Abstract.
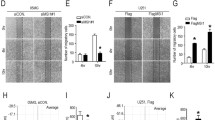
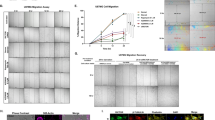
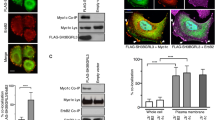
A key regulatory mechanism in cell motility is the control of myosin activity, which in non-muscle cells is determined by phosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chain (MRLC). Here we show that MRLC-interacting protein (MIR)-interacting saposin-like protein (MSAP) enhances cell spreading in fibroblasts and migration of rat C6 glioma cells through increases in MRLC phosphorylation. Overexpression of MSAP enhanced the motility of glioma cells measured in matrigel invasion chambers and using a scratch assay. Downregulation of MSAP by RNA interference significantly decreased glioma cell migration and phosphorylation of MRLC. Inhibition of the corresponding MRLC kinase by ML-7 did not affect migration of MSAP-overexpressing cells. The present results show that MSAP controls glioma cell migration via enhancement of MRLC phosphorylation. This effect is independent of the activity of MRLC kinase. Thus, MSAP is a novel modulator of cell motility that influences migration of glioma cells and possibly other tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 9 February 2005; received after revision 2 March 2005; accepted 21 March 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bornhauser, B.C., Lindholm, D. MSAP enhances migration of C6 glioma cells through phosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chain. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 1260–1266 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5055-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5055-x