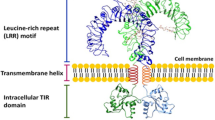
Abstract
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are essential players in the innate immune response to invading pathogens. Although extensive research efforts have provided a considerable wealth of information on how TLRs function, substantial gaps in our knowledge still prevent the definition of a complete picture of TLR signaling. However, several recent studies describe additional layers of complexity in the regulation of TLR ligand recognition, adaptor recruitment, posttranslational modifications of signaling proteins, and the newly described, autonomous role of the TLR4 co-receptor CD14. In this review, by using it as model system for the whole TLR family, we attempt to provide a complete description of the signal transduction pathways triggered by TLR4, with a particular emphasis on the molecular and cell biological aspects regulating its function. Finally, we discuss a recently reported model of CD14-dependent signaling and highlight its biological implications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janeway CA Jr (1989) Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 54:1–13
West AP, Koblansky AA, Ghosh S (2006) Recognition and signaling by toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:409–437
Gay NJ, Gangloff M (2007) Structure and function of Toll receptors and their ligands. Annu Rev Biochem 76:141–165
Beutler B, Jiang Z, Georgel P, Crozat K, Croker B, Rutschmann S, Du X, Hoebe K (2006) Genetic analysis of host resistance: Toll-like receptor signaling and immunity at large. Annu Rev Immunol 24:353–389
Barton GM, Kagan JC (2009) A cell biological view of Toll-like receptor function: regulation through compartmentalization. Nat Rev Immunol 8:535–542
Barton GM, Kagan JC, Medzhitov R (2006) Intracellular localization of Toll-like receptor 9 prevents recognition of self DNA but facilitates access to viral DNA. Nat Immunol 1:49–56
Ewald SE, Lee BL, Lau L, Wickliffe KE, Shi GP, Chapman HA, Barton GM (2008) The ectodomain of Toll-like receptor 9 is cleaved to generate a functional receptor. Nature 7222:658–662
Park B, Brinkmann MM, Spooner E, Lee CC, Kim YM, Ploegh HL (2008) Proteolytic cleavage in an endolysosomal compartment is required for activation of Toll-like receptor 9. Nat Immunol 12:1407–1414
Erridge C, Bennett-Guerrero E, Poxton IR (2002) Structure and function of lipopolysaccharides. Microbes Infect 8:837–851
Rietschel ET, Kirikae T, Schade FU, Ulmer AJ, Holst O, Brade H, Schmidt G, Mamat U, Grimmecke HD, Kusumoto S et al (1993) The chemical structure of bacterial endotoxin in relation to bioactivity. Immunobiology 187(3–5):169–190
Tobias PS, Soldau K, Ulevitch RJ (1986) Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide-binding acute phase reactant from rabbit serum. J Exp Med 3:777–793
Schumann RR, Leong SR, Flaggs GW, Gray PW, Wright SD, Mathison JC, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ (1990) Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science 4975:1429–1431
Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ, Mathison JC (1990) CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 4975:1431–1433
Pugin J, Heumann ID, Tomasz A, Kravchenko VV, Akamatsu Y, Nishijima M, Glauser MP, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ (1994) CD14 is a pattern recognition receptor. Immunity 6:509–516
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr (1997) A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 6640:394–397
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 5396:2085–2088
Shimazu R, Akashi S, Ogata H, Nagai Y, Fukudome K, Miyake K, Kimoto M (1999) MD-2, a molecule that confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J Exp Med 11:1777–1782
Beamer LJ, Carroll SF, Eisenberg D (1997) Crystal structure of human BPI and two bound phospholipids at 2.4 angstrom resolution. Science 5320:1861–1864
Iovine N, Eastvold J, Elsbach P, Weiss JP, Gioannini TL (2002) The carboxyl-terminal domain of closely related endotoxin-binding proteins determines the target of protein–lipopolysaccharide complexes. J Biol Chem 10:7970–7978
Hailman E, Lichenstein HS, Wurfel MM, Miller DS, Johnson DA, Kelley M, Busse LA, Zukowski MM, Wright SD (1994) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein accelerates the binding of LPS to CD14. J Exp Med 1:269–277
Lamping N, Dettmer R, Schroder NW, Pfeil D, Hallatschek W, Burger R, Schumann RR (1998) LPS-binding protein protects mice from septic shock caused by LPS or Gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Invest 10:2065–2071
Wurfel MM, Hailman E, Wright SD (1995) Soluble CD14 acts as a shuttle in the neutralization of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by LPS-binding protein and reconstituted high density lipoprotein. J Exp Med 5:1743–1754
Gutsmann T, Muller M, Carroll SF, MacKenzie RC, Wiese A, Seydel U (2001) Dual role of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein in neutralization of LPS and enhancement of LPS-induced activation of mononuclear cells. Infect Immun 11:6942–6950
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS (1995) Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol 13:437–457
Kim JI, Lee CJ, Jin MS, Lee CH, Paik SG, Lee H, Lee JO (2005) Crystal structure of CD14 and its implications for lipopolysaccharide signaling. J Biol Chem 12:11347–11351
Gioannini TL, Teghanemt A, Zhang D, Coussens NP, Dockstader W, Ramaswamy S, Weiss JP (2004) Isolation of an endotoxin-MD-2 complex that produces Toll-like receptor 4-dependent cell activation at picomolar concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 12:4186–4191
Haziot A, Ferrero E, Kontgen F, Hijiya N, Yamamoto S, Silver J, Stewart CL, Goyert SM (1996) Resistance to endotoxin shock and reduced dissemination of Gram-negative bacteria in CD14-deficient mice. Immunity 4:407–414
Perera PY, Vogel SN, Detore GR, Haziot A, Goyert SM (1997) CD14-dependent and CD14-independent signaling pathways in murine macrophages from normal and CD14 knockout mice stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or taxol. J Immunol 9:4422–4429
Yu B, Hailman E, Wright SD (1997) Lipopolysaccharide binding protein and soluble CD14 catalyze exchange of phospholipids. J Clin Invest 2:315–324
Juan TS, Hailman E, Kelley MJ, Wright SD, Lichenstein HS (1995) Identification of a domain in soluble CD14 essential for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) signaling but not LPS binding. J Biol Chem 29:17237–17242
da Silva Correia J, Soldau K, Christen U, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ (2001) Lipopolysaccharide is in close proximity to each of the proteins in its membrane receptor complex. Transfer from CD14 to TLR4 and MD-2. J Biol Chem 24:21129–21135
Vasselon T, Hailman E, Thieringer R, Detmers PA (1999) Internalization of monomeric lipopolysaccharide occurs after transfer out of cell surface CD14. J Exp Med 4:509–521
Poltorak A, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Citterio S, Beutler B (2000) Physical contact between lipopolysaccharide and toll-like receptor 4 revealed by genetic complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 5:2163–2167
Triantafilou M, Triantafilou K (2002) Lipopolysaccharide recognition: CD14, TLRs and the LPS-activation cluster. Trends Immunol 6:301–304
Gangloff SC, Hijiya N, Haziot A, Goyert SM (1999) Lipopolysaccharide structure influences the macrophage response via CD14-independent and CD14-dependent pathways. Clin Infect Dis 3:491–496
Jiang Z, Georgel P, Du X, Shamel L, Sovath S, Mudd S, Huber M, Kalis C, Keck S, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Beutler B (2005) CD14 is required for MyD88-independent LPS signaling. Nat Immunol 6:565–570
Zughaier SM, Zimmer SM, Datta A, Carlson RW, Stephens DS (2005) Differential induction of the toll-like receptor 4-MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling pathways by endotoxins. Infect Immun 5:2940–2950
Suzuki KG, Fujiwara TK, Edidin M, Kusumi A (2007) Dynamic recruitment of phospholipase C gamma at transiently immobilized GPI-anchored receptor clusters induces IP3-Ca2+ signaling: single-molecule tracking study 2. J Cell Biol 4:731–742
Suzuki KG, Fujiwara TK, Sanematsu F, Iino R, Edidin M, Kusumi A (2007) GPI-anchored receptor clusters transiently recruit Lyn and G alpha for temporary cluster immobilization and Lyn activation: single-molecule tracking study 1. J Cell Biol 4:717–730
Pugin J, Kravchenko VV, Lee JD, Kline L, Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS (1998) Cell activation mediated by glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored or transmembrane forms of CD14. Infect Immun 3:1174–1180
Zanoni I, Ostuni R, Capuano G, Collini M, Caccia M, Ronchi AE, Rocchetti M, Mingozzi F, Foti M, Chirico G, Costa B, Zaza A, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Granucci F (2009) CD14 regulates the dendritic cell life cycle after LPS exposure through NFAT activation. Nature 7252:264–268
Nagai Y, Akashi S, Nagafuku M, Ogata M, Iwakura Y, Akira S, Kitamura T, Kosugi A, Kimoto M, Miyake K (2002) Essential role of MD-2 in LPS responsiveness and TLR4 distribution. Nat Immunol 7:667–672
Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Ogawa T, Takeda Y, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J Immunol 7:3749–3752
Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H, Lee JO (2009) The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature 7242:1191–1195
Kim HM, Park BS, Kim JI, Kim SE, Lee J, Oh SC, Enkhbayar P, Matsushima N, Lee H, Yoo OJ, Lee JO (2007) Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell 5:906–917
Ohto U, Fukase K, Miyake K, Satow Y (2007) Crystal structures of human MD-2 and its complex with antiendotoxic lipid IVa. Science 5831:1632–1634
Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K (2008) TLR accessory molecules. Curr Opin Immunol 4:420–425
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 6:673–687
Ingalls RR, Golenbock DT (1995) CD11c/CD18, a transmembrane signaling receptor for lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med 4:1473–1479
Ingalls RR, Arnaout MA, Golenbock DT (1997) Outside-in signaling by lipopolysaccharide through a tailless integrin. J Immunol 1:433–438
Zarewych DM, Kindzelskii AL, Todd RF 3rd, Petty HR (1996) LPS induces CD14 association with complement receptor type 3, which is reversed by neutrophil adhesion. J Immunol 2:430–433
Medvedev AE, Flo T, Ingalls RR, Golenbock DT, Teti G, Vogel SN, Espevik T (1998) Involvement of CD14 and complement receptors CR3 and CR4 in nuclear factor-kappaB activation and TNF production induced by lipopolysaccharide and group B streptococcal cell walls. J Immunol 9:4535–4542
Flo TH, Ryan L, Kilaas L, Skjak-Braek G, Ingalls RR, Sundan A, Golenbock DT, Espevik T (2000) Involvement of CD14 and beta2-integrins in activating cells with soluble and particulate lipopolysaccharides and mannuronic acid polymers. Infect Immun 12:6770–6776
Perera PY, Mayadas TN, Takeuchi O, Akira S, Zaks-Zilberman M, Goyert SM, Vogel SN (2001) CD11b/CD18 acts in concert with CD14 and Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 to elicit full lipopolysaccharide and taxol-inducible gene expression. J Immunol 1:574–581
Kagan JC, Medzhitov R (2006) Phosphoinositide-mediated adaptor recruitment controls Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 5:943–955
Lingwood D, Simons K (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 5961:46–50
Simons K, Toomre D (2000) Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:31–39
Triantafilou K, Triantafilou M, Dedrick RL (2001) A CD14-independent LPS receptor cluster. Nat Immunol 4:338–345
Triantafilou M, Miyake K, Golenbock DT, Triantafilou K (2002) Mediators of innate immune recognition of bacteria concentrate in lipid rafts and facilitate lipopolysaccharide-induced cell activation. J Cell Sci Pt 12:2603–2611
Triantafilou M, Morath S, Mackie A, Hartung T, Triantafilou K (2004) Lateral diffusion of Toll-like receptors reveals that they are transiently confined within lipid rafts on the plasma membrane. J Cell Sci Pt 17:4007–4014
Wesche H, Henzel WJ, Shillinglaw W, Li S, Cao Z (1997) MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 6:837–847
Muzio M, Ni J, Feng P, Dixit VM (1997) IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 5343:1612–1615
Kawai T, Adachi O, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity 1:115–122
Dunne A, Ejdeback M, Ludidi PL, O’Neill LA, Gay NJ (2003) Structural complementarity of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domains in Toll-like receptors and the adaptors Mal and MyD88. J Biol Chem 42:41443–41451
Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie AG, Jefferies CA, Mansell AS, Brady G, Brint E, Dunne A, Gray P, Harte MT, McMurray D, Smith DE, Sims JE, Bird TA, O’Neill LA (2001) Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction. Nature 6851:78–83
Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2001) TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 9:835–841
Horng T, Barton GM, Flavell RA, Medzhitov R (2002) The adaptor molecule TIRAP provides signalling specificity for Toll-like receptors. Nature 6913:329–333
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Sanjo H, Uematsu S, Kaisho T, Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kobayashi M, Fujita T, Takeda K, Akira S (2002) Essential role for TIRAP in activation of the signalling cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4. Nature 6913:324–329
Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Funami K, Akazawa T, Seya T (2003) TICAM-1, an adaptor molecule that participates in Toll-like receptor 3-mediated interferon-beta induction. Nat Immunol 2:161–167
Hoebe K, Du X, Georgel P, Janssen E, Tabeta K, Kim SO, Goode J, Lin P, Mann N, Mudd S, Crozat K, Sovath S, Han J, Beutler B (2003) Identification of Lps2 as a key transducer of MyD88-independent TIR signalling. Nature 6950:743–748
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Sanjo H, Takeuchi O, Sugiyama M, Okabe M, Takeda K, Akira S (2003) Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 5633:640–643
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Uematsu S, Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Takeda K, Akira S (2003) TRAM is specifically involved in the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated MyD88-independent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 11:1144–1150
Carty M, Goodbody R, Schroder M, Stack J, Moynagh PN, Bowie AG (2006) The human adaptor SARM negatively regulates adaptor protein TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Immunol 10:1074–1081
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S, Medzhitov R (2008) TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol 4:361–368
McLaughlin S, Murray D (2005) Plasma membrane phosphoinositide organization by protein electrostatics. Nature 7068:605–611
Botelho RJ, Teruel M, Dierckman R, Anderson R, Wells A, York JD, Meyer T, Grinstein S (2000) Localized biphasic changes in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate at sites of phagocytosis. J Cell Biol 7:1353–1368
Honda A, Nogami M, Yokozeki T, Yamazaki M, Nakamura H, Watanabe H, Kawamoto K, Nakayama K, Morris AJ, Frohman MA, Kanaho Y (1999) Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase alpha is a downstream effector of the small G protein ARF6 in membrane ruffle formation. Cell 5:521–532
Wan T, Liu T, Zhang H, Tang S, Min W (2010) AIP1 functions as Arf6-GAP to negatively regulate TLR4 signaling. J Biol Chem 6:3750–3757
Cuzzola M, Mancuso G, Beninati C, Biondo C, Genovese F, Tomasello F, Flo TH, Espevik T, Teti G (2000) Beta 2 integrins are involved in cytokine responses to whole Gram-positive bacteria. J Immunol 11:5871–5876
Rowe DC, McGettrick AF, Latz E, Monks BG, Gay NJ, Yamamoto M, Akira S, O’Neill LA, Fitzgerald KA, Golenbock DT (2006) The myristoylation of TRIF-related adaptor molecule is essential for Toll-like receptor 4 signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 16:6299–6304
Husebye H, Halaas O, Stenmark H, Tunheim G, Sandanger O, Bogen B, Brech A, Latz E, Espevik T (2006) Endocytic pathways regulate Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and link innate and adaptive immunity. EMBO J 4:683–692
Tanimura N, Saitoh S, Matsumoto F, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K (2008) Roles for LPS-dependent interaction and relocation of TLR4 and TRAM in TRIF-signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1:94–99
Scott CC, Dobson W, Botelho RJ, Coady-Osberg N, Chavrier P, Knecht DA, Heath C, Stahl P, Grinstein S (2005) Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis directs actin remodeling during phagocytosis. J Cell Biol 1:139–149
Palsson-McDermott EM, Doyle SL, McGettrick AF, Hardy M, Husebye H, Banahan K, Gong M, Golenbock D, Espevik T, O’Neill LA (2009) TAG, a splice variant of the adaptor TRAM, negatively regulates the adaptor MyD88-independent TLR4 pathway. Nat Immunol 6:579–586
Chuang TH, Ulevitch RJ (2004) Triad3A, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase regulating Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 5:495–502
McLaughlin S, Wang J, Gambhir A, Murray D (2002) PIP(2) and proteins: interactions, organization, and information flow. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 31:151–175
McGettrick AF, Brint EK, Palsson-McDermott EM, Rowe DC, Golenbock DT, Gay NJ, Fitzgerald KA, O’Neill LA (2006) TRIF-related adapter molecule is phosphorylated by PKC{epsilon} during Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 24:9196–9201
Barbalat R, Lau L, Locksley RM, Barton GM (2009) Toll-like receptor 2 on inflammatory monocytes induces type I interferon in response to viral but not bacterial ligands. Nat Immunol 11:1200–1207
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 3:344–362
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 6824:37–40
Cao Z, Henzel WJ, Gao X (1996) IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science 5252:1128–1131
Janssens S, Beyaert R (2003) Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members. Mol Cell 2:293–302
Li S, Strelow A, Fontana EJ, Wesche H (2002) IRAK-4: a novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 8:5567–5572
Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Duncan GS, Millar DG, Wada T, Mirtsos C, Takada H, Wakeham A, Itie A, Li S, Penninger JM, Wesche H, Ohashi PS, Mak TW, Yeh WC (2002) Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature 6882:750–756
Yamin TT, Miller DK (1997) The interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase is degraded by proteasomes following its phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 34:21540–21547
An H, Hou J, Zhou J, Zhao W, Xu H, Zheng Y, Yu Y, Liu S, Cao X (2008) Phosphatase SHP-1 promotes TLR- and RIG-I-activated production of type I interferon by inhibiting the kinase IRAK1. Nat Immunol 5:542–550
Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L, Martinon F, Plumpton C, Maschera B, Lewis A, Ray K, Tschopp J, Volpe F (2000) Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor. Nat Cell Biol 6:346–351
Didierlaurent A, Brissoni B, Velin D, Aebi N, Tardivel A, Kaslin E, Sirard JC, Angelov G, Tschopp J, Burns K (2006) Tollip regulates proinflammatory responses to interleukin-1 and lipopolysaccharide. Mol Cell Biol 3:735–742
Burns K, Janssens S, Brissoni B, Olivos N, Beyaert R, Tschopp J (2003) Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4. J Exp Med 2:263–268
Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV (1996) TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 6599:443–446
Jiang Z, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Qian Y, Matsumoto K, Li X (2002) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase-dependent IL-1-induced signaling complexes phosphorylate TAK1 and TAB 2 at the plasma membrane and activate TAK1 in the cytosol. Mol Cell Biol 20:7158–7167
Takaesu G, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Kishida S, Li X, Stark GR, Matsumoto K (2001) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase leads to activation of TAK1 by inducing TAB 2 translocation in the IL-1 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 7:2475–2484
Windheim M, Stafford M, Peggie M, Cohen P (2008) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) induces the Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 to facilitate NEMO binding and the activation of IkappaBalpha kinase. Mol Cell Biol 5:1783–1791
Thomas JA, Allen JL, Tsen M, Dubnicoff T, Danao J, Liao XC, Cao Z, Wasserman SA (1999) Impaired cytokine signaling in mice lacking the IL-1 receptor-associated kinase. J Immunol 2:978–984
Li X, Commane M, Burns C, Vithalani K, Cao Z, Stark GR (1999) Mutant cells that do not respond to interleukin-1 (IL-1) reveal a novel role for IL-1 receptor-associated kinase. Mol Cell Biol 7:4643–4652
Kawagoe T, Sato S, Matsushita K, Kato H, Matsui K, Kumagai Y, Saitoh T, Kawai T, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2008) Sequential control of Toll-like receptor-dependent responses by IRAK1 and IRAK2. Nat Immunol 6:684–691
Wesche H, Gao X, Li X, Kirschning CJ, Stark GR, Cao Z (1999) IRAK-M is a novel member of the Pelle/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family. J Biol Chem 27:19403–19410
Kobayashi K, Hernandez LD, Galan JE, Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2002) IRAK-M is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 2:191–202
Bradley JR, Pober JS (2001) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Oncogene 44:6482–6491
Gohda J, Matsumura T, Inoue J (2004) Cutting edge: TNFR-associated factor (TRAF) 6 is essential for MyD88-dependent pathway but not toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-beta (TRIF)-dependent pathway in TLR signaling. J Immunol 5:2913–2917
Deng L, Wang C, Spencer E, Yang L, Braun A, You J, Slaughter C, Pickart C, Chen ZJ (2000) Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin–conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell 2:351–361
Chen ZJ, Sun LJ (2009) Nonproteolytic functions of ubiquitin in cell signaling. Mol Cell 3:275–286
Fan Y, Yu Y, Shi Y, Sun W, Xie M, Ge N, Mao R, Chang A, Xu G, Schneider MD, Zhang H, Fu S, Qin J, Yang J (2010) Lysine 63-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 at lysine 158 is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha- and interleukin-1beta-induced IKK/NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation. J Biol Chem 8:5347–5360
Kanayama A, Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Hong M, Shaito A, Chiu YH, Deng L, Chen ZJ (2004) TAB 2 and TAB 3 activate the NF-kappaB pathway through binding to polyubiquitin chains. Mol Cell 4:535–548
Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ (2006) Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol Cell 2:245–257
Wu CJ, Conze DB, Li T, Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD (2006) Sensing of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitination by NEMO is a key event in NF-kappaB activation [corrected]. Nat Cell Biol 4:398–406
Takatsuna H, Kato H, Gohda J, Akiyama T, Moriya A, Okamoto Y, Yamagata Y, Otsuka M, Umezawa K, Semba K, Inoue J (2003) Identification of TIFA as an adapter protein that links tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) to interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) in IL-1 receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 14:12144–12150
Ea CK, Sun L, Inoue J, Chen ZJ (2004) TIFA activates IkappaB kinase (IKK) by promoting oligomerization and ubiquitination of TRAF6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 43:15318–15323
Motshwene PG, Moncrieffe MC, Grossmann JG, Kao C, Ayaluru M, Sandercock AM, Robinson CV, Latz E, Gay NJ (2009) An oligomeric signaling platform formed by the Toll-like receptor signal transducers MyD88 and IRAK-4. J Biol Chem 37:25404–25411
Hacker H, Redecke V, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Hsu LC, Wang GG, Kamps MP, Raz E, Wagner H, Hacker G, Mann M, Karin M (2006) Specificity in Toll-like receptor signalling through distinct effector functions of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Nature 7073:204–207
Yamamoto M, Okamoto T, Takeda K, Sato S, Sanjo H, Uematsu S, Saitoh T, Yamamoto N, Sakurai H, Ishii KJ, Yamaoka S, Kawai T, Matsuura Y, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2006) Key function for the Ubc13 E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in immune receptor signaling. Nat Immunol 9:962–970
Fukushima T, Matsuzawa S, Kress CL, Bruey JM, Krajewska M, Lefebvre S, Zapata JM, Ronai Z, Reed JC (2007) Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 is a critical component of TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-mediated inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 15:6371–6376
Xu M, Skaug B, Zeng W, Chen ZJ (2009) A ubiquitin replacement strategy in human cells reveals distinct mechanisms of IKK activation by TNFalpha and IL-1beta. Mol Cell 2:302–314
Xia ZP, Sun L, Chen X, Pineda G, Jiang X, Adhikari A, Zeng W, Chen ZJ (2009) Direct activation of protein kinases by unanchored polyubiquitin chains. Nature 7260:114–119
Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, McNally E, Pickart C, Ma A (2004) The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol 10:1052–1060
Shembade N, Ma A, Harhaj EW (2010) Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 5969:1135–1139
Reiley WW, Zhang M, Jin W, Losiewicz M, Donohue KB, Norbury CC, Sun SC (2006) Regulation of T cell development by the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Nat Immunol 4:411–417
Oganesyan G, Saha SK, Guo B, He JQ, Shahangian A, Zarnegar B, Perry A, Cheng G (2006) Critical role of TRAF3 in the Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent antiviral response. Nature 7073:208–211
Matsuzawa A, Tseng PH, Vallabhapurapu S, Luo JL, Zhang W, Wang H, Vignali DA, Gallagher E, Karin M (2008) Essential cytoplasmic translocation of a cytokine receptor-assembled signaling complex. Science 5889:663–668
Tseng PH, Matsuzawa A, Zhang W, Mino T, Vignali DA, Karin M (2010) Different modes of ubiquitination of the adaptor TRAF3 selectively activate the expression of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Immunol 1:70–75
Newton K, Matsumoto ML, Wertz IE, Kirkpatrick DS, Lill JR, Tan J, Dugger D, Gordon N, Sidhu SS, Fellouse FA, Komuves L, French DM, Ferrando RE, Lam C, Compaan D, Yu C, Bosanac I, Hymowitz SG, Kelley RF, Dixit VM (2008) Ubiquitin chain editing revealed by polyubiquitin linkage-specific antibodies. Cell 4:668–678
Sato S, Sanjo H, Takeda K, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Yamamoto M, Kawai T, Matsumoto K, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2005) Essential function for the kinase TAK1 in innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 11:1087–1095
Wang C, Deng L, Hong M, Akkaraju GR, Inoue J, Chen ZJ (2001) TAK1 is a ubiquitin-dependent kinase of MKK and IKK. Nature 6844:346–351
Ishitani T, Takaesu G, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Shibuya H, Gaynor RB, Matsumoto K (2003) Role of the TAB 2-related protein TAB 3 in IL-1 and TNF signaling. EMBO J 23:6277–6288
Kishimoto K, Matsumoto K, Ninomiya-Tsuji J (2000) TAK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is activated by autophosphorylation within its activation loop. J Biol Chem 10:7359–7364
Shi M, Deng W, Bi E, Mao K, Ji Y, Lin G, Wu X, Tao Z, Li Z, Cai X, Sun S, Xiang C, Sun B (2008) TRIM30 alpha negatively regulates TLR-mediated NF-kappa B activation by targeting TAB 2 and TAB 3 for degradation. Nat Immunol 4:369–377
Laplantine E, Fontan E, Chiaravalli J, Lopez T, Lakisic G, Veron M, Agou F, Israel A (2009) NEMO specifically recognizes K63-linked poly-ubiquitin chains through a new bipartite ubiquitin-binding domain. EMBO J 19:2885–2895
Conze DB, Wu CJ, Thomas JA, Landstrom A, Ashwell JD (2008) Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IRAK-1 is required for interleukin-1 receptor- and toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 10:3538–3547
Ordureau A, Smith H, Windheim M, Peggie M, Carrick E, Morrice N, Cohen P (2008) The IRAK-catalysed activation of the E3 ligase function of Pellino isoforms induces the Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IRAK1. Biochem J 1:43–52
Rahighi S, Ikeda F, Kawasaki M, Akutsu M, Suzuki N, Kato R, Kensche T, Uejima T, Bloor S, Komander D, Randow F, Wakatsuki S, Dikic I (2009) Specific recognition of linear ubiquitin chains by NEMO is important for NF-kappaB activation. Cell 6:1098–1109
Tokunaga F, Sakata S, Saeki Y, Satomi Y, Kirisako T, Kamei K, Nakagawa T, Kato M, Murata S, Yamaoka S, Yamamoto M, Akira S, Takao T, Tanaka K, Iwai K (2009) Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-kappaB activation. Nat Cell Biol 2:123–132
Wang W, Zhou G, Hu MC, Yao Z, Tan TH (1997) Activation of the hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1)-dependent, stress-activated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-activated kinase (TAK1), a kinase mediator of TGF beta signal transduction. J Biol Chem 36:22771–22775
Zhong J, Kyriakis JM (2007) Dissection of a signaling pathway by which pathogen-associated molecular patterns recruit the JNK and p38 MAPKs and trigger cytokine release. J Biol Chem 33:24246–24254
Yang J, Lin Y, Guo Z, Cheng J, Huang J, Deng L, Liao W, Chen Z, Liu Z, Su B (2001) The essential role of MEKK3 in TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. Nat Immunol 7:620–624
Huang Q, Yang J, Lin Y, Walker C, Cheng J, Liu ZG, Su B (2004) Differential regulation of interleukin 1 receptor and Toll-like receptor signaling by MEKK3. Nat Immunol 1:98–103
Sato S, Sugiyama M, Yamamoto M, Watanabe Y, Kawai T, Takeda K, Akira S (2003) Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta (TRIF) associates with TNF receptor-associated factor 6 and TANK-binding kinase 1, and activates two distinct transcription factors, NF-kappa B and IFN-regulatory factor-3, in the Toll-like receptor signaling. J Immunol 8:4304–4310
Meylan E, Burns K, Hofmann K, Blancheteau V, Martinon F, Kelliher M, Tschopp J (2004) RIP1 is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 3-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol 5:503–507
Cusson-Hermance N, Khurana S, Lee TH, Fitzgerald KA, Kelliher MA (2005) Rip1 mediates the Trif-dependent toll-like receptor 3- and 4-induced NF-{kappa}B activation but does not contribute to interferon regulatory factor 3 activation. J Biol Chem 44:36560–36566
Ermolaeva MA, Michallet MC, Papadopoulou N, Utermohlen O, Kranidioti K, Kollias G, Tschopp J, Pasparakis M (2008) Function of TRADD in tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling and in TRIF-dependent inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol 9:1037–1046
Pobezinskaya YL, Kim YS, Choksi S, Morgan MJ, Li T, Liu C, Liu Z (2008) The function of TRADD in signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 9:1047–1054
Chang M, Jin W, Sun SC (2009) Peli1 facilitates TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling and proinflammatory cytokine production. Nat Immunol 10:1089–1095
Nagata S (1997) Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 3:355–365
Kaiser WJ, Offermann MK (2005) Apoptosis induced by the toll-like receptor adaptor TRIF is dependent on its receptor interacting protein homotypic interaction motif. J Immunol 8:4942–4952
Ruckdeschel K, Pfaffinger G, Haase R, Sing A, Weighardt H, Hacker G, Holzmann B, Heesemann J (2004) Signaling of apoptosis through TLRs critically involves toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta, but not MyD88, in bacteria-infected murine macrophages. J Immunol 5:3320–3328
Chaudhary PM, Eby MT, Jasmin A, Kumar A, Liu L, Hood L (2000) Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by caspase 8 and its homologs. Oncogene 39:4451–4460
Su H, Bidere N, Zheng L, Cubre A, Sakai K, Dale J, Salmena L, Hakem R, Straus S, Lenardo M (2005) Requirement for caspase-8 in NF-kappaB activation by antigen receptor. Science 5714:1465–1468
Lemmers B, Salmena L, Bidere N, Su H, Matysiak-Zablocki E, Murakami K, Ohashi PS, Jurisicova A, Lenardo M, Hakem R, Hakem A (2007) Essential role for caspase-8 in Toll-like receptors and NFkappaB signaling. J Biol Chem 10:7416–7423
Pichlmair A, Reis e Sousa C (2007) Innate recognition of viruses. Immunity 3:370–383
Honda K, Takaoka A, Taniguchi T (2006) Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 3:349–360
Sharma S, tenOever BR, Grandvaux N, Zhou GP, Lin R, Hiscott J (2003) Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 5622:1148–1151
Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe DC, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Coyle AJ, Liao SM, Maniatis T (2003) IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 5:491–496
McWhirter SM, Fitzgerald KA, Rosains J, Rowe DC, Golenbock DT, Maniatis T (2004) IFN-regulatory factor 3-dependent gene expression is defective in Tbk1-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1:233–238
An H, Zhao W, Hou J, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zheng Y, Xu H, Qian C, Zhou J, Yu Y, Liu S, Feng G, Cao X (2006) SHP-2 phosphatase negatively regulates the TRIF adaptor protein-dependent type I interferon and proinflammatory cytokine production. Immunity 6:919–928
Cheng G, Baltimore D (1996) TANK, a co-inducer with TRAF2 of TNF- and CD 40L-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Genes Dev 8:963–973
Fujita F, Taniguchi Y, Kato T, Narita Y, Furuya A, Ogawa T, Sakurai H, Joh T, Itoh M, Delhase M, Karin M, Nakanishi M (2003) Identification of NAP1, a regulatory subunit of IkappaB kinase-related kinases that potentiates NF-kappaB signaling. Mol Cell Biol 21:7780–7793
Ryzhakov G, Randow F (2007) SINTBAD, a novel component of innate antiviral immunity, shares a TBK1-binding domain with NAP1 and TANK. EMBO J 13:3180–3190
Pomerantz JL, Baltimore D (1999) NF-kappaB activation by a signaling complex containing TRAF2, TANK and TBK1, a novel IKK-related kinase. EMBO J 23:6694–6704
Guo B, Cheng G (2007) Modulation of the interferon antiviral response by the TBK1/IKKi adaptor protein TANK. J Biol Chem 16:11817–11826
Gatot JS, Gioia R, Chau TL, Patrascu F, Warnier M, Close P, Chapelle JP, Muraille E, Brown K, Siebenlist U, Piette J, Dejardin E, Chariot A (2007) Lipopolysaccharide-mediated interferon regulatory factor activation involves TBK1-IKKepsilon-dependent Lys(63)-linked polyubiquitination and phosphorylation of TANK/I-TRAF. J Biol Chem 43:31131–31146
Chariot A, Leonardi A, Muller J, Bonif M, Brown K, Siebenlist U (2002) Association of the adaptor TANK with the I kappa B kinase (IKK) regulator NEMO connects IKK complexes with IKK epsilon and TBK1 kinases. J Biol Chem 40:37029–37036
Zhao T, Yang L, Sun Q, Arguello M, Ballard DW, Hiscott J, Lin R (2007) The NEMO adaptor bridges the nuclear factor-kappaB and interferon regulatory factor signaling pathways. Nat Immunol 6:592–600
Sasai M, Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Inoue N, Fujita F, Nakanishi M, Seya T (2005) Cutting edge: NF-kappaB-activating kinase-associated protein 1 participates in TLR3/Toll-IL-1 homology domain-containing adapter molecule-1-mediated IFN regulatory factor 3 activation. J Immunol 1:27–30
Zeng W, Xu M, Liu S, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2009) Key role of Ubc5 and lysine-63 polyubiquitination in viral activation of IRF3. Mol Cell 2:315–325
Kayagaki N, Phung Q, Chan S, Chaudhari R, Quan C, O’Rourke KM, Eby M, Pietras E, Cheng G, Bazan JF, Zhang Z, Arnott D, Dixit VM (2007) DUBA: a deubiquitinase that regulates type I interferon production. Science 5856:1628–1632
Kawagoe T, Takeuchi O, Takabatake Y, Kato H, Isaka Y, Tsujimura T, Akira S (2009) TANK is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling and is critical for the prevention of autoimmune nephritis. Nat Immunol 9:965–972
Wang C, Chen T, Zhang J, Yang M, Li N, Xu X, Cao X (2009) The E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 ‘preferentially’ promotes TLR-mediated production of type I interferon. Nat Immunol 7:744–752
Granucci F, Feau S, Angeli V, Trottein F, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P (2003) Early IL-2 production by mouse dendritic cells is the result of microbial-induced priming. J Immunol 10:5075–5081
Granucci F, Vizzardelli C, Pavelka N, Feau S, Persico M, Virzi E, Rescigno M, Moro G, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P (2001) Inducible IL-2 production by dendritic cells revealed by global gene expression analysis. Nat Immunol 9:882–888
Granucci F, Zanoni I, Pavelka N, Van Dommelen SL, Andoniou CE, Belardelli F, Degli Esposti MA, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P (2004) A contribution of mouse dendritic cell-derived IL-2 for NK cell activation. J Exp Med 3:287–295
Crabtree GR, Olson EN (2002) NFAT signaling: choreographing the social lives of cells. Cell 109:S67–S79
Dellis O, Dedos SG, Tovey SC, Taufiq Ur R, Dubel SJ, Taylor CW (2006) Ca2+ entry through plasma membrane IP3 receptors. Science 5784:229–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ostuni, R., Zanoni, I. & Granucci, F. Deciphering the complexity of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 4109–4134 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0464-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0464-x