Abstract.
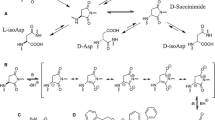
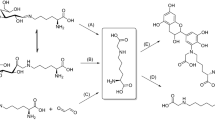
We examined chemical reactions in mouse lysozyme after incubation under physiological conditions (pH 7 and 37°C). After incubation for 8 weeks, racemization was observed specifically at Asn127 among the 19 Asp/Asn residues in mouse lysozyme. Furthermore, analysis of the primary structure showed that the racemized residue was not Asp, but Asn, which demonstrates that deamidation and isomerization did not occur. These results mean that this racemization occurs without forming a succinimide intermediate. This is the first example of D-asparaginyl formation in a protein occurring during the racemization process under physiological conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 16 September 2004; received after revision 26 October 2004; accepted 12 November 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueno, K., Ueda, T., Sakai, K. et al. Evidence for a novel racemization process of an asparaginyl residue in mouse lysozyme under physiological conditions. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 199–205 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4412-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4412-5