Abstract.
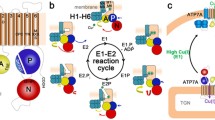
Menkes disease is caused by mutations in the copper-transporting P1B-type ATPase ATP7A. ATP7A has a dual function: it serves to incorporate copper into copper-dependent enzymes, and it maintains intracellular copper levels by removing excess copper from the cytosol. To accomplish both functions, the protein traffics between different cellular locations depending on copper levels.The mechanism for sensing the concentration of copper, for trafficking, as well as the details of the mechanism of copper translocation across the membrane are unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 24 September 2007; received after revision 12 October 2007; accepted 17 October 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertini, I., Rosato, A. Menkes disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 89–91 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7439-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7439-6