Abstract
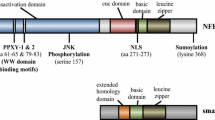
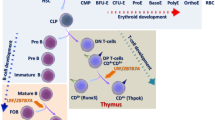
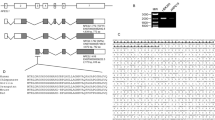
NFE2L3 [Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 3] or NRF3, a member of the Cap‘n’Collar (CNC) family, is a basic-region leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that was first identified over 10 years ago. Contrary to its extensively studied homolog NFE2L2 (NRF2), the regulation and function of the NFE2L3 protein have not yet attracted as much attention. Nevertheless, several recent reports have now shed light on the possible roles of NFE2L3. Structural and biochemical studies revealed a series of domains and modifications that are critical for its cellular regulation. The control of the subcellular localization of NFE2L3 appears to be essential for understanding its role in various cellular processes. Importantly, newer studies provide fascinating insights linking NFE2L3 to differentiation, inflammation, and carcinogenesis. Here, we present an overview of the current level of knowledge of NFE2L3 transcription factor biology in humans and mice. From being the Cinderella of the CNC transcription factors for many years, NFE2L3 may now rapidly come into its own.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sykiotis GP, Bohmann D (2010) Stress-activated Cap‘n’Collar transcription factors in aging and human disease. Sci Signal 3(112):re3. doi:10.1126/scisignal.3112re3
Mignotte V, Wall L, deBoer E, Grosveld F, Romeo PH (1989) Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res 17(1):37–54
Mohler J, Vani K, Leung S, Epstein A (1991) Segmentally restricted, cephalic expression of a leucine zipper gene during Drosophila embryogenesis. Mech Dev 34(1):3–9
Bowerman B, Eaton BA, Priess JR (1992) skn-1, a maternally expressed gene required to specify the fate of ventral blastomeres in the early C. elegans embryo. Cell 68(6):1061–1075
Chan JY, Han XL, Kan YW (1993) Cloning of Nrf1, an NF-E2-related transcription factor, by genetic selection in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(23):11371–11375
Caterina JJ, Donze D, Sun CW, Ciavatta DJ, Townes TM (1994) Cloning and functional characterization of LCR-F1: a bZIP transcription factor that activates erythroid-specific, human globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 22(12):2383–2391
Luna L, Johnsen O, Skartlien AH, Pedeutour F, Turc-Carel C, Prydz H, Kolsto AB (1994) Molecular cloning of a putative novel human bZIP transcription factor on chromosome 17q22. Genomics 22(3):553–562
Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, Cao A, Kan YW (1994) Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(21):9926–9930
Kobayashi A, Ito E, Toki T, Kogame K, Takahashi S, Igarashi K, Hayashi N, Yamamoto M (1999) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a new Cap‘n’Collar family transcription factor Nrf3. J Biol Chem 274(10):6443–6452
Chenais B, Derjuga A, Massrieh W, Red-Horse K, Bellingard V, Fisher SJ, Blank V (2005) Functional and placental expression analysis of the human NRF3 transcription factor. Mol Endocrinol 19(1):125–137. doi:10.1210/me.2003-0379
Derjuga A, Gourley TS, Holm TM, Heng HH, Shivdasani RA, Ahmed R, Andrews NC, Blank V (2004) Complexity of CNC transcription factors as revealed by gene targeting of the Nrf3 locus. Mol Cell Biol 24(8):3286–3294
Oyake T, Itoh K, Motohashi H, Hayashi N, Hoshino H, Nishizawa M, Yamamoto M, Igarashi K (1996) Bach proteins belong to a novel family of BTB-basic leucine zipper transcription factors that interact with MafK and regulate transcription through the NF-E2 site. Mol Cell Biol 16(11):6083–6095
Kerppola TK, Curran T (1994) Maf and Nrl can bind to AP-1 sites and form heterodimers with Fos and Jun. Oncogene 9(3):675–684
Toki T, Itoh J, Kitazawa J, Arai K, Hatakeyama K, Akasaka J, Igarashi K, Nomura N, Yokoyama M, Yamamoto M, Ito E (1997) Human small Maf proteins form heterodimers with CNC family transcription factors and recognize the NF-E2 motif. Oncogene 14(16):1901–1910
Landschulz WH, Johnson PF, McKnight SL (1988) The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 240(4860):1759–1764
Perdomo J, Fock EL, Kaur G, Yan F, Khachigian LM, Jans DA, Chong BH (2010) A monopartite sequence is essential for P45 NF-E2 nuclear translocation, transcriptional activity and platelet production. J Thromb Haemost. 8:2542–2553. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04058.x
Theodore M, Kawai Y, Yang J, Kleshchenko Y, Reddy SP, Villalta F, Arinze IJ (2008) Multiple nuclear localization signals function in the nuclear import of the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem 283(14):8984–8994. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709040200
Hoshino H, Kobayashi A, Yoshida M, Kudo N, Oyake T, Motohashi H, Hayashi N, Yamamoto M, Igarashi K (2000) Oxidative stress abolishes leptomycin B-sensitive nuclear export of transcription repressor Bach2 that counteracts activation of Maf recognition element. J Biol Chem 275(20):15370–15376
Ohira M, Seki N, Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nomura N, Ohara O (1998) Characterization of a human homolog (BACH1) of the mouse Bach1 gene encoding a BTB-basic leucine zipper transcription factor and its mapping to chromosome 21q22.1. Genomics 47(2):300–306. pii:S0888754397950801
Blouin JL, Duriaux Sail G, Guipponi M, Rossier C, Pappasavas MP, Antonarakis SE (1998) Isolation of the human BACH1 transcription regulator gene, which maps to chromosome 21q22.1. Hum Genet 102(3):282–288
Ito N, Watanabe-Matsui M, Igarashi K, Murayama K (2009) Crystal structure of the Bach1 BTB domain and its regulation of homodimerization. Genes Cells 14(2):167–178. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01259.x
Itoh K, Igarashi K, Hayashi N, Nishizawa M, Yamamoto M (1995) Cloning and characterization of a novel erythroid cell-derived CNC family transcription factor heterodimerizing with the small Maf family proteins. Mol Cell Biol 15(8):4184–4193
Johnsen O, Skammelsrud N, Luna L, Nishizawa M, Prydz H, Kolsto AB (1996) Small Maf proteins interact with the human transcription factor TCF11/Nrf1/LCR-F1. Nucleic Acids Res 24(21):4289–4297
Johnsen O, Murphy P, Prydz H, Kolsto AB (1998) Interaction of the CNC-bZIP factor TCF11/LCR-F1/Nrf1 with MafG: binding-site selection and regulation of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 26(2):512–520
Marini MG, Chan K, Casula L, Kan YW, Cao A, Moi P (1997) hMAF, a small human transcription factor that heterodimerizes specifically with Nrf1 and Nrf2. J Biol Chem 272(26):16490–16497
Motohashi H, Shavit JA, Igarashi K, Yamamoto M, Engel JD (1997) The world according to Maf. Nucleic Acids Res 25(15):2953–2959
McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Chanas SA, Henderson CJ, McLellan LI, Wolf CR, Cavin C, Hayes JD (2001) The Cap‘n’Collar basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-related factor 2) controls both constitutive and inducible expression of intestinal detoxification and glutathione biosynthetic enzymes. Cancer Res 61(8):3299–3307
Blank V (2008) Small Maf proteins in mammalian gene control: mere dimerization partners or dynamic transcriptional regulators? J Mol Biol 376:913–925
Venugopal R, Jaiswal AK (1998) Nrf2 and Nrf1 in association with Jun proteins regulate antioxidant response element-mediated expression and coordinated induction of genes encoding detoxifying enzymes. Oncogene 17(24):3145–3156
Jeyapaul J, Jaiswal AK (2000) Nrf2 and c-Jun regulation of antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated expression and induction of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene. Biochem Pharmacol 59(11):1433–1439. pii:S0006-2952(00)00256-2
Motohashi H, O’Connor T, Katsuoka F, Engel J, Yamamoto M (2002) Integration and diversity of the regulatory network composed of Maf and CNC families of transcription factors. Gene 294(1–2):1
Blank V, Andrews NC (1997) The Maf transcription factors: regulators of differentiation. Trends Biochem Sci 22(11):437–441
Rushmore TH, Morton MR, Pickett CB (1991) The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem 266(18):11632–11639
Klaunig JE, Kamendulis LM, Hocevar BA (2010) Oxidative stress and oxidative damage in carcinogenesis. Toxicol Pathol 38(1):96–109. doi:10.1177/0192623309356453
Kundu JK, Surh YJ (2010) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling as a potential target for chemoprevention of inflammation-associated carcinogenesis. Pharm Res 27(6):999–1013. doi:10.1007/s11095-010-0096-8
Martin-Montalvo A, Villalba JM, Navas P, de Cabo R (2010) NRF2, cancer and calorie restriction. Oncogene. 30:505–520. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.492
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N (2010) Nrf2: friend or foe for chemoprevention? Carcinogenesis 31(1):90–99. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp231
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284(20):13291–13295. doi:10.1074/jbc.R900010200
Li W, Kong AN (2009) Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol Carcinog 48(2):91–104. doi:10.1002/mc.20465
Kwak MK, Kensler TW (2010) Targeting NRF2 signaling for cancer chemoprevention. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244(1):66–76. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.08.028
Beyer TA, Auf dem Keller U, Braun S, Schafer M, Werner S (2007) Roles and mechanisms of action of the Nrf2 transcription factor in skin morphogenesis, wound repair and skin cancer. Cell Death Differ 14(7):1250–1254. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402133
Zhang DD (2006) Mechanistic studies of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metab Rev 38(4):769–789. doi:10.1080/03602530600971974
Lau A, Villeneuve NF, Sun Z, Wong PK, Zhang DD (2008) Dual roles of Nrf2 in cancer. Pharmacol Res 58(5–6):262–270. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2008.09.003
Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2004) Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med 10(11):549–557
Hayes JD, McMahon M (2009) NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 34(4):176–188. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2008.12.008
Hayes JD, McMahon M (2001) Molecular basis for the contribution of the antioxidant responsive element to cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Lett 174(2):103–113
Maher J, Yamamoto M (2010) The rise of antioxidant signaling—the evolution and hormetic actions of Nrf2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244(1):4–15. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2010.01.011
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M (2006) Nrf2-Keap1 regulation of cellular defense mechanisms against electrophiles and reactive oxygen species. Adv Enzyme Regul 46:113–140
Itoh K (2009) Disease regulation by Nrf2 antioxidant system. Seikagaku 81(6):447–455
Jaiswal AK (2004) Nrf2 signaling in coordinated activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med 36(10):1199–1207
Kaspar JW, Niture SK, Jaiswal AK (2009) Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 47(9):1304–1309. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.035
Niture SK, Kaspar JW, Shen J, Jaiswal AK (2010) Nrf2 signaling and cell survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244(1):37–42. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.06.009
Tong KI, Kobayashi A, Katsuoka F, Yamamoto M (2006) Two-site substrate recognition model for the Keap1-Nrf2 system: a hinge and latch mechanism. Biol Chem 387(10–11):1311–1320. doi:10.1515/BC.2006.164
Kobayashi A, Ohta T, Yamamoto M (2004) Unique function of the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in the inducible expression of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol 378:273–286
Florczyk U, Loboda A, Stachurska A, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J (2010) Role of Nrf2 transcription factor in cellular response to oxidative stress. Postepy Biochem 56(2):147–155
Men’shikova EB, Tkachev VO, Zenkov NK (2010) Redox-dependent signaling system Nrf2/are in inflammation. Mol Biol (Mosk) 44(3):389–404
Jaganjac M (2010) Possible involvement of granulocyte oxidative burst in Nrf2 signaling in cancer. Indian J Med Res 131:609–616
Boutten A, Goven D, Boczkowski J, Bonay M (2010) Oxidative stress targets in pulmonary emphysema: focus on the Nrf2 pathway. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14(3):329–346. doi:10.1517/14728221003629750
Jung KA, Kwak MK (2010) The Nrf2 system as a potential target for the development of indirect antioxidants. Molecules 15(10):7266–7291. doi:10.3390/molecules15107266
Andrews NC (1994) Erythroid transcription factor NF-E2 coordinates hemoglobin synthesis. Pediatr Res 36(4):419–423
Shivdasani RA (1996) The role of transcription factor NF-E2 in megakaryocyte maturation and platelet production. Stem Cells 14(Suppl 1):112–115. doi:10.1002/stem.5530140714
Andrews NC (1998) The NF-E2 transcription factor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30(4):429–432
Itou E (1999) The role of NF-E2 related transcription factors in hematopoiesis. Rinsho Ketsueki 40(4):280–283
Shivdasani RA (2001) Molecular and transcriptional regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation. Stem Cells 19(5):397–407. doi:10.1634/stemcells.19-5-397
Biswas M, Chan JY (2010) Role of Nrf1 in antioxidant response element-mediated gene expression and beyond. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244(1):16–20. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.034
Igarashi K, Ota K, Nakame A (2009) Regulation of cellular senescence by Bach1. Nippon Rinsho 67(7):1423–1428
Hira S, Tomita T, Matsui T, Igarashi K, Ikeda-Saito M (2007) Bach1, a heme-dependent transcription factor, reveals presence of multiple heme binding sites with distinct coordination structure. IUBMB Life 59(8–9):542–551. doi:10.1080/15216540701225941
Igarashi K, Sun J (2006) The heme-Bach1 pathway in the regulation of oxidative stress response and erythroid differentiation. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(1–2):107–118
Muto A (2005) Bach2 orchestrates the transcriptional programme of B cell activation. Seikagaku 77(5):427–431
Igarashi K, Ochiai K, Muto A (2007) Architecture and dynamics of the transcription factor network that regulates B-to-plasma cell differentiation. J Biochem 141(6):783–789. doi:10.1093/jb/mvm106
Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2007) Carcinogenesis and transcriptional regulation through Maf recognition elements. Cancer Sci 98(2):135–139
Motohashi H (2003) Small Maf proteins as transcription factors regulating maturation and maintenance of the cell. Seikagaku 75(9):1193–1201
Motohashi H (2000) Small Maf proteins in bZip transcription factor net-work. Seikagaku 72(4):291–295
Chan JY, Cheung MC, Moi P, Chan K, Kan YW (1995) Chromosomal localization of the human NF-E2 family of bZIP transcription factors by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 95(3):265–269
Zhang Y, Kobayashi A, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD (2009) The Nrf3 transcription factor is a membrane-bound glycoprotein targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum through its N-terminal homology box 1 sequence. J Biol Chem 284(5):3195–3210. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805337200
Funatsu N, Inoue T, Nakamura S (2004) Gene expression analysis of the late embryonic mouse cerebral cortex using DNA microarray: identification of several region- and layer-specific genes. Cereb Cortex 14(9):1031–1044. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh063
Kokot A, Metze D, Mouchet N, Galibert MD, Schiller M, Luger TA, Bohm M (2009) Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone counteracts the suppressive effect of UVB on Nrf2 and Nrf-dependent gene expression in human skin. Endocrinology 150(7):3197–3206. doi:10.1210/en.2008-1315
Chevillard G, Nouhi Z, Anna D, Paquet M, Blank V (2010) Nrf3-deficient mice are not protected against acute lung and adipose tissue damages induced by butylated hydroxytoluene. FEBS Lett 584(5):923–928. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.028
Pepe AE, Xiao Q, Zampetaki A, Zhang Z, Kobayashi A, Hu Y, Xu Q (2010) Crucial role of nrf3 in smooth muscle cell differentiation from stem cells. Circ Res 106(5):870–879. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.211417
Terui K, Takahashi Y, Kitazawa J, Toki T, Yokoyama M, Ito E (2000) Expression of transcription factors during megakaryocytic differentiation of CD34+ cells from human cord blood induced by thrombopoietin. Tohoku J Exp Med 192(4):259–273
Braun S, Hanselmann C, Gassmann MG, auf dem Keller U, Born-Berclaz C, Chan K, Kan YW, Werner S (2002) Nrf2 transcription factor, a novel target of keratinocyte growth factor action which regulates gene expression and inflammation in the healing skin wound. Mol Cell Biol 22(15):5492–5505
Nouhi Z, Chevillard G, Derjuga A, Blank V (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum association and N-linked glycosylation of the human Nrf3 transcription factor. FEBS Lett 581(28):5401–5406. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.10.041
Willenbrock K, Kuppers R, Renne C, Brune V, Eckerle S, Weidmann E, Brauninger A, Hansmann ML (2006) Common features and differences in the transcriptome of large cell anaplastic lymphoma and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica 91(5):596–604
Kuppers R, Klein U, Schwering I, Distler V, Brauninger A, Cattoretti G, Tu Y, Stolovitzky GA, Califano A, Hansmann ML, Dalla-Favera R (2003) Identification of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cell-specific genes by gene expression profiling. J Clin Invest 111(4):529–537. doi:10.1172/JCI16624
Rhee DK, Park SH, Jang YK (2008) Molecular signatures associated with transformation and progression to breast cancer in the isogenic MCF10 model. Genomics 92(6):419–428. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.08.005
Etchevers HC (2005) The Cap‘n’Collar family member NF-E2-related factor 3 (Nrf3) is expressed in mesodermal derivatives of the avian embryo. Int J Dev Biol 49(2–3):363–367. doi:10.1387/ijdb.041942he
Sankaranarayanan K, Jaiswal AK (2004) Nrf3 negatively regulates antioxidant-response element-mediated expression and antioxidant induction of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase1 gene. J Biol Chem 279(49):50810–50817
Wang W, Chan JY (2006) Nrf1 is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane by an N-terminal transmembrane domain. Inhibition of nuclear translocation and transacting function. J Biol Chem 281(28):19676–19687. doi:10.1074/jbc.M602802200
Zhang Y, Crouch DH, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD (2006) Negative regulation of the Nrf1 transcription factor by its N-terminal domain is independent of Keap1: Nrf1, but not Nrf2, is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J 399(3):373–385
Zhang Y, Lucocq JM, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD (2007) The N-terminal homology box 1 (NHB1) sequence in transcription factor Nrf1 is required to anchor it to the endoplasmic reticulum and also to enable its Asn-glycosylation. Biochem J 408:161–172
Shivdasani RA, Orkin SH (1995) Erythropoiesis and globin gene expression in mice lacking the transcription factor NF-E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(19):8690–8694
Farmer SC, Sun CW, Winnier GE, Hogan BL, Townes TM (1997) The bZIP transcription factor LCR-F1 is essential for mesoderm formation in mouse development. Genes Dev 11(6):786–798
Muto A, Tashiro S, Nakajima O, Hoshino H, Takahashi S, Sakoda E, Ikebe D, Yamamoto M, Igarashi K (2004) The transcriptional programme of antibody class switching involves the repressor Bach2. Nature 429(6991):566–571
Sun J, Hoshino H, Takaku K, Nakajima O, Muto A, Suzuki H, Tashiro S, Takahashi S, Shibahara S, Alam J, Taketo MM, Yamamoto M, Igarashi K (2002) Hemoprotein Bach1 regulates enhancer availability of heme oxygenase-1 gene. EMBO J 21(19):5216–5224
Chan K, Lu R, Chang JC, Kan YW (1996) NRF2, a member of the NFE2 family of transcription factors, is not essential for murine erythropoiesis, growth, and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(24):13943–13948
Shivdasani RA, Rosenblatt MF, Zucker-Franklin D, Jackson CW, Hunt P, Saris CJ, Orkin SH (1995) Transcription factor NF-E2 is required for platelet formation independent of the actions of thrombopoietin/MGDF in megakaryocyte development. Cell 81(5):695–704
Chan JY, Kwong M, Lu R, Chang J, Wang B, Yen TS, Kan YW (1998) Targeted disruption of the ubiquitous CNC-bZIP transcription factor, Nrf-1, results in anemia and embryonic lethality in mice. EMBO J 17(6):1779–1787
Chevillard G, Paquet M, Blank V (2011) Nfe2l3 (Nrf3) deficiency predisposes mice to T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. Blood 117(6):2005–2008. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-02-271460
Pfeifer GP, Denissenko MF, Olivier M, Tretyakova N, Hecht SS, Hainaut P (2002) Tobacco smoke carcinogens, DNA damage and p53 mutations in smoking-associated cancers. Oncogene 21(48):7435–7451. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205803
Thieblemont C, Nasser V, Felman P, Leroy K, Gazzo S, Callet-Bauchu E, Loriod B, Granjeaud S, Gaulard P, Haioun C, Traverse-Glehen A, Baseggio L, Bertucci F, Birnbaum D, Magrangeas F, Minvielle S, Avet-Loiseau H, Salles G, Coiffier B, Berger F, Houlgatte R (2004) Small lymphocytic lymphoma, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma exhibit distinct gene-expression profiles allowing molecular diagnosis. Blood 103(7):2727–2737. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-06-2160
Obrador-Hevia A, Fernandez de Mattos S, Villalonga P, Rodriguez J (2009) Molecular biology of mantle cell lymphoma: from profiling studies to new therapeutic strategies. Blood Rev 23(5):205–216. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2009.03.001
Rizzatti EG, Falcao RP, Panepucci RA, Proto-Siqueira R, Anselmo-Lima WT, Okamoto OK, Zago MA (2005) Gene expression profiling of mantle cell lymphoma cells reveals aberrant expression of genes from the PI3K-AKT, WNT and TGFbeta signalling pathways. Br J Haematol 130(4):516–526. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05630.x
Ortega-Paino E, Fransson J, Ek S, Borrebaeck CA (2008) Functionally associated targets in mantle cell lymphoma as defined by DNA microarrays and RNA interference. Blood 111(3):1617–1624. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-068791
Almstrup K, Ottesen AM, Sonne SB, Hoei-Hansen CE, Leffers H, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skakkebaek NE (2005) Genomic and gene expression signature of the pre-invasive testicular carcinoma in situ. Cell Tissue Res 322(1):159–165. doi:10.1007/s00441-005-1084-x
Almstrup K, Leffers H, Lothe RA, Skakkebaek NE, Sonne SB, Nielsen JE, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skotheim RI (2007) Improved gene expression signature of testicular carcinoma in situ. Int J Androl 30(4):292–302. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00758.x (discussion 303)
Witschi H, Malkinson AM, Thompson JA (1989) Metabolism and pulmonary toxicity of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT). Pharmacol Ther 42(1):89–113
Paola RD, Cuzzocrea S (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and acute lung injury. PPAR Res 2007:63745. doi:10.1155/2007/63745
Miyakawa Y, Takahashi M, Furukawa F, Toyoda K, Sato H, Hayashi Y (1986) Pneumotoxicity of butylated hydroxytoluene applied dermally to CD-1 mice. Toxicol Lett 34(1):99–105
Kitaya K, Yasuo T, Yamaguchi T, Fushiki S, Honjo H (2007) Genes regulated by interferon-gamma in human uterine microvascular endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med 20(5):689–697
Chowdhury I, Mo Y, Gao L, Kazi A, Fisher AB, Feinstein SI (2009) Oxidant stress stimulates expression of the human peroxiredoxin 6 gene by a transcriptional mechanism involving an antioxidant response element. Free Radic Biol Med 46(2):146–153. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.09.027
Ben-Yehudah A, CAt Easley, Hermann BP, Castro C, Simerly C, Orwig KE, Mitalipov S, Schatten G (2010) Systems biology discoveries using non-human primate pluripotent stem and germ cells: novel gene and genomic imprinting interactions as well as unique expression patterns. Stem Cell Res Ther 1(3):24. doi:10.1186/scrt24
Byrne JA, Pedersen DA, Clepper LL, Nelson M, Sanger WG, Gokhale S, Wolf DP, Mitalipov SM (2007) Producing primate embryonic stem cells by somatic cell nuclear transfer. Nature 450(7169):497–502. doi:10.1038/nature06357
Sritanaudomchai H, Ma H, Clepper L, Gokhale S, Bogan R, Hennebold J, Wolf D, Mitalipov S (2010) Discovery of a novel imprinted gene by transcriptional analysis of parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells. Hum Reprod 25(8):1927–1941. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq144
Liu H, Zhu F, Yong J, Zhang P, Hou P, Li H, Jiang W, Cai J, Liu M, Cui K, Qu X, Xiang T, Lu D, Chi X, Gao G, Ji W, Ding M, Deng H (2008) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from adult rhesus monkey fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 3(6):587–590. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2008.10.014
Painter JN, Anderson CA, Nyholt DR, Macgregor S, Lin J, Lee SH, Lambert A, Zhao ZZ, Roseman F, Guo Q, Gordon SD, Wallace L, Henders AK, Visscher PM, Kraft P, Martin NG, Morris AP, Treloar SA, Kennedy SH, Missmer SA, Montgomery GW, Zondervan KT (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies a locus at 7p15.2 associated with endometriosis. Nat Genet 43(1):51–54. doi:10.1038/ng.731
Heid IM, Jackson AU, Randall JC, Winkler TW, Qi L, Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Zillikens MC, Speliotes EK, Magi R, Workalemahu T, White CC, Bouatia-Naji N, Harris TB, Berndt SI, Ingelsson E, Willer CJ, Weedon MN, Luan J, Vedantam S, Esko T, Kilpelainen TO, Kutalik Z, Li S, Monda KL, Dixon AL, Holmes CC, Kaplan LM, Liang L, Min JL, Moffatt MF, Molony C, Nicholson G, Schadt EE, Zondervan KT, Feitosa MF, Ferreira T, Allen HL, Weyant RJ, Wheeler E, Wood AR, Estrada K, Goddard ME, Lettre G, Mangino M, Nyholt DR, Purcell S, Smith AV, Visscher PM, Yang J, McCarroll SA, Nemesh J, Voight BF, Absher D, Amin N, Aspelund T, Coin L, Glazer NL, Hayward C, Heard-Costa NL, Hottenga JJ, Johansson A, Johnson T, Kaakinen M, Kapur K, Ketkar S, Knowles JW, Kraft P, Kraja AT, Lamina C, Leitzmann MF, McKnight B, Morris AP, Ong KK, Perry JR, Peters MJ, Polasek O, Prokopenko I, Rayner NW, Ripatti S, Rivadeneira F, Robertson NR, Sanna S, Sovio U, Surakka I, Teumer A, van Wingerden S, Vitart V, Zhao JH, Cavalcanti-Proenca C, Chines PS, Fisher E, Kulzer JR, Lecoeur C, Narisu N, Sandholt C, Scott LJ, Silander K, Stark K, Tammesoo ML, Teslovich TM, Timpson NJ, Watanabe RM, Welch R, Chasman DI, Cooper MN, Jansson JO, Kettunen J, Lawrence RW, Pellikka N, Perola M, Vandenput L, Alavere H, Almgren P, Atwood LD, Bennett AJ, Biffar R, Bonnycastle LL, Bornstein SR, Buchanan TA, Campbell H, Day IN, Dei M, Dorr M, Elliott P, Erdos MR, Eriksson JG, Freimer NB, Fu M, Gaget S, Geus EJ, Gjesing AP, Grallert H, Grassler J, Groves CJ, Guiducci C, Hartikainen AL, Hassanali N, Havulinna AS, Herzig KH, Hicks AA, Hui J, Igl W, Jousilahti P, Jula A, Kajantie E, Kinnunen L, Kolcic I, Koskinen S, Kovacs P, Kroemer HK, Krzelj V, Kuusisto J, Kvaloy K, Laitinen J, Lantieri O, Lathrop GM, Lokki ML, Luben RN, Ludwig B, McArdle WL, McCarthy A, Morken MA, Nelis M, Neville MJ, Pare G, Parker AN, Peden JF, Pichler I, Pietilainen KH, Platou CG, Pouta A, Ridderstrale M, Samani NJ, Saramies J, Sinisalo J, Smit JH, Strawbridge RJ, Stringham HM, Swift AJ, Teder-Laving M, Thomson B, Usala G, van Meurs JB, van Ommen GJ, Vatin V, Volpato CB, Wallaschofski H, Walters GB, Widen E, Wild SH, Willemsen G, Witte DR, Zgaga L, Zitting P, Beilby JP, James AL, Kahonen M, Lehtimaki T, Nieminen MS, Ohlsson C, Palmer LJ, Raitakari O, Ridker PM, Stumvoll M, Tonjes A, Viikari J, Balkau B, Ben-Shlomo Y, Bergman RN, Boeing H, Smith GD, Ebrahim S, Froguel P, Hansen T, Hengstenberg C, Hveem K, Isomaa B, Jorgensen T, Karpe F, Khaw KT, Laakso M, Lawlor DA, Marre M, Meitinger T, Metspalu A, Midthjell K, Pedersen O, Salomaa V, Schwarz PE, Tuomi T, Tuomilehto J, Valle TT, Wareham NJ, Arnold AM, Beckmann JS, Bergmann S, Boerwinkle E, Boomsma DI, Caulfield MJ, Collins FS, Eiriksdottir G, Gudnason V, Gyllensten U, Hamsten A, Hattersley AT, Hofman A, Hu FB, Illig T, Iribarren C, Jarvelin MR, Kao WH, Kaprio J, Launer LJ, Munroe PB, Oostra B, Penninx BW, Pramstaller PP, Psaty BM, Quertermous T, Rissanen A, Rudan I, Shuldiner AR, Soranzo N, Spector TD, Syvanen AC, Uda M, Uitterlinden A, Volzke H, Vollenweider P, Wilson JF, Witteman JC, Wright AF, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M, Borecki IB, Deloukas P, Frayling TM, Groop LC, Haritunians T, Hunter DJ, Kaplan RC, North KE, O’Connell JR, Peltonen L, Schlessinger D, Strachan DP, Hirschhorn JN, Assimes TL, Wichmann HE, Thorsteinsdottir U, van Duijn CM, Stefansson K, Cupples LA, Loos RJ, Barroso I, McCarthy MI, Fox CS, Mohlke KL, Lindgren CM (2010) Meta-analysis identifies 13 new loci associated with waist-hip ratio and reveals sexual dimorphism in the genetic basis of fat distribution. Nat Genet 42(11):949–960. doi:10.1038/ng.685
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Zaynab Nouhi, Meenakshi Kannan, Anna Derjuga, Jadwiga Gasiorek, and Koren K. Mann for critical reading of the manuscript and fruitful discussions. This work was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship of the Fonds de la recherche en santé du Québec (FRSQ) to GC and a grant from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (MOP-97932) to VB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chevillard, G., Blank, V. NFE2L3 (NRF3): the Cinderella of the Cap‘n’Collar transcription factors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 3337–3348 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0747-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0747-x