Abstract
Objective
Tripterine (Trip) is frequently applied to alleviate inflammation in various diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages have both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory functions. However, whether Trip can inhibit cell inflammation in gouty arthritis (GA) remains undiscovered and whether the mechanism involved in macrophage polarization is also undetermined. This paper aims to study the effects of Trip on inflammation and macrophage polarization in GA.
Methods
Monosodium urate (MSU) crystals were used to establish GA mouse models, and bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were induced to construct GA cell models. Pretreatments of Trip and injection of Antagomir-449a/Agomir-449a were performed on mice for 6 days. The effects of Trip and miR-449 on toe swelling, joint damage of GA mouse were examined. The alternations on cell morphology, cell proliferation marker Ki67, inflammatory cytokines, NLRP3 inflammasome, and NF-κB signaling-related proteins were also determined both in vivo and in vitro. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay and RIP assay were adopted to estimate the targeting relationship between miR-449a and NLRP3.
Results
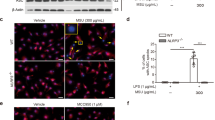
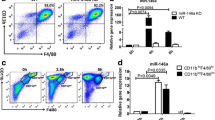
GA mouse model had increased M1 macrophage, intensified inflammation response, along with suppressed miR-449a expression. Following administration of Trip attenuated cell inflammation, promoted macrophage polarize to M2 phenotype, elevated miR-449a expression, repressed the phosphorylation levels of NF-κB signaling-related proteins, and diminished IκBα expression in vivo and in vitro. However, inhibition of miR-449a hindered the favorable effect of Trip on GA and increased NLRP3 inflammasome expression. MiR-449a directly targeted NLRP3. Overexpression of NLRP3 partially eliminated the biological effects of miR-449a agonist.
Conclusion
Trip regulates macrophage polarization through miR-449a/NLRP3 axis and the STAT3/NF-κB pathway to mitigate GA. The elucidation on the molecular mechanism of Trip in GA may provide theoretical guidance for clinical therapy of GA.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 September 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01630-x
References
Cleophas MC, Crisan TO, Joosten LA. Factors modulating the inflammatory response in acute gouty arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29:163–70.
Lee HE, Yang G, Kim ND, Jeong S, Jung Y, Choi JY, et al. Targeting ASC in NLRP3 inflammasome by caffeic acid phenethyl ester: a novel strategy to treat acute gout. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38622.
Dinesh P, Rasool M. Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid suppresses TXNIP mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in MSU crystal stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through the upregulation of Nrf2 transcription factor and alleviates MSU crystal induced inflammation in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;44:26–37.
Wang Y, Viollet B, Terkeltaub R, Liu-Bryan R. AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses urate crystal-induced inflammation and transduces colchicine effects in macrophages. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:286–94.
Ruiz-Miyazawa KW, Staurengo-Ferrari L, Mizokami SS, Domiciano TP, Vicentini F, Camilios-Neto D, et al. Quercetin inhibits gout arthritis in mice: induction of an opioid-dependent regulation of inflammasome. Inflammopharmacology. 2017;25(5):555–70.
Vergadi E, Ieronymaki E, Lyroni K, Vaporidi K, Tsatsanis C. Akt signaling pathway in macrophage activation and M1/M2 polarization. J Immunol. 2017;198:1006–14.
Liu Y, Tang H, Liu X, Chen H, Feng N, Zhang J, et al. Frontline Science: Reprogramming COX-2, 5-LOX, and CYP4A-mediated arachidonic acid metabolism in macrophages by salidroside alleviates gouty arthritis. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;105:11–24.
Mei J, Zhou F, Qiao H, Li H, Tang T. Nerve modulation therapy in gouty arthritis: targeting increased sFRP2 expression in dorsal root ganglion regulates macrophage polarization and alleviates endothelial damage. Theranostics. 2019;9:3707–22.
Ti D, Hao H, Tong C, Liu J, Dong L, Zheng J, et al. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med. 2015;13:308.
Wang J, Yang Q, Zhang Q, Yin C, Zhou L, Zhou J, et al. Invariant natural killer T cells ameliorate monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty inflammation in mice. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1710.
Venkatesha SH, Dudics S, Astry B, Moudgil KD. Control of autoimmune inflammation by celastrol, a natural triterpenoid. Pathog Dis. 2016;74:ftw059.
Venkatesha SH, Moudgil KD. Celastrol and its role in controlling chronic diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;928:267–89.
Song X, Zhang Y, Dai E, Du H, Wang L. Mechanism of action of celastrol against rheumatoid arthritis: a network pharmacology analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105725.
Peng X, Wang J, Li X, Lin L, Xie G, Cui Z, et al. Targeting mast cells and basophils with anti-fcepsilonrialpha fab-conjugated celastrol-loaded micelles suppresses allergic inflammation. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11:2286–99.
Li X, Wei W, Zhao Z, Lv S. Tripterine up-regulates miR-223 to alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced damage in murine chondrogenic ATDC5 cells. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019;33:2058738418824521.
Yu Y, Koehn CD, Yue Y, Li S, Thiele GM, Hearth-Holmes MP, et al. Celastrol inhibits inflammatory stimuli-induced neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Curr Mol Med. 2015;15:401–10.
Luo D, Guo Y, Cheng Y, Zhao J, Wang Y, Rong J. Natural product celastrol suppressed macrophage M1 polarization against inflammation in diet-induced obese mice via regulating Nrf2/HO-1, MAP kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9:2069–82.
Jiang L, Hao C, Li Z, Zhang P, Wang S, Yang S, et al. miR-449a induces EndMT, promotes the development of atherosclerosis by targeting the interaction between AdipoR2 and E-cadherin in lipid rafts. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:2293–304.
Cai Y, Jiang C, Zhu J, Xu K, Ren X, Xu L, et al. miR-449a inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and inflammation by regulating high-mobility group box protein 1 and forms a mutual inhibition loop with Yin Yang 1 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21:134.
Guo C, Fu R, Wang S, Huang Y, Li X, Zhou M, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194:231–43.
Zou Y, Hu W. Investigation of gene expression profiles in a rat adjuvant arthritis model suggests an effective role of triptolide via PI3K-AKT signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17:3999–4006.
Wang Y, Wei D, Lai Z, Le Y. Triptolide inhibits CC chemokines expressed in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006;6:1825–32.
Yifan W, Dengming W, Zheng L, Yanping L, Junkan S. Triptolide inhibits CCR5 expressed in synovial tissue of rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Pharmacol Rep. 2007;59:795–9.
Ying W, Cheruku PS, Bazer FW, Safe SH, Zhou B. Investigation of macrophage polarization using bone marrow derived macrophages. J Vis Exp. 2013. https://doi.org/10.3791/50323.
Burja B, Kuret T, Janko T, Topalovic D, Zivkovic L, Mrak-Poljsak K, et al. Olive leaf extract attenuates inflammatory activation and DNA damage in human arterial endothelial cells. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019;6:56.
Schauer C, Janko C, Munoz LE, Zhao Y, Kienhofer D, Frey B, et al. Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines. Nat Med. 2014;20:511–7.
Pope RM, Tschopp J. The role of interleukin-1 and the inflammasome in gout: implications for therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:3183–8.
Scott O, Roifman CM. NF-kappaB pathway and the Goldilocks principle: Lessons from human disorders of immunity and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:1688–701.
Ben-David H, Livneh A, Lidar M, Feld O, Haj Yahia S, Grossman C, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 is overexpressed in Familial Mediterranean fever patients and is inhibited by colchicine treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32:651–61.
Patel U, Rajasingh S, Samanta S, Cao T, Dawn B, Rajasingh J. Macrophage polarization in response to epigenetic modifiers during infection and inflammation. Drug Discov Today. 2017;22:186–93.
Kashyap D, Sharma A, Tuli HS, Sak K, Mukherjee T, Bishayee A. Molecular targets of celastrol in cancer: recent trends and advancements. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018;128:70–81.
Bian M, Du X, Cui J, Wang P, Wang W, Zhu W, et al. Celastrol protects mouse retinas from bright light-induced degeneration through inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13:50.
Abu Bakar MH, Sarmidi MR, Tan JS, Mohamad Rosdi MN. Celastrol attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in palmitate-mediated insulin resistance in C3A hepatocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;799:73–83.
Lin L, Sun Y, Wang D, Zheng S, Zhang J, Zheng C. Celastrol ameliorates ulcerative colitis-related colorectal cancer in mice via suppressing inflammatory responses and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6:320.
Xiong Y, Yan Y, Li Y. Tripterine alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury by up-regulation of miR-146a in HaCaT cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;105:798–804.
Yan Y, Jiang W, Liu L, Wang X, Ding C, Tian Z, et al. Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell. 2015;160:62–73.
Xin W, Wang Q, Zhang D, Wang C. A new mechanism of inhibition of IL-1beta secretion by celastrol through the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;814:240–7.
Yu X, Zhao Q, Zhang X, Zhang H, Liu Y, Wu X, et al. Celastrol ameliorates inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Oncotarget. 2017;8:67300–14.
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:6425–40.
Fan Y, Mao R, Yang J. NF-kappaB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer. Protein Cell. 2013;4:176–85.
Liu Z, Han Y, Zhao F, Zhao Z, Tian J, Jia K. Nobiletin suppresses high-glucose-induced inflammation and ECM accumulation in human mesangial cells through STAT3/NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:3467–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01630-x
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Tripterine ameliorates monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis by altering macrophage polarization via the miR-449a/NLRP3 axis. Inflamm. Res. 70, 323–341 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01439-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01439-0