Abstract
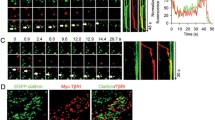
This study examined the role of Rab5a GTPase in regulating hCG-induced internalization and trafficking of the hCG-LH receptor complex in transfected 293T cells. Coexpression of wild-type Rab5a (WT) or constitutively active Rab5a (Q79L) with LHR significantly increased hCG-induced LHR internalization. Conversely, coexpression of dominant negative Rab5a (S34N) with LHR reduced internalization. Confocal microscopy showed LHR colocalizing with Rab5a (WT) and Rab5a (Q79L) in punctuate structures. Coexpression of Rab5a (WT) and Rab5a (Q79L) with LHR significantly increased colocalization of LHR in early endosomes. Conversely, dominant negative Rab5a (S34N) decreased this colocalization. While Rab5a stimulated internalization of LHR, it significantly decreased LHR recycling to the cell surface and increased degradation. Dominant negative Rab5a (S34N) increased LHR recycling and decreased degradation. These results suggest that Rab5a plays a role in LHR trafficking by facilitating internalization and fusion to early endosomes, increasing the degradation of internalized receptor resulting in a reduction in LHR recycling.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascoli M, Fanelli F, Segaloff DL (2002) The lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor, a 2002 perspective. Endocr Rev 23:141–174
Menon KM, Clouser CL, Nair AK (2005) Gonadotropin receptors: role of post-translational modifications and post-transcriptional regulation. Endocrine 26:249–257
Menon KM, Munshi UM, Clouser CL, Nair AK (2004) Regulation of luteinizing hormone/human chorionic gonadotropin receptor expression: a perspective. Biol Reprod 70:861–866
Baratti-Elbaz C, Chinea N, Lahuna O, Lo-osfelt H, Pichon C, Milgrom E (1999) Internalization and recycling pathways of the thyrotropin receptor. Mol Endocrinol 13:1751–1765
Nakamura K, Liu X, Ascoli M (2000) Seven non-contiguous intracellular residues of the lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor dictate the rate of agonist-induced internalization and its sensitivity to non-visual arrestins. J Biol Chem 275:241–247
Galet C, Ascoli M (2006) A constitutively active mutant of the human lutropin receptor (hLHR-L457R) escapes lysosomal targeting and degradation. Mol Endocrinol 20:2931–2945
Zerial M, McBride H (2001) Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:107–1017
Grosshans BL, Ortiz D, Novick P (2006) Rabs and their effectors: achieving specificity in membrane traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:11821–11827
Stenmark H (2009) Seeing is believing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:582
Schwartz SL, Cao C, Pylypenko O, Rak A, Wandinger-Ness A (2007) Rab GTPases at a glance. J Cell Sci 120:3905–3910
Somsel Rodman J, Wandinger-Ness A (2000) Rab GTPases coordinate endocytosis. J Cell Sci 113:183–192
Li H, Li HF, Felder RA, Periasamy A, Jose PA (2008) Rab4 and Rab11 coordinately regulate the recycling of angiotensin II type I receptor as demonstrated by fluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy. J Biomed Opt 13:031206
Progida C, Cogli L, Piro F, De Luca A, Bakke O, Bucci C (2010) Rab7b controls trafficking from endosomes to the TGN. J Cell Sci 123:1480–1491
Seachrist JL, Laporte SA, Dale LB, Babwah AV, Caron MG, Anborgh PH, Ferguson SS (2002) Rab5 association with the angiotensin II type 1A receptor promotes Rab5 GTP binding and vesicular fusion. J Biol Chem 277:679–685
O’Keeffe MB, Reid HM, Kinsella BT (2008) Agonist-dependent internalization and trafficking of the human prostacyclin receptor: a direct role for Rab5a GTPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:1914–1928
Hunker CM, Kruk I, Hall J, Giambini H, Veisaga ML, Barbieri MA (2006) Role of Rab5 in insulin receptor-mediated endocytosis and signaling. Arch Biochem Biophys 449:130–142
Conti F, Sertic S, Reversi A, Chini B (2009) Intracellular trafficking of the human oxytocin receptor: evidence of receptor recycling via a Rab4/Rab5 “short cycle”. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:532–542
Ding Q, Wang Z, Chen Y (2009) Endocytosis of adiponectin receptor 1 through a clathrin-and Rab5-dependent pathway. Cell Res 19:317–327
Iwata K, Ito K, Fukuzaki A, Inaki K, Haga T (1999) Dynamin and rab5 regulate GRK2-dependent internalization of dopamine D2 receptors. Eur J Biochem 263:596–602
Schmidlin F, Dery O, DeFea KO, Slice L, Patierno S, Sternini C, Grady EF, Bunnett NW (2001) Dynamin and Rab5a-dependent trafficking and signaling of the neurokinin 1 receptor. J Biol Chem 276:25427–25437
Dale LB, Seachrist JL, Babwah AV, Ferguson SS (2004) Regulation of angiotensin II type 1A receptor intracellular retention, degradation, and recycling by Rab5, Rab7, and Rab11 GTPases. J Biol Chem 279:13110–13118
Jopling HM, Odell AF, Hooper NM, Zachary IC, Walker JH, Ponnambalam S (2009) Rab GTPase regulation of VEGFR2 trafficking and signaling in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1119–1124
Munshi UM, Peegel H, Menon KM (2001) Palmitoylation of the luteinizing Hormone/human chorionic gonadotropin receptor regulates receptor interaction with the arrestin-mediated internalization pathway. Eur J Biochem 268:1631–1639
Bradbury FA, Menon KM (1999) Evidence that constitutively active luteinizing hormone/human chorionic gonadotropin receptors are rapidly internalized. Biochemistry 38:8703–8712
Kawate N, Menon KM (1994) Palmitoylation of luteinizing hormone/human choriogonadotropin receptors in transfected cells. Abolition of palmitoylation by mutation of Cys-621 and Cys-622 residues in the cytoplasmic tail increases ligand- induced internalization of the receptor. J Biol Chem 269:30651–30658
Lazari MF, Liu X, Nakamura K, Benovic JL, Ascoli M (1999) Role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases on the agonist-induced phosphorylation and internalization of the follitropin receptor. Mol Endocrinol 13:866–878
Nakamura K, Ascoli M (1999) A dileucine-based motif in the C-terminal tail of the lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor inhibits endocytosis of the agonist-receptor complex. Mol Pharmacol 56:728–736
Kishi M, Ascoli M (2000) The C-terminal tail of the rat lutropin/choriogonadotropin (CG) receptor independently modulates human (h)CG-induced internalization of the cell surface receptor and the lysosomal targeting of the internalized hCG-receptor complex. Mol Endocrinol 14:926–936
Barbieri MA, Li G, Mayorga LS, Stahl PD (1996) Characterization of Rab5:Q79L-stimulated endosome fusion. Arch Biochem Biophys 326:64–72
Stenmark H, Parton RG, Steele-Mortimer O, Lütcke A, Gruenberg J, Zerial M (1994) Inhibition of rab5 GTPase activity stimulates membrane fusion in endocytosis. EMBO J 13:1287–1296
Munshi UM, Clouser CL, Peegel H, Menon KM (2005) Evidence that palmitoylation of carboxyl terminus cysteine residues of the human luteinizing hormone receptor regulates postendocytic processing. Mol Endocrinol 19:749–758
Laifenfeld D, Patzek LJ, McPhie DL, Chen Y, Levites Y, Cataldo AM, Neve RL (2007) Rab5 mediates an amyloid precursor protein signaling pathway that leads to apoptosis. J Neurosci 27:7141–7153
Soldati T, Schliwa M (2006) Powering membrane traffic in endocytosis and recycling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:897–908
Nair AK, Menon KM (2005) Regulation of luteinizing hormone receptor expression: evidence of translational suppression in vitro by a hormonally regulated mRNA-binding protein and its endogenous association with luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA in the ovary. J Biol Chem 280:42809–42816
Chen PI, Kong C, Su X, Stahl PD (2009) Rab5 isoforms differentially regulate the trafficking and degradation of epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 284:30328–30338
Holmes KD, Babwah AV, Dale LB, Poulter MO, Ferguson SS (2006) Differential regulation of corticotropin releasing factor 1alpha receptor endocytosis and trafficking by beta-arrestins and Rab GTPases. J Neurochem 96:934–949
Hirota Y, Kuronita T, Fujita H, Tanaka Y (2007) A role for Rab5 activity in the biogenesis of endosomal and lysosomal compartments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364:40–47
Seachrist JL, Anborgh PH, Ferguson SS (2000) beta 2-adrenergic receptor internalization, endosomal sorting, and plasma membrane recycling are regulated by rab GTPases. J Biol Chem 275:27221–27228
Dinneen JL, Ceresa BP (2004) Continual expression of Rab5 (Q79L) causes a ligand-independent EGFR internalization and diminishes EGFR activity. Traffic 5:606–615
Shi A, Sun L, Banerjee R, Tobin M, Zhang Y, Grant BD (2009) Regulation of endosomal clathrin and retromer-mediated endosome to Golgi retrograde transport by the J-domain protein RME-8. EMBO J 28:3290–3302
Sonnichsen B, DeRenzis S, Nielson E, Rietdorf J, Zerial M (2000) Distinct membrane domains on endosomes in the recycling pathway visualized by multicolor imaging of Rab4, Rab5 and Rab11. J Cell Biol 149:901–914
Rink J, Ghigo E, Kalaidzidis Y, Zerial M (2005) Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late endosomes. Cell 122:735–749
Del Conte-Zerial P, Brusch L, Rink JC, Collinet C, Kalaidzidis Y, Zerial M, Deutsch A (2008) Membrane identity and GTPase cascades regulated by toggle and cut-out Switches. Mol Syst Biol 4:206
Poteryaev D, Datta S, Ackema K, Zerial M, Spang A (2010) Identification of the switch in early-to-late endosome transition. Cell 141:497–508
Galet C, Min L, Narayanan R, Kishi M, Weigel NL, Ascoli M (2003) Identification of transferable two-amino-acid motif (gt) present in the c-terminal tail of the human lutropin receptor that redirects internalized g protein-coupled receptors from a degradation to a recycling pathway. Mol Endocrinol 17:411–422
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant R37 HD06656. We are grateful to Helle Peegel and other members of the laboratory for critical reading of the manuscript and many helpful suggestions. The confocal microscopic studies described here utilized the Morphology and Image Analysis Core (MIAC) facility at the University of Michigan Diabetes Research and training center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Gulappa and C. L. Clouser contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulappa, T., Clouser, C.L. & Menon, K.M.J. The role of Rab5a GTPase in endocytosis and post-endocytic trafficking of the hCG-human luteinizing hormone receptor complex. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 2785–2795 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0594-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0594-1