima H, Honda K, Furukawa K, Yamashita S, Urano T (2002) Aurora-B associated protein phosphatases as negative regulators of kinase activation. Oncogene 21(20):3103–3111. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205432
Foley EA, Maldonado M, Kapoor TM (2011) Formation of stable attachments between kinetochores and microtubules depends on the B56-PP2A phosphatase. Nat Cell Biol 13(10):1265–1271. doi:10.1038/ncb2327 (ncb2327 [pii])
Espert A, Uluocak P, Bastos RN, Mangat D, Graab P, Gruneberg U (2014) PP2A-B56 opposes Mps1 phosphorylation of Knl1 and thereby promotes spindle assembly checkpoint silencing. J Cell Biol 206(7):833–842. doi:10.1083/jcb.201406109 (jcb.201406109 [pii])
Bastos RN, Cundell MJ, Barr FA (2014) KIF4A and PP2A-B56 form a spatially restricted feedback loop opposing Aurora B at the anaphase central spindle. J Cell Biol 207(6):683–693. doi:10.1083/jcb.201409129 (jcb.201409129 [pii])
Hayashi-Takanaka Y, Yamagata K, Nozaki N, Kimura H (2009) Visualizing histone modifications in living cells: spatiotemporal dynamics of H3 phosphorylation during interphase. J Cell Biol 187(6):781–790. doi:10.1083/jcb.200904137 (jcb.200904137 [pii])
Neumann B, Walter T, Heriche JK, Bulkescher J, Erfle H, Conrad C, Rogers P, Poser I, Held M, Liebel U, Cetin C, Sieckmann F, Pau G, Kabbe R, Wunsche A, Satagopam V, Schmitz MH, Chapuis C, Gerlich DW, Schneider R, Eils R, Huber W, Peters JM, Hyman AA, Durbin R, Pepperkok R, Ellenberg J (2010) Phenotypic profiling of the human genome by time-lapse microscopy reveals cell division genes. Nature 464(7289):721–727. doi:10.1038/nature08869 (nature08869 [pii])
Munoz-Barrera M, Monje-Casas F (2014) Increased Aurora B activity causes continuous disruption of kinetochore-microtubule attachments and spindle instability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(38):E3996–E4005. doi:10.1073/pnas.1408017111 (1408017111 [pii])
Ricke RM, Jeganathan KB, van Deursen JM (2011) Bub1 overexpression induces aneuploidy and tumor formation through Aurora B kinase hyperactivation. J Cell Biol 193(6):1049–1064. doi:10.1083/jcb.201012035 (jcb.201012035 [pii])
Sun L, Gao J, Dong X, Liu M, Li D, Shi X, Dong JT, Lu X, Liu C, Zhou J (2008) EB1 promotes Aurora-B kinase activity through blocking its inactivation by protein phosphatase 2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(20):7153–7158. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710018105 (0710018105 [pii])
Yeh PC, Yeh CC, Chen YC, Juang YL (2012) RED, a spindle pole-associated protein, is required for kinetochore localization of MAD1, mitotic progression, and activation of the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Biol Chem 287(15):11704–11716. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.299131 (M111.299131 [pii])
Carmena M, Wheelock M, Funabiki H, Earnshaw WC (2012) The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC): from easy rider to the godfather of mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(12):789–803. doi:10.1038/nrm3474 (nrm3474 [pii])
Terada Y, Tatsuka M, Suzuki F, Yasuda Y, Fujita S, Otsu M (1998) AIM-1: a mammalian midbody-associated protein required for cytokinesis. EMBO J 17(3):667–676. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.3.667
Tatsuka M, Katayama H, Ota T, Tanaka T, Odashima S, Suzuki F, Terada Y (1998) Multinuclearity and increased ploidy caused by overexpression of the aurora- and Ipl1-like midbody-associated protein mitotic kinase in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 58(21):4811–4816
Goto H, Kiyono T, Tomono Y, Kawajiri A, Urano T, Furukawa K, Nigg EA, Inagaki M (2006) Complex formation of Plk1 and INCENP required for metaphase-anaphase transition. Nat Cell Biol 8(2):180–187. doi:10.1038/ncb1350 (ncb1350 [pii])
Ohkura H, Yanagida M (1991) S. pombe gene sds22+ essential for a midmitotic transition encodes a leucine-rich repeat protein that positively modulates protein phosphatase-1. Cell 64(1):149–157 (0092-8674(91)90216-L [pii])
Posch M, Khoudoli GA, Swift S, King EM, Deluca JG, Swedlow JR (2010) Sds22 regulates aurora B activity and microtubule-kinetochore interactions at mitosis. J Cell Biol 191(1):61–74. doi:10.1083/jcb.200912046 (jcb.200912046 [pii])
Ceulemans H, Vulsteke V, De Maeyer M, Tatchell K, Stalmans W, Bollen M (2002) Binding of the concave surface of the Sds22 superhelix to the alpha 4/alpha 5/alpha 6-triangle of protein phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem 277(49):47331–47337. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206838200 (M206838200 [pii])
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2015R1D1A4A01016293) and Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF funded by the Korean government, MSIP (2015016662) and (No. 2011-0030074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Jeong, A.L., Park, J.S. et al. IK-guided PP2A suppresses Aurora B activity in the interphase of tumor cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 3375–3386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2162-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2162-9